- Sep 15, 2025
- 13 min read
In a competitive landscape, consistency isn't a luxury; it's the bedrock of scalable success. While to-do lists manage daily tasks, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) standardize excellence, ensuring critical processes are performed correctly and safely, every single time. This systematic approach is what separates high-growth companies from those that remain stagnant, bogged down by preventable mistakes and inefficiencies.
SOPs eliminate guesswork, reduce errors, and empower your team to operate with confidence and precision. They are the essential blueprints for everything from complex CRM workflows and logistics tracking to routine equipment maintenance and outbound calling campaigns. For project managers, operations teams, and business owners alike, well-designed SOPs are the key to unlocking true operational control and automation.
But where do you start? This guide moves beyond theory to provide eight comprehensive standard operating procedure examples from diverse industries. We will not just show you what they look like; we will break down their structure, analyze their strategic value, and offer actionable takeaways you can implement immediately. By the end, you'll have a clear framework and tangible inspiration to transform your own operations from chaotic to controlled.
1. Equipment Maintenance and Calibration SOP
An Equipment Maintenance and Calibration SOP is a crucial document that provides a systematic process for ensuring all tools and machinery function correctly and within specified tolerances. This type of standard operating procedure is vital in industries where precision is non-negotiable, such as in pharmaceutical manufacturing for maintaining HPLC systems or in hospitals for calibrating MRI machines. Its primary goal is to prevent equipment failure, ensure data integrity, and maintain operational consistency, which directly impacts product quality and safety.
Strategic Breakdown
This SOP moves equipment care from a reactive "fix-it-when-it-breaks" model to a proactive, scheduled approach. It mandates regular checks, cleaning, servicing, and calibration, all documented meticulously. This process is heavily influenced by quality management systems like ISO 9001 and regulations like the FDA's Good Manufacturing Practices, making it a cornerstone of compliance and operational excellence. By standardizing maintenance, companies minimize costly downtime and extend the lifespan of valuable assets.
Actionable Takeaways
Implement a Digital System: Use a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) to automate scheduling, track service history, and manage spare parts inventory.
Cross-Train Your Team: Ensure multiple staff members are trained on critical maintenance procedures to avoid single points of failure.
Document Everything: Record every maintenance activity, deviation, and corrective action. This log is essential for audits and for identifying recurring equipment issues.
Optimize Scheduling: For more advanced strategies, you can learn more about how to master equipment maintenance scheduling for maximum uptime.
The following decision tree illustrates a simplified logic for determining when calibration is necessary, helping teams make consistent and timely maintenance choices.
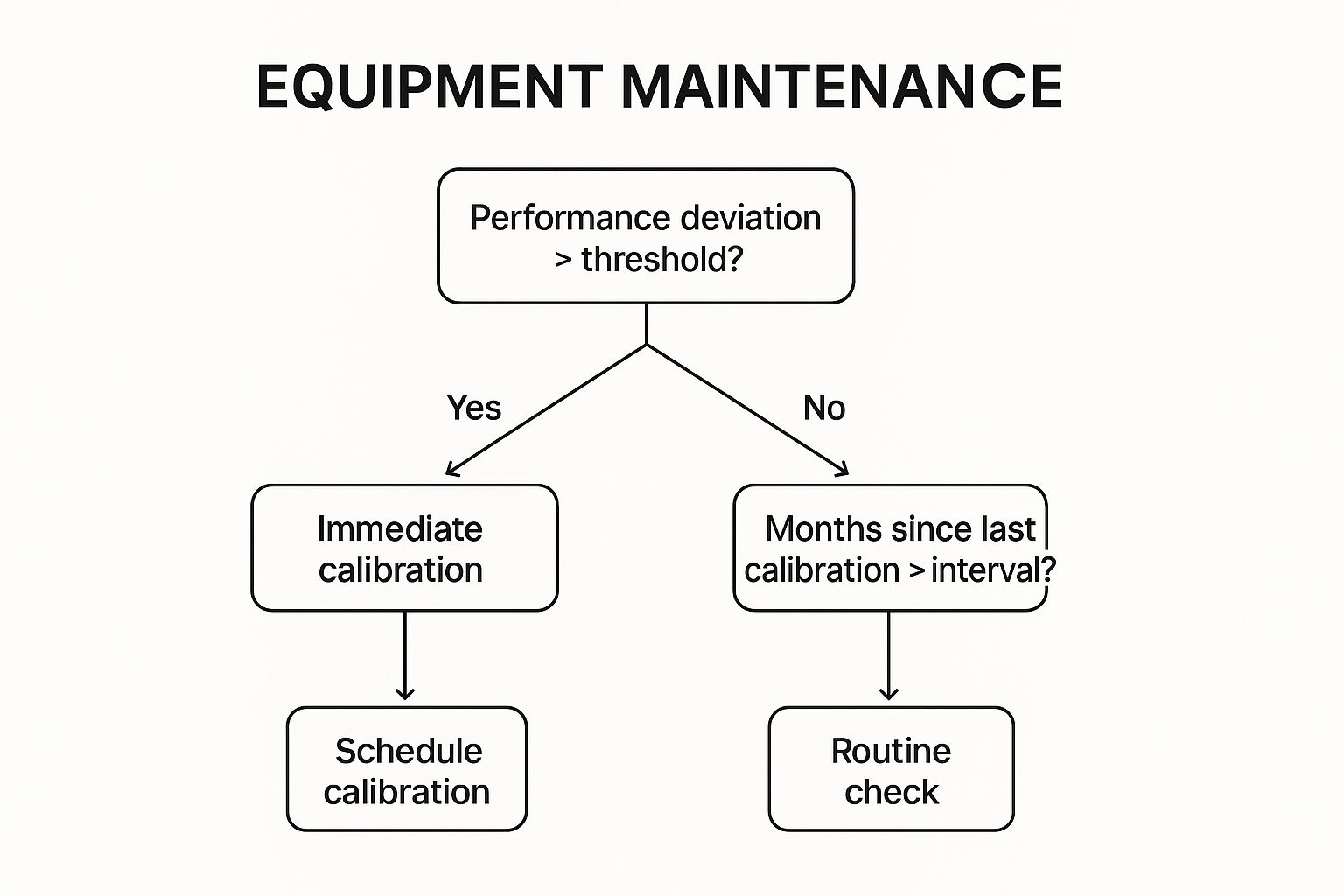
This visual guide shows that calibration can be triggered by either a performance issue or a scheduled interval, ensuring multiple safeguards are in place.
2. Customer Service Response Protocol SOP
A Customer Service Response Protocol SOP is a comprehensive framework that standardizes how customer inquiries, complaints, and requests are handled across all communication channels. This type of standard operating procedure is essential for companies aiming to deliver consistent, high-quality support, such as Zappos with its legendary customer service program or Amazon with its customer-centric support protocols. Its primary goal is to define response timeframes, escalation paths, and communication standards to ensure every customer interaction reinforces brand trust and satisfaction.

Strategic Breakdown
This SOP transforms customer service from a chaotic, ad-hoc function into a predictable, scalable system. It establishes clear rules for everything from the initial greeting to post-resolution follow-up, empowering agents to act decisively. Influenced by the "customer obsession" philosophy popularized by figures like Jeff Bezos, this approach uses tools like ServiceNow or Salesforce to create a single source of truth for every customer interaction. By standardizing responses and escalations, businesses can dramatically improve key metrics like First Contact Resolution (FCR) and Customer Satisfaction (CSAT).
Actionable Takeaways
Implement a Tiered Support System: Structure your team into tiers (e.g., Tier 1 for general inquiries, Tier 2 for technical issues) to ensure problems are routed to the most qualified agent efficiently.
Create Response Templates: Develop a library of pre-approved response templates for common questions and issues. This speeds up response times while ensuring brand voice consistency.
Establish Clear Escalation Triggers: Define specific conditions that trigger an escalation, such as unresolved issues after a set time or requests from high-value clients, to prevent customer frustration.
Use CRM to Track History: Leverage a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system to log all interactions. This gives agents full context for every conversation, leading to more personalized and effective support.
3. Data Backup and Recovery SOP
A Data Backup and Recovery SOP is a critical IT procedure that establishes systematic processes for backing up organizational data, testing backup integrity, and executing recovery steps in case of data loss. This type of standard operating procedure is essential for business continuity, protecting against threats like hardware failure, cyberattacks, and natural disasters. It's a foundational document for any organization that handles valuable information, from financial institutions protecting transaction data to healthcare organizations safeguarding patient records.

Strategic Breakdown
This SOP transforms data protection from a hopeful afterthought into a defined, repeatable, and testable business function. It formalizes schedules, retention policies, and recovery protocols, ensuring that data can be restored quickly and reliably, minimizing downtime and potential revenue loss. The procedure is often built around established frameworks like the 3-2-1 rule (three copies, two different media, one off-site) and is a core component of compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. By standardizing these actions, companies build resilience and demonstrate due diligence in protecting their digital assets.
Actionable Takeaways
Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Maintain at least three copies of your data, store them on two different types of media (e.g., local disk and cloud), and keep one copy off-site.
Test Your Backups Regularly: A backup is only useful if it can be restored. Schedule and perform regular recovery tests to validate backup integrity and practice the restoration process.
Automate and Monitor: Use automated backup solutions with built-in monitoring and alerting. This ensures backups run on schedule and immediately notifies the IT team of any failures.
Document Recovery Steps: Clearly outline the step-by-step procedure for data recovery. This documentation is invaluable during a high-stress incident and is crucial when handling complex processes like database restoration, which you can read about in this guide to data migration best practices for a seamless transition.
4. Employee Onboarding and Training SOP
An Employee Onboarding and Training SOP is a formalized document that outlines a consistent, repeatable process for integrating new hires into an organization. This procedure guides a new team member's journey from their pre-boarding activities through full productivity, covering orientation, role-specific training, and cultural immersion. It is essential in any industry for ensuring new employees feel welcomed, prepared, and aligned with company goals, such as in tech companies like Salesforce using its Trailhead platform for structured learning or in healthcare systems standardizing clinical training. Its main objective is to reduce ramp-up time, improve employee retention, and maintain a consistent company culture.
Strategic Breakdown
This SOP transforms onboarding from a simple administrative checklist into a strategic talent development initiative. It mandates a structured experience that includes pre-boarding communication, a comprehensive first-week plan, and scheduled checkpoints to monitor progress. This approach, championed by organizations like the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), shifts the focus from merely completing paperwork to purposefully engaging and equipping new talent. By standardizing this process, companies can ensure every new hire receives the same high-quality introduction to their role and the company's values, directly impacting long-term performance and loyalty.
Actionable Takeaways
Start Before Day One: Implement a pre-boarding process where you send a welcome kit, share team introductions, and provide access to necessary documents to build excitement and reduce first-day anxiety.
Assign an Onboarding Buddy: Pair each new hire with an experienced team member who can answer informal questions and help them navigate the company culture, separate from their direct manager.
Structure Training Modules: Break down complex job functions into smaller, digestible training modules delivered over several weeks. Use learning platforms to track completion and assess comprehension.
Create a Feedback Loop: Schedule regular check-ins at the 30, 60, and 90-day marks to gather feedback from the new hire about the onboarding process, allowing for continuous improvement.
5. Laboratory Sample Testing and Analysis SOP
A Laboratory Sample Testing and Analysis SOP is a rigorous scientific procedure that standardizes how samples are received, processed, tested, and reported. This type of SOP is foundational in settings where accuracy and reproducibility are paramount, such as clinical laboratories processing patient samples or environmental agencies analyzing water quality. The primary goal is to ensure the integrity of the analytical process from start to finish, maintaining a clear chain of custody and guaranteeing that results are reliable and defensible.
Strategic Breakdown
This standard operating procedure example transitions laboratory work from an individual-dependent art to a system-driven science. It mandates strict protocols for every step, including sample acceptance criteria, preparation methods, instrument operation, and data reporting. Heavily guided by standards like ISO/IEC 17025 and regulations such as the FDA's Good Laboratory Practices (GLP), this SOP is a non-negotiable component of quality assurance. By standardizing these complex workflows, labs minimize human error, prevent cross-contamination, and ensure that test results can be confidently reproduced and audited.
Actionable Takeaways
Implement a LIMS: Use a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) to automate sample tracking, manage test queues, and securely store results, reducing manual documentation errors.
Conduct Proficiency Testing: Regularly participate in external proficiency testing programs to validate your methods and benchmark your lab's performance against industry standards.
Maintain Detailed Records: Document every action, from sample receipt to the final report. This includes instrument logs, calibration records, and any deviations from the procedure.
Establish Critical Value Protocols: Create clear, immediate communication protocols for reporting results that fall outside of normal ranges and could indicate a critical issue.
6. Financial Transaction Processing SOP
A Financial Transaction Processing SOP is a comprehensive procedure that governs how financial transactions are initiated, authorized, processed, and recorded. This type of standard operating procedure establishes critical controls, approval hierarchies, and audit trails to ensure accuracy, prevent fraud, and maintain financial integrity. It is essential for organizations of all sizes, from corporations managing accounts payable workflows to investment firms handling securities transactions, as it forms the backbone of financial accountability and regulatory compliance.
Strategic Breakdown
This SOP transitions financial management from an ad-hoc, risky activity to a structured, auditable process. It standardizes every step, from initial request to final reconciliation, ensuring that no single individual has unchecked control over a transaction. This segregation of duties is a core principle influenced by frameworks like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the COSO framework. By defining clear roles and requiring specific documentation for approvals and verifications, the SOP creates a transparent system that safeguards assets and builds trust with stakeholders, auditors, and regulatory bodies.
Actionable Takeaways
Automate with Financial Software: Implement robust financial management systems like SAP or Oracle to automate workflows, enforce approval hierarchies, and create immutable audit logs.
Conduct Regular Audits: Routinely test transaction controls and perform internal audits to identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Maintain Clear Documentation: Insist on meticulous record-keeping for every transaction, including invoices, purchase orders, and approval signatures. This documentation is your primary defense during an audit.
Train for Fraud Prevention: Provide ongoing training to staff on recognizing common fraud schemes, phishing attempts, and social engineering tactics that target financial processes.
7. Safety Incident Response and Investigation SOP
A Safety Incident Response and Investigation SOP is a critical procedure that outlines the immediate actions, investigation methods, and corrective measures after a safety incident, accident, or near-miss. This type of standard operating procedure is essential for organizations committed to protecting their workforce and meeting regulatory standards, such as a construction company responding to a fall or a chemical facility managing an exposure event. Its primary purpose is to ensure employee well-being, facilitate transparent reporting, and prevent future occurrences by systematically analyzing root causes.
Strategic Breakdown
This SOP shifts the organizational mindset from reactive damage control to proactive, systematic improvement. It establishes clear, step-by-step protocols for everything from immediate first aid and securing the scene to conducting a thorough, blame-free investigation. Influenced heavily by frameworks from OSHA and NIOSH, this procedure is foundational to a robust safety management system. By standardizing the response, companies can ensure regulatory compliance, reduce liability, and foster a culture where safety is a shared responsibility. This process is also a key component of a larger risk management strategy; when preparing for unexpected disruptions, a comprehensive business continuity plan template can provide a broader framework for organizational resilience.
Actionable Takeaways
Establish a Blame-Free Reporting Culture: Encourage employees to report all incidents and near-misses without fear of reprisal, as this data is vital for identifying hidden risks.
Use Standardized Forms: Implement consistent digital or physical forms for incident reports and root cause analysis (like the "5 Whys" method) to ensure all necessary data is captured.
Train Designated Responders: Ensure specific team members are trained in first aid, incident scene management, and investigation protocols to lead an effective and orderly response.
Communicate Lessons Learned: Actively share findings and corrective actions from investigations across all relevant departments to prevent similar incidents from happening elsewhere.
8. Document Control and Management SOP
A Document Control and Management SOP establishes the systematic process for how all organizational documents are created, reviewed, approved, distributed, and archived. This type of standard operating procedure is fundamental for industries where information integrity is paramount, such as in ISO-certified companies managing quality manuals or legal firms handling sensitive case files. Its primary goal is to ensure document accuracy, enforce version control, and maintain compliance, thereby protecting information and supporting consistent business operations.
Strategic Breakdown
This SOP transforms document handling from a chaotic, ad-hoc activity into a structured, secure lifecycle management process. It defines clear rules for who can create, modify, and approve documents, preventing unauthorized changes and ensuring a single source of truth. Popularized by frameworks like ISO 9001 and enabled by platforms like SharePoint, this procedure is a cornerstone of quality management and information governance. By standardizing document control, companies mitigate compliance risks, improve audit readiness, and enhance operational efficiency.
Actionable Takeaways
Establish Clear Naming Conventions: Implement a standardized file naming system (e.g., ) to make documents easily searchable and identifiable.
Automate Workflows: Use an electronic document management system (EDMS) to automate the review and approval process, sending notifications to stakeholders and tracking progress.
Provide Role-Based Training: Ensure all employees are trained on their specific responsibilities within the document lifecycle, from creation to secure disposal.
Audit Regularly: Periodically review document access logs and version histories to ensure compliance and identify potential security gaps. For more in-depth strategies, explore these 9 document management best practices for 2025.
8 SOP Examples Comparison Guide
SOP Title | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Equipment Maintenance and Calibration SOP | Moderate to High: specialized technical knowledge needed | High: time, technical staff, possible vendor support | Reduced equipment downtime; measurement accuracy; compliance | Pharma, healthcare, manufacturing, labs | Extends equipment life; ensures reliability; cost-saving over time |
Customer Service Response Protocol SOP | Moderate: requires training and updates | Moderate: CRM systems, trained staff | Consistent, timely customer interactions; higher satisfaction | Retail, e-commerce, hospitality | Faster resolution; improved retention; accountability |
Data Backup and Recovery SOP | High: complex IT setup and monitoring | High: infrastructure, software, security | Minimized data loss; business continuity; regulatory compliance | Financial, healthcare, government, e-commerce | Quick recovery; protects against cyber threats; peace of mind |
Employee Onboarding and Training SOP | Moderate: extensive program development | Moderate to High: trainers, materials, platforms | Reduced turnover; faster productivity; consistent training | All industries with significant staffing needs | Improved engagement; accountability; structured learning |
Laboratory Sample Testing and Analysis SOP | High: rigorous protocols and training | High: lab equipment, specialized staff | Reliable, reproducible results; regulatory compliance | Clinical, environmental, food safety, pharma labs | Traceability; reduces errors; quality control |
Financial Transaction Processing SOP | Moderate to High: multi-level controls | Moderate: software and trained personnel | Fraud prevention; accurate records; regulatory compliance | Banks, corporations, investment firms, government agencies | Clear audit trails; streamlined but controlled process |
Safety Incident Response and Investigation SOP | Moderate to High: training, documentation | Moderate: training, investigation resources | Reduced injuries; legal compliance; improved safety culture | Manufacturing, construction, chemical, healthcare | Systematic analysis; liability protection; culture building |
Document Control and Management SOP | Moderate: workflow and change management | Moderate: document management systems | Document accuracy; version control; regulatory compliance | ISO-certified companies, pharma, legal, government agencies | Consistency; audit trails; improved info sharing |
From Examples to Execution: Your Next Steps
We've explored eight diverse standard operating procedure examples, moving from the technical precision of equipment calibration to the critical human element of employee onboarding. Each example, whether for data recovery or customer service, illustrates a universal truth: structured processes are the bedrock of operational excellence and sustainable growth.
The power of these documents lies not in rigid, unchangeable rules, but in their ability to provide a clear, repeatable framework. A well-crafted SOP is a strategic tool that transforms tribal knowledge into a shared, accessible company asset. It empowers your team with the autonomy to act confidently, knowing they are following a tested and approved method.
Distilling Strategy from Structure
Across all the examples, from financial processing to safety incident response, several core principles emerged. These are the strategic takeaways you can apply directly to your own procedure development.
Clarity Over Complexity: The best SOPs use simple language, visual aids like flowcharts, and a logical step-by-step structure. The goal is immediate comprehension, not academic thoroughness.
Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Ambiguity is the enemy of efficiency. Every effective SOP clearly states who is responsible for what at each stage of the process.
Embedded Checks and Balances: Notice how the data backup SOP included verification steps and the financial SOP required approvals. Building in these checkpoints is crucial for quality control and risk mitigation.
A Foundation for Automation: A clearly documented procedure is the first step toward powerful automation. You cannot automate a chaotic or undefined workflow; an SOP provides the necessary blueprint for tools like Zapier, Make.com, or custom CRM workflows.
Your Action Plan for Implementation
Viewing these standard operating procedure examples should be a catalyst for action, not just a source of information. The transition from theory to practice is where the real value is unlocked. Don't let the scope of a full operational overhaul intimidate you; progress begins with a single, well-defined step.
Here is a simple, actionable path forward:
Identify a High-Impact Process: Start by targeting one recurring bottleneck or area of frequent error in your business. Is it your sales outreach, client onboarding, or project management workflow?
Draft a "Version 1.0" SOP: Don't aim for perfection. Create a simple, one-page document outlining the essential steps. Focus on making it 80% right and getting it into the hands of your team quickly.
Gather Feedback and Iterate: The initial draft is a starting point. Ask the employees who perform the task for their input. What steps are missing? What could be clearer? Refine the document based on real-world use.
Embrace Automation: Once the process is stable and documented, explore opportunities for automation. Can you use a tool like GoHighLevel or n8n to handle repetitive communication, data entry, or task assignments?
Mastering the art of creating and implementing SOPs moves your business from reactive problem-solving to proactive, strategic execution. It builds a resilient, scalable operation where consistency and quality are not accidental but engineered by design.
Ready to transform your documented procedures into powerful, automated workflows? At Flow Genius, we specialize in turning your SOPs into seamless, efficient systems that run on their own, freeing up your team to focus on what matters most. Schedule a discovery call with Flow Genius today and let's build your operational playbook together.