10 Business Process Automation Strategies to Scale in 2025
- Aug 6, 2025
- 16 min read
In today's competitive market, efficiency isn't just an advantage; it's a core requirement for survival. Businesses are constantly searching for ways to do more with less, eliminate human error, and free up talented teams for high-value strategic work. The most direct path to achieving this is by moving beyond repetitive manual tasks and embracing a culture of automation. This article cuts through the noise to provide a detailed, actionable roadmap for doing just that.
We will explore 10 powerful business process automation strategies, moving from foundational concepts like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Workflow Automation to more advanced approaches such as AI-Powered Intelligent Automation and Hyperautomation. You will gain practical insights into how these strategies can be implemented across diverse industries, whether you're managing complex logistics, integrating software ecosystems, or optimizing field service operations.
Each strategy is presented not as a theoretical concept, but as a tangible tool for transformation. For companies aiming to accelerate this journey, specialized consultancies can design and implement custom workflows that translate these strategies into measurable results. By understanding these approaches, you can begin to reclaim countless hours, reduce operational friction, and build a framework for scalable, sustainable growth.
1. Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Your Digital Workforce
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is one of the most accessible and powerful business process automation strategies available today. It involves deploying software “bots” that replicate human actions to execute repetitive, rule-based tasks directly within your existing user interfaces. Think of it as a digital workforce that can log into applications, copy-paste data, move files, and fill out forms, all without needing complex API integrations.

This non-invasive approach makes RPA an ideal starting point for businesses looking to automate legacy systems or high-volume transactional processes. Because bots interact with applications just like a person would, you can achieve significant efficiency gains without overhauling your core IT infrastructure.
When and Why to Use RPA
RPA is best suited for processes that are stable, rule-based, and involve structured data. It excels in environments where you need to bridge gaps between systems that don't have APIs. For example, Walmart uses RPA to automate invoice processing and manage accounts payable, significantly reducing manual effort. Similarly, Telefonica automated customer service requests, achieving a 90% straight-through processing rate and freeing up agents for more complex issues.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To successfully deploy RPA, focus on a strategic rollout:
Start Small: Identify high-volume, low-complexity tasks like data entry or report generation for quick wins. This builds momentum and demonstrates ROI fast.
Standardize Processes: Before automating, ensure the target workflow is standardized and optimized. Automating a flawed process only magnifies its inefficiencies.
Establish Governance: Create clear guidelines for bot development, deployment, and maintenance. Implement change management to help your team adapt to working alongside a digital workforce.
Monitor Performance: Regularly track bot performance and exception rates. This allows you to identify issues early and continuously improve your automations. Popular tools like UiPath and Automation Anywhere provide robust monitoring dashboards.
2. Workflow Automation: Orchestrating Your Business Engine
Workflow automation focuses on orchestrating the sequence of tasks, data, and handoffs that constitute a business process. Unlike RPA, which mimics human actions, workflow automation defines and executes the entire process logic, routing work between people and systems based on predefined rules. It ensures that approvals, data transfers, and notifications happen automatically, creating a seamless flow from start to finish.

This strategy is foundational to many successful business process automation strategies because it provides the structural backbone for how work gets done. By defining the "who, what, and when" for each step, it eliminates bottlenecks, prevents tasks from falling through the cracks, and provides full visibility into process status. For a deeper dive into the mechanics, you can explore what workflow automation is and how it can be applied.
When and Why to Use Workflow Automation
Workflow automation is ideal for multi-step, multi-stakeholder processes that require clear rules, approvals, and system integrations. It shines in scenarios like employee onboarding, expense report approvals, and customer support case escalation. For instance, Siemens streamlined its procurement cycle by 60% with workflow automation, while American Express automated expense reporting to cut processing time from days to just hours.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To implement workflow automation effectively, a clear plan is essential:
Map Processes Thoroughly: Before you automate, create a detailed visual map of the current process. Identify every task, decision point, and stakeholder to ensure nothing is missed.
Design for Exceptions: Your workflow should gracefully handle exceptions and edge cases. Define clear escalation paths for when a task is overdue or an approval is rejected.
Implement a Gradual Rollout: Start with a pilot group or a single department to test and refine the workflow. This minimizes disruption and allows you to gather feedback before a company-wide deployment.
Prioritize User Training: Ensure everyone involved understands their role in the new automated workflow. Provide comprehensive training and clear documentation to drive adoption and prevent confusion.
3. API-First Integration Strategy
An API-First Integration Strategy is a forward-thinking approach to business process automation strategies that treats Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) as core products, not afterthoughts. It involves designing and building APIs first, which then serve as the foundational building blocks for connecting applications, data, and services. This enables seamless, real-time data exchange and process automation across your entire technology stack, creating a truly interconnected ecosystem.
This method moves beyond point-to-point connections and fosters a flexible, scalable, and reusable integration framework. By prioritizing APIs, you empower both internal teams and external partners to innovate and automate processes without disrupting core systems. It’s the engine that powers modern, composable enterprises.
When and Why to Use an API-First Strategy
This strategy is ideal when you need to achieve deep, real-time integration and build a scalable platform. It's essential for businesses that rely on a microservices architecture or want to create an ecosystem for partners and third-party developers. For example, Stripe’s API-first model allows millions of businesses to integrate payment processing directly into their applications. Similarly, Salesforce's robust API ecosystem facilitates the vast majority of its customer data interactions, proving how APIs can automate and extend platform functionality.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To successfully adopt an API-first approach, build with intention:
Design for Consumers: Create APIs with clear, comprehensive documentation and strict versioning. Treat your API consumers (whether internal or external) as customers.
Implement Robust Security: Secure your APIs from the start with authentication, authorization, and throttling. Use an API gateway for centralized policy enforcement and management.
Follow Established Standards: Adhere to RESTful design principles and industry standards to ensure your APIs are predictable, reliable, and easy for developers to use.
Monitor and Analyze: Continuously track API performance, uptime, and usage analytics. Tools from providers like MuleSoft and Postman offer powerful monitoring capabilities to optimize your API landscape.
4. Low-Code/No-Code Automation Platforms
Low-Code/No-Code (LC/NC) platforms democratize automation by empowering business users and citizen developers to build applications and workflows with minimal to no coding. These platforms use visual interfaces, pre-built modules, and drag-and-drop functionality, allowing teams to quickly design and deploy solutions. This accelerates development and brings automation capabilities directly to the people who understand the business processes best.
This approach significantly reduces reliance on specialized IT teams, allowing for faster and more agile development cycles. By placing powerful tools in the hands of business users, companies can foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement from the ground up, making this one of the most transformative business process automation strategies available.
When and Why to Use Low-Code/No-Code
LC/NC platforms are ideal when you need to rapidly develop and deploy custom applications or automate departmental workflows. They excel at bridging operational gaps where off-the-shelf software is too rigid and full-code development is too slow or expensive. For instance, Progressive Insurance automated complex claims processing using Appian, improving speed by 50%. Similarly, T-Mobile leveraged OutSystems to build over 500 applications, cutting development time by an incredible 70%.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To get the most out of Low-Code/No-Code platforms, focus on empowerment and control:
Establish Clear Governance: Create policies for citizen developers that define what they can build, what data they can access, and the required approval processes.
Provide Training and Support: Equip your business users with the knowledge they need through structured training programs and dedicated support channels. Check out this guide to see how automation for small business can be implemented with these tools.
Start with Simple Processes: Begin with low-risk, high-impact projects like internal request forms or simple approval workflows to build confidence before tackling more complex systems.
Implement Quality Assurance: Ensure all citizen-developed applications undergo proper testing. A peer-review process or a dedicated QA team can maintain high standards and prevent issues. Platforms like Mendix and Bubble facilitate this.
5. AI-Powered Intelligent Automation
AI-Powered Intelligent Automation, often called Hyperautomation, elevates business process automation strategies by integrating artificial intelligence (AI) with traditional automation. This powerful combination allows systems to handle unstructured data, make complex decisions, and learn from outcomes. It moves beyond simple rule-based tasks by incorporating technologies like machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision to manage variable and unpredictable workflows.
Unlike RPA, which follows explicit instructions, intelligent automation can interpret context, analyze patterns, and adapt its actions. This enables the automation of end-to-end processes that previously required human judgment, unlocking significant operational efficiency and creating a more resilient, adaptive business model.
When and Why to Use Intelligent Automation
Intelligent Automation is essential when processes involve unstructured data, cognitive decision-making, and dynamic conditions. It is the ideal strategy for complex scenarios that are too variable for standard automation. For example, HSBC uses AI to analyze transaction patterns and automate fraud detection with 95% accuracy. Similarly, Deutsche Bank leverages intelligent document processing (IDP) to automate Know Your Customer (KYC) checks, reducing manual review time by over 80%.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively integrate intelligent automation, a data-centric approach is key:
Start with Defined Use Cases: Begin with processes where training data is readily available, such as invoice processing or customer sentiment analysis. This ensures your AI models have a solid foundation.
Ensure Data Quality: The performance of any AI model depends on the quality of its training data. Prioritize cleaning, standardizing, and organizing your data before implementation.
Implement Human Oversight: Use a "human-in-the-loop" model, especially in the early stages. This allows for human verification of AI decisions, builds trust, and helps refine the model.
Plan for Continuous Improvement: AI models are not static. Regularly monitor their performance, retrain them with new data, and plan for ongoing optimization to maintain accuracy and relevance. Popular platforms like IBM Watson and Google AI Platform offer tools for this.
6. Process Mining and Discovery: Uncovering Your True Workflow
Process mining is one of the most powerful diagnostic business process automation strategies, acting as an X-ray for your operations. It leverages event log data from your existing systems (like ERPs and CRMs) to automatically generate a visual map of how your processes actually run, not just how you think they run. This provides objective, data-driven insights into hidden bottlenecks, costly deviations, and compliance issues.
This discovery-first approach allows you to pinpoint the root causes of inefficiency before you even think about automation. By understanding the reality of your workflows, you can make informed decisions, ensuring you automate the right processes for the maximum impact.
When and Why to Use Process Mining
Process mining is ideal for complex, high-volume processes where a lack of visibility is causing performance issues. It’s perfect for answering questions like, “Why is our order-to-cash cycle so long?” or “Where are the delays in our customer support ticket resolution?” For example, Uber used Celonis to optimize its driver onboarding process, reducing time-to-activation by 35%. Similarly, BMW analyzed its production workflows, increasing overall efficiency by 15%. For organizations looking to optimize their operations, delving deeper into a systematic approach for understanding business processes is crucial, such as exploring their approach to processes.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To get the most from process mining, follow a structured approach:
Ensure Data Quality: Start by gathering high-quality, comprehensive event logs. The accuracy of your insights depends entirely on the data you feed the system.
Target High-Impact Areas: Begin with a process that has a clear business impact, like procure-to-pay or customer onboarding, to demonstrate value quickly.
Involve Process Owners: Collaborate with the people who execute the process daily. Their domain expertise is essential for correctly interpreting the discovered process maps and identifying meaningful opportunities.
Prioritize Automation Initiatives: Use the findings to build a business case for specific automation projects. Address the biggest bottlenecks and deviations first for the highest ROI. Popular tools include Microsoft Process Advisor and Signavio.
7. Event-Driven Architecture (EDA): Real-Time Process Automation
Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) is a powerful software pattern where processes are triggered by "events," such as a new customer signup, a completed payment, or a sensor reading. Rather than services constantly asking each other for updates, they subscribe to event streams and react automatically when something happens. This creates highly responsive, decoupled, and scalable business process automation strategies that operate in real time.
This model allows different parts of your business to communicate and act instantly without being tightly linked. When one system generates an event, other subscribed systems can immediately kick off their own automated workflows, from sending notifications to updating inventory, creating an agile and interconnected operational environment.
When and Why to Use EDA
EDA is ideal for scenarios requiring immediate responses and high scalability. It excels in complex ecosystems where multiple systems need to react to business activities as they occur. For example, Netflix uses EDA to process billions of viewing events, automating everything from content recommendations to playback monitoring. Similarly, Goldman Sachs leverages an event-driven model for real-time trading automation and immediate risk management calculations based on market changes.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement an Event-Driven Architecture, focus on system resilience and clarity:
Design Clear Event Schemas: Define a standardized, versioned structure for your events. A clear schema ensures that all services interpret event data correctly, preventing integration errors.
Implement Robust Error Handling: Plan for failures. Use dead-letter queues (DLQs) to capture and isolate events that fail processing, so you can analyze and resolve issues without halting the entire workflow.
Use Event Sourcing for Audits: Store a complete, immutable log of all events. This not only creates a perfect audit trail but also allows you to "replay" events to reconstruct system states or debug problems.
Monitor System Health: Employ comprehensive monitoring for event producers, brokers, and consumers. Track metrics like event throughput and processing latency with tools like Amazon EventBridge to ensure your automation pipelines are healthy.
8. Hyperautomation: The Ultimate End-to-End Automation
Hyperautomation goes beyond single-tool solutions by combining multiple complementary technologies to automate as many business processes as possible. Coined by Gartner, it represents a disciplined, business-driven approach that orchestrates the use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and process mining to achieve true, end-to-end automation at an enterprise scale.
This holistic strategy allows businesses to not only automate tasks but also to discover, analyze, and continuously improve entire workflows. By integrating a "digital twin" of the organization, hyperautomation identifies bottlenecks and opportunities, creating a virtuous cycle of improvement that drives transformative efficiency.
The following infographic illustrates the core components that converge to enable hyperautomation.
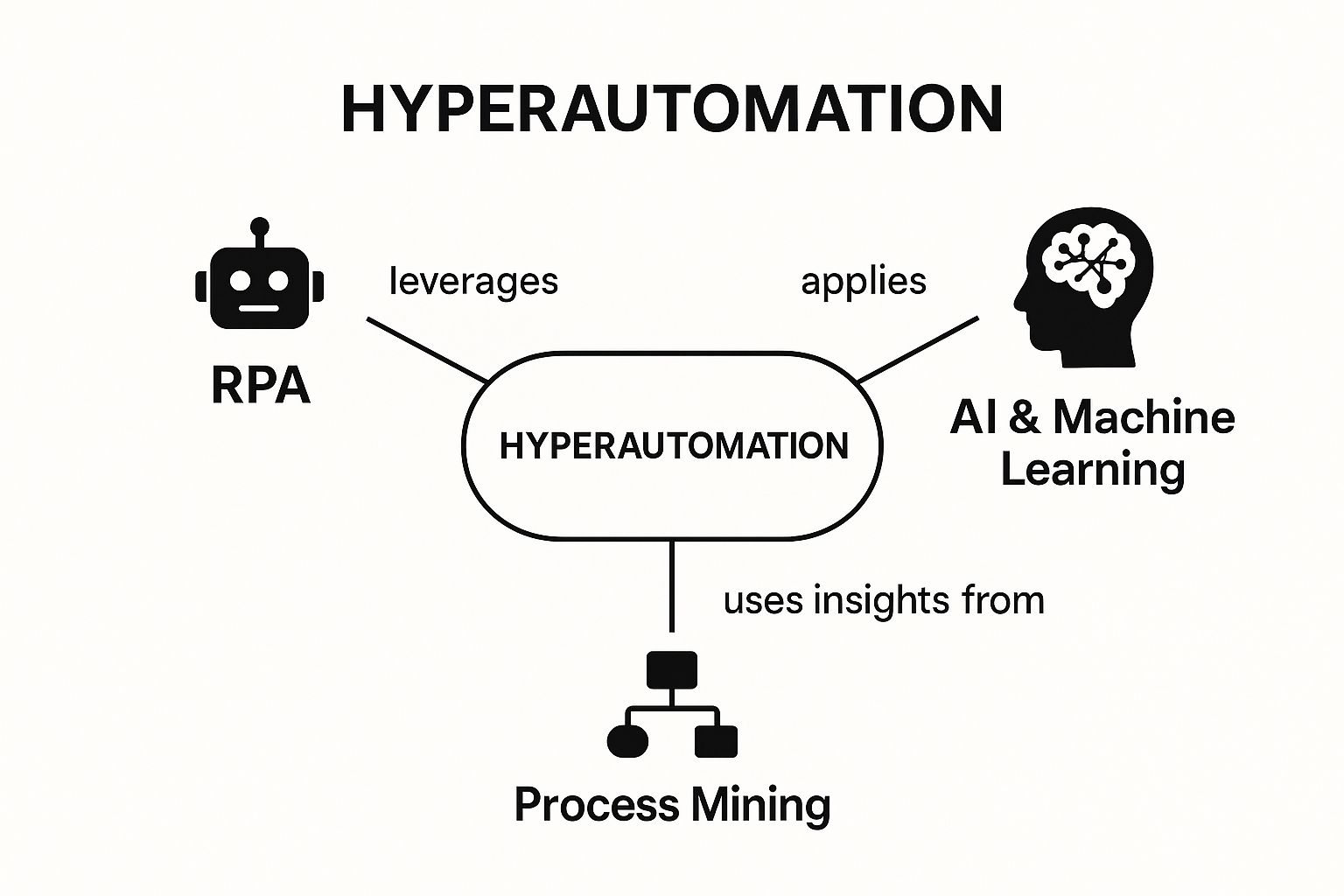
This visualization highlights how hyperautomation is not a single technology but a powerful fusion of process mining for discovery, RPA for task execution, and AI for intelligent decision-making.
When and Why to Use Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is ideal for large-scale digital transformation initiatives where the goal is to create a fully optimized, agile, and resilient enterprise. It's not for automating a single task but for reimagining and automating complex, cross-departmental processes from start to finish. For example, Siemens leveraged hyperautomation to achieve 95% automation in its financial closing processes, while Deutsche Telekom reduced manual work by 70% through its comprehensive implementation. This strategy is one of the most advanced business process automation strategies for achieving unparalleled operational excellence.
Actionable Implementation Tips
A successful hyperautomation journey requires a strategic, top-down approach:
Develop a Comprehensive Roadmap: Start with a clear vision and a detailed strategy. Identify which end-to-end processes offer the highest potential for impact and ROI.
Establish a Center of Excellence (CoE): Create a dedicated team to govern your automation initiatives, set standards, manage resources, and ensure alignment with business goals.
Standardize Before You Automate: Use process mining tools to analyze and optimize workflows before applying automation. Automating a broken or inefficient process will only amplify its flaws.
Focus on Change Management: Prepare your workforce for the shift. Emphasize upskilling and reskilling to transition employees from repetitive tasks to higher-value roles that complement the automated ecosystem. Leading platforms like UiPath and Automation Anywhere provide tools to support this comprehensive approach.
9. Business Process Management (BPM) Systems
Business Process Management (BPM) systems offer a comprehensive, top-down approach to process automation. Unlike tools that target individual tasks, BPM platforms provide a holistic framework to design, execute, monitor, and continuously optimize entire end-to-end business processes. They combine workflow automation, business rules engines, and robust analytics to align operational activities directly with strategic business objectives.
This strategy treats processes as valuable company assets that require active management and evolution. It moves beyond simple task automation to orchestrate complex workflows involving multiple people, systems, and departments, ensuring everything works in concert to achieve a specific business outcome.
When and Why to Use BPM
BPM is one of the most powerful business process automation strategies for complex, core operations that are central to your company’s value proposition. It is ideal for processes that require human intervention, complex decision-making, and integration across multiple systems. For example, ING Bank implemented a BPM system from Appian for its loan origination process, cutting approval times from weeks to days. Similarly, Allianz used Pega BPM to automate insurance claims, reducing settlement time by 40% and improving customer satisfaction.
Actionable Implementation Tips
A successful BPM initiative requires a strategic mindset and careful planning:
Align with Business Goals: Start by identifying which core processes directly impact strategic objectives like customer retention or market expansion. This ensures your automation efforts deliver meaningful business value.
Invest in Process Analysis: Before building anything, thoroughly map, analyze, and redesign the target process. The goal is to optimize the workflow first, then automate the improved version.
Implement in Phases: Roll out your BPM solution in manageable stages with clear success metrics for each phase. This approach minimizes risk and allows for iterative improvements.
Ensure Stakeholder Engagement: Involve key stakeholders from all affected departments early and often. Provide comprehensive training to ensure user adoption and a smooth transition.
10. Cloud-Native Automation: Scalable and Resilient Workflows
Cloud-native automation shifts away from on-premise solutions, leveraging modern cloud architectures like microservices, containers, and serverless computing. This approach involves building and running automation solutions that are designed specifically for the cloud, enabling them to be exceptionally scalable, resilient, and cost-effective. Instead of a single, monolithic process, tasks are broken down and deployed as independent services that scale on demand.
This strategy is foundational for businesses aiming for agility and operational excellence. It allows automation to grow dynamically with business needs, handling fluctuating workloads without manual intervention or over-provisioning expensive hardware. It's one of the most powerful business process automation strategies for companies born in or migrating to the digital age.
When and Why to Use Cloud-Native Automation
This approach is ideal for businesses that require high availability, dynamic scalability, and cost efficiency. It is particularly effective for data-intensive applications and services with unpredictable usage patterns. For instance, Spotify uses a cloud-native microservices architecture to automate its massive-scale music recommendation and playlist generation engines. Similarly, Airbnb leverages cloud automation to dynamically scale its infrastructure to handle surges in booking traffic, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement cloud-native automation, focus on building for the cloud from day one:
Design for Cloud Patterns: Don't just "lift and shift" old processes. Re-architect workflows using microservices and serverless functions to fully benefit from the cloud's elasticity.
Use Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC): Employ tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to define and manage your infrastructure through code. This ensures consistent, reproducible, and automated deployments.
Implement Robust Monitoring: Utilize cloud-native monitoring tools like Prometheus or Datadog to track performance, manage costs, and gain deep visibility into your distributed systems.
Prioritize Security and Compliance: Invest in cloud security expertise and implement automated compliance checks to protect data and meet regulatory requirements in a dynamic environment. For a deeper dive, you can explore guides on digital process automation.
Automation Strategies Comparison Matrix
Automation Type | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Medium – Quick setup for rule-based tasks | Moderate – Licenses & bot management | High accuracy, cost reduction, 24/7 operation | High-volume transactional tasks (data entry, invoices) | Non-invasive, fast ROI, frees employees |
Workflow Automation | Medium to High – Depends on process design | Moderate to High – Integration needs | Improved process visibility, reduced cycle times | Cross-departmental workflows (onboarding, approvals) | Enhances collaboration, real-time tracking |
API-First Integration Strategy | High – Requires technical expertise | High – Skilled developers, API management | Scalable, flexible integrations, rapid deployment | Enterprise system and SaaS integrations | Future-proof, supports multiple platforms |
Low-Code/No-Code Automation Platforms | Low to Medium – Visual setup, minimal coding | Low to Moderate – Platform licenses, some training | Faster deployment, empowers business users | Department-level automation, prototyping | Reduces IT dependency, quick time-to-market |
AI-Powered Intelligent Automation | High – Complex models and training needed | High – Data, compute, AI expertise | Handles unstructured data, continuous learning | Document processing, chatbots, predictive maintenance | Adaptive, processes complex inputs |
Process Mining and Discovery | Medium to High – Data access & analysis needed | Moderate – Data infrastructure, licenses | Data-driven insights, process optimization | Pre-automation analysis, compliance monitoring | Objective bottleneck identification |
Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) | High – Requires event design & monitoring | High – Infrastructure & development complexity | Real-time responsiveness and scalability | Real-time trading, IoT, microservices orchestration | Highly scalable, loosely coupled systems |
Hyperautomation | Very High – Multi-technology orchestration | Very High – Multiple tools and expertise | End-to-end automation, faster ROI | Large enterprises, full digital transformation | Synergistic tech integration, continuous improvement |
Business Process Management (BPM) Systems | High – Complex configuration and design | High – Infrastructure, licensing, analysis | Holistic process control, governance | Complex, regulated processes (banking, healthcare) | Flexible, strong compliance and analytics |
Cloud-Native Automation | High – Requires cloud and container expertise | Moderate to High – Cloud services & monitoring | Scalability, elasticity, cost efficiency | Scalable apps, dynamic processes with variable loads | Auto-scaling, fast updates, cloud-native features |
From Strategy to Action: Implementing Your Automation Plan
We have journeyed through ten distinct and powerful business process automation strategies, from the task-oriented precision of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to the holistic, all-encompassing vision of Hyperautomation. You have seen how API-first integrations create a connected technological nervous system and how low-code platforms like Make.com and Zapier put the power of creation directly into the hands of your team. The path forward is no longer about asking if you should automate, but how and where you should begin.
The key takeaway is that these strategies are not mutually exclusive. The most resilient and efficient businesses often build a hybrid model, a customized mosaic of automation tactics. A roofing contractor might use a workflow automation tool for CRM updates while leveraging an API to pull real-time weather data. A technology company could combine an event-driven architecture with AI-powered intelligent automation to proactively manage its cloud infrastructure and respond to security threats in milliseconds.
Your Blueprint for Implementation
Embarking on this journey requires a pragmatic, step-by-step approach. The goal is not to overhaul your entire operation overnight but to build sustainable momentum. Begin by identifying the "low-hanging fruit": processes that are repetitive, time-consuming, and have a clear, measurable impact on your daily operations.
Consider these immediate next steps:
Conduct a Process Audit: Map out a single, high-impact workflow. Document every manual step, from data entry in your CRM to outbound calling sequences. This clarity is the foundation of effective automation.
Start Small, Scale Smart: Select one of the business process automation strategies discussed, like a simple workflow automation using Zapier or Make.com, to tackle that initial process. Measure the time saved and the errors eliminated.
Champion the Wins: Share the results with your team. Demonstrating a tangible return on investment, even a small one, builds the internal support and cultural shift necessary for broader adoption.
Key Insight: Successful automation is a strategic initiative, not just a technical one. It begins with understanding your operational pain points and aligning your chosen technology with clear business objectives, such as improved customer response times, reduced operational costs, or enhanced data accuracy.
The value of mastering these concepts extends far beyond simply reclaiming a few hours in the workday. It's about building a business that is agile, scalable, and fundamentally more competitive. By systematically removing manual bottlenecks, you empower your employees to focus on high-value work: strategy, customer relationships, and innovation. You create an operational foundation that can adapt to market changes, handle increased demand without a proportional increase in headcount, and deliver a consistently superior customer experience. The path from strategy to action is clear, and the tools are more accessible than ever. The time to build your automated future is now.
Are you ready to transform your strategic plans into tangible, automated workflows? The team at Flow Genius specializes in bridging the gap between automation concepts and real-world execution, using powerful platforms like Zapier, Make.com, and custom scripts to build solutions tailored to your unique business needs. Visit Flow Genius to see how our expertise can accelerate your journey to peak operational efficiency.