10 Supply Chain Management Best Practices for 2025
- Matthew Amann

- Jul 3, 2025
- 18 min read
In today's volatile global market, a resilient and efficient supply chain is not just a competitive advantage; it is a fundamental necessity for survival and growth. Businesses across diverse sectors, from technology companies and infrastructure project managers to commercial cleaning services and roofing contractors, face unprecedented pressures. These challenges range from unpredictable demand shifts and logistical bottlenecks to geopolitical disruptions that can halt operations without warning. The key to navigating this complexity lies in adopting robust supply chain management best practices that enhance visibility, agility, and collaboration.
Stagnant, manual processes are no longer viable. They create friction, inflate costs, and leave organizations vulnerable to even minor shocks. This is where strategic automation and intelligent oversight become transformative. For any business aiming to synchronize logistics, automate workflows in platforms like Zapier or Make.com, or optimize resource management, the principles of modern supply chain excellence are critical. By implementing proven strategies, companies can turn operational challenges into opportunities for innovation, building a responsive and predictive network that drives profitability and ensures long-term stability.
This guide provides a comprehensive roundup of the most impactful supply chain management practices. We will move beyond theory to deliver actionable insights, practical implementation steps, and real-world examples tailored for immediate application. You will learn how to streamline your operations from end to end, reduce waste, and build a truly resilient supply chain prepared for the demands of tomorrow.
1. Demand Forecasting and Planning
Effective supply chain management begins with a clear understanding of what your customers will want and when they will want it. This is the core of demand forecasting and planning, a foundational best practice that involves using historical sales data, market trends, and statistical models to predict future customer demand. Getting this right prevents both costly overstocking and frustrating stockouts, directly impacting your bottom line and customer loyalty.
Companies like Walmart have mastered this by using sophisticated forecasting to manage inventory across thousands of stores, ensuring products are always available without tying up excessive capital. Similarly, Amazon’s groundbreaking anticipatory shipping model predicts demand with such precision that it pre-positions inventory in warehouses closer to potential buyers, even before an order is placed.
How to Implement Demand Forecasting
Integrating robust forecasting doesn't have to be overly complex from the start. The key is to build a process that aligns with your business's maturity and resources.
Start Simple, Scale Smart: Begin with basic models like moving averages or exponential smoothing. As you gather more data and expertise, you can graduate to more advanced statistical methods or even machine learning algorithms for greater accuracy.
Collaborate for Clarity: Your sales and marketing teams possess invaluable on-the-ground intelligence about upcoming promotions, competitor activities, and shifting customer sentiment. Involving them in the forecasting process adds a qualitative layer that quantitative data alone cannot provide.
Review and Refine: Demand is not static. Set up a regular cadence, whether monthly or quarterly, to review forecast performance against actual sales. This allows you to adjust your models and assumptions, continuously improving their accuracy.
Key Insight: The goal of demand forecasting isn't to achieve 100% accuracy, which is impossible. Instead, the objective is to reduce uncertainty and make more informed inventory, production, and logistics decisions.
To effectively measure the performance of your forecasting efforts, it's crucial to track specific metrics. The following summary highlights the essential indicators for evaluating your forecasting accuracy.
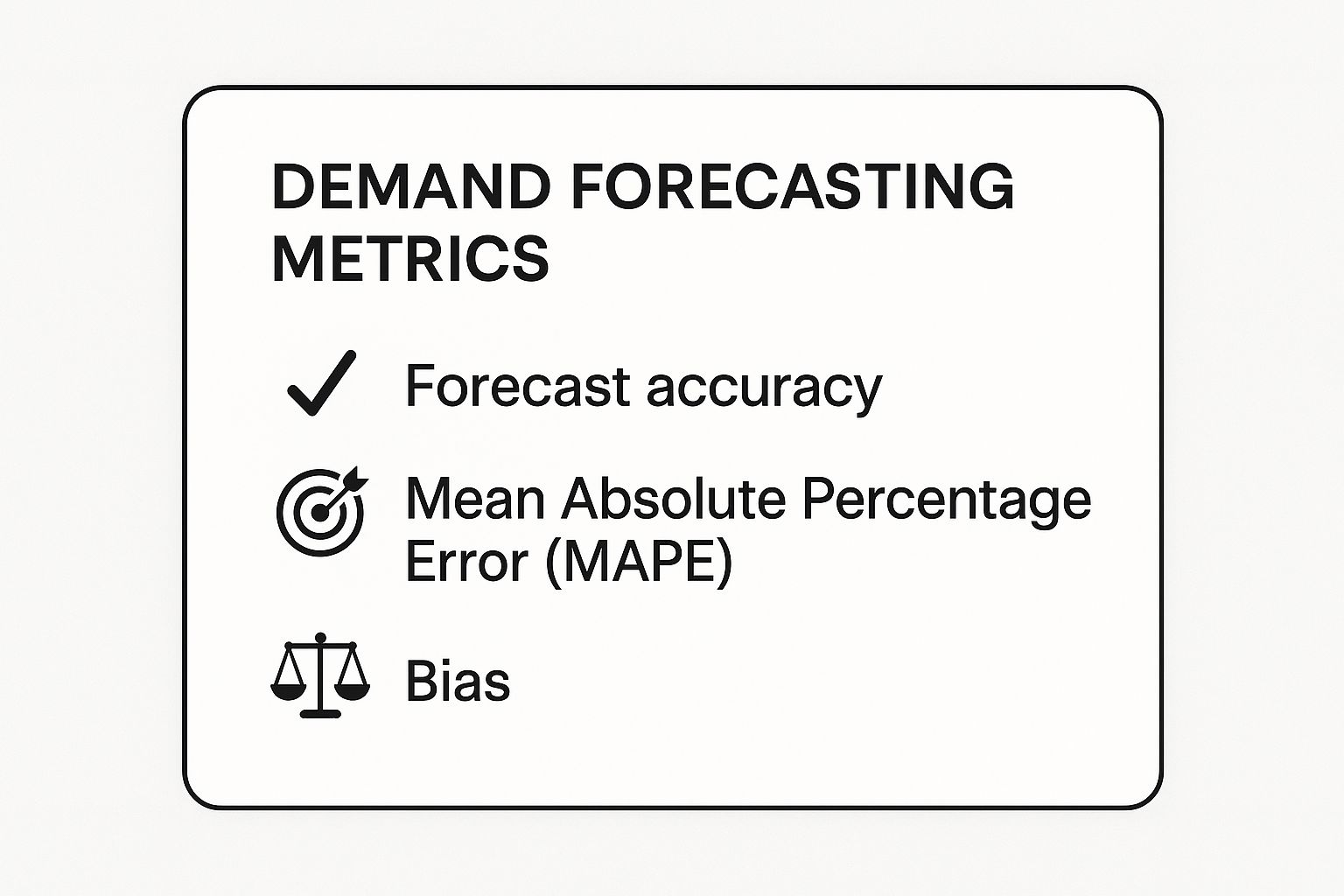
Tracking these key metrics provides a clear, quantitative view of your forecasting success, enabling you to pinpoint and correct systematic errors, such as consistently over or under-forecasting. By focusing on these numbers, you can turn forecasting from a guessing game into a strategic business advantage.
2. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
Your supply chain is only as strong as its weakest link, and often, that link involves your suppliers. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) moves beyond transactional purchasing to a strategic approach where you manage interactions with companies providing goods and services. This best practice centers on developing collaborative partnerships, evaluating supplier performance, and fostering mutual value that drives innovation, reduces risk, and improves efficiency.
Legendary examples include Toyota, which builds deep, long-term partnerships through its supplier development program to ensure continuous improvement and quality. Likewise, Apple enforces a strict supplier responsibility program to maintain high ethical and environmental standards, protecting its brand and ensuring a resilient supply chain. These companies treat suppliers not as vendors, but as extensions of their own operations.
How to Implement Supplier Relationship Management
Building a robust SRM program is a strategic investment in your supply chain’s stability and performance. The goal is to create a framework for collaboration and shared success.
Segment and Strategize: Not all suppliers are equal. Segment them based on their strategic importance, spend, and risk. High-risk, high-spend suppliers require deep, collaborative partnerships, while low-spend, low-risk suppliers can be managed with more automated, transactional processes.
Establish Clear Performance Metrics: You cannot manage what you do not measure. Develop a supplier scorecard with key performance indicators (KPIs) like on-time delivery, quality acceptance rates, and cost competitiveness. Conduct regular business reviews to discuss performance and identify joint improvement opportunities.
Foster a Win-Win Mentality: The most successful partnerships are mutually beneficial. Look for opportunities to create value for your suppliers, such as offering longer-term contracts for better pricing or investing in joint innovation initiatives. This turns a simple buyer-seller dynamic into a powerful strategic alliance.
Key Insight: Effective SRM is not about squeezing every last cent from your suppliers. It’s about building a resilient, collaborative ecosystem where shared goals lead to greater innovation, reduced risk, and a more competitive advantage for all parties involved.
For businesses looking to deepen their understanding and application of these principles, exploring vendor relationship management best practices can provide a more detailed roadmap. By focusing on collaboration and strategic alignment, you transform your supply base from a potential liability into a significant strategic asset.
3. Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization is a critical best practice in supply chain management that moves beyond simple tracking. It involves strategically maintaining just the right amount of inventory to meet demand without incurring unnecessary costs from overstocking or losing sales due to stockouts. This is achieved by balancing carrying costs, ordering costs, and the risk of shortages using data analysis and sophisticated inventory models.

This practice is famously demonstrated by Dell's build-to-order model, which minimizes finished goods inventory by assembling products only after a customer places an order. Similarly, industrial giant Caterpillar leverages a global optimization system to manage its vast parts inventory, saving hundreds of millions by ensuring the right part is in the right place at the right time. These companies prove that optimized inventory is a powerful competitive advantage.
How to Implement Inventory Optimization
Achieving optimal inventory levels requires a systematic approach that combines strategy with the right tools. To practically implement inventory optimization, leveraging effective tools like these inventory management Excel templates can be highly beneficial for businesses of all sizes.
Implement ABC Analysis: Prioritize your efforts by categorizing inventory items. 'A' items are your high-value products that contribute most to profit, 'B' items are of moderate importance, and 'C' items are high-volume, low-value goods. This allows you to apply stricter controls to the items that matter most.
Set Data-Driven Safety Stock Levels: Instead of guessing, use statistical models that account for demand variability and lead time fluctuations to calculate the ideal safety stock. This ensures you have a buffer against uncertainty without tying up excess capital.
Leverage Technology for Real-Time Visibility: Use inventory management software or systems to gain real-time visibility into stock levels across all locations. This data is the foundation for making smart, timely replenishment decisions. Explore how to boost efficiency with automated inventory management to take this a step further.
Key Insight: True inventory optimization isn't just about reducing stock levels. It's about having the right inventory, in the right quantity, at the right location, at the right time, and for the right cost.
4. Risk Management and Resilience
In today's volatile global landscape, a resilient supply chain is no longer a luxury but a necessity. This is where risk management becomes one of the most critical supply chain management best practices. It involves systematically identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential disruptions, from geopolitical instability and natural disasters to supplier bankruptcies. The goal is to build a supply chain that can absorb shocks and recover quickly, ensuring business continuity.
Companies that excel in this area treat risk management as a continuous, proactive process. For instance, Cisco developed a sophisticated program to score suppliers based on risk factors, enabling it to preemptively address vulnerabilities. Similarly, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies like 3M and Honeywell demonstrated resilience by rapidly reconfiguring production lines and activating alternative sourcing strategies to meet unprecedented demand for personal protective equipment.
How to Implement Risk Management
Building a resilient supply chain requires a structured approach to identifying and neutralizing threats before they escalate into full-blown crises. You can start by integrating these key actions into your operations.
Map Your Vulnerabilities: Conduct a thorough mapping of your entire supply chain, from raw material suppliers to final delivery. This exercise is crucial for identifying single points of failure, such as relying on one supplier for a critical component or a single logistics hub.
Develop Supplier Scorecards: Go beyond cost and quality metrics when evaluating suppliers. Integrate risk indicators into your scorecards, such as financial stability, geographic location, and their own risk mitigation plans. This provides a holistic view of your supplier base.
Plan for Disruptions: Don't wait for a crisis to happen. Use scenario planning to model your response to major potential disruptions like a key port closure, a trade policy shift, or a cyberattack. This helps you create and test contingency plans and establish clear crisis management protocols.
Key Insight: Resilience isn't about avoiding all risks, an impossible task. It’s about building the capacity to withstand disruptions and bounce back stronger, turning potential crises into manageable operational challenges.
To effectively manage supply chain risk, it is vital to have a clear framework for identifying and categorizing potential threats. The following summary outlines the primary types of risks that can impact your operations.
By understanding and actively monitoring these risk categories, you can develop targeted mitigation strategies. This structured approach moves your organization from a reactive stance to a proactive one, safeguarding your operations and protecting your bottom line.
5. Technology Integration and Digitalization
In today's interconnected world, one of the most crucial supply chain management best practices is embracing technology. Technology integration and digitalization involve leveraging digital tools like IoT, AI, blockchain, and cloud computing to automate processes, enhance visibility, and facilitate data-driven decisions. This transforms a traditional, siloed supply chain into a smart, agile, and transparent network that can respond to disruptions in real time.
Industry leaders demonstrate the power of this approach. Walmart uses blockchain to provide unprecedented food traceability, enhancing safety and consumer trust. DHL deploys Internet of Things (IoT) sensors on shipments to offer real-time tracking and condition monitoring, while Maersk's digital platform, TradeLens, connects the entire shipping ecosystem, streamlining communication and documentation for all stakeholders.
How to Implement Technology Integration
Successfully weaving technology into your supply chain requires a strategic, phased approach rather than a complete overhaul. The goal is to build a connected ecosystem that delivers tangible value.
Start with Pilot Projects: Begin with a small-scale pilot project to test a new technology, like AI-powered forecasting or IoT tracking, on a specific product line or region. This allows you to demonstrate value, work out kinks, and build a business case for broader implementation.
Prioritize Integration and Scalability: Choose technology solutions that can integrate seamlessly with your existing systems (like your ERP or WMS) and scale as your business grows. Avoid creating new data silos with standalone, incompatible tools.
Focus on People and Process: Technology is only effective if people use it correctly. Invest in user training and change management to ensure high adoption rates. Clearly define new processes and workflows to support the digital tools. You can create a comprehensive plan by following a digital transformation roadmap on flowgenius.ai.
Key Insight: Digitalization isn't about adopting technology for its own sake. It’s about strategically applying tools to solve specific problems, such as reducing manual errors, improving end-to-end visibility, or increasing operational efficiency.
6. Lean Supply Chain Management
Lean supply chain management is a strategic approach focused on systematically eliminating waste and removing any activity that doesn't add value for the end customer. This methodology, rooted in continuous improvement, aims to create a streamlined, efficient, and responsive flow of goods and information from supplier to consumer, ultimately minimizing inventory, reducing lead times, and boosting overall profitability.
The Toyota Production System (TPS) is the quintessential example, pioneering lean principles to create a manufacturing powerhouse. Similarly, Zara’s fast-fashion model relies on a lean supply chain to move designs from concept to store shelves in weeks, holding minimal inventory. Dell’s original direct-to-customer model also embodied lean thinking by eliminating retail intermediaries and building computers based on actual orders.
How to Implement a Lean Supply Chain
Adopting lean principles requires a deep commitment to process optimization and a culture of continuous improvement. The goal is to build a system that is both efficient and flexible enough to adapt to customer demand.
Map Your Value Stream: The first step is to visualize your entire supply chain process, from raw materials to final delivery. This value stream map helps identify bottlenecks, delays, and non-value-added activities (waste) that can be targeted for elimination.
Implement a Pull System: Instead of producing goods based on forecasts (a "push" system), a lean approach uses a "pull" system. Production and material orders are triggered by actual customer demand, like a JIT (Just-In-Time) inventory strategy. This drastically reduces the risk of overproduction and excess inventory.
Cultivate Strong Supplier Partnerships: A lean supply chain is impossible without reliable, collaborative suppliers. Work closely with partners to improve communication, shorten lead times, and ensure quality. Treat them as extensions of your own operations, sharing data and planning collaboratively to create a seamless flow.
Key Insight: Lean is not about doing more with less; it's about eliminating waste to create more value with the same resources. Every process, delay, and piece of inventory should be questioned: "Does this add value for the customer?" If the answer is no, it's a target for improvement.
To successfully integrate this methodology, it's essential to track progress with clear, relevant metrics. The summary below highlights the key performance indicators for evaluating the effectiveness of your lean initiatives.
Tracking these metrics provides tangible proof of your progress. A decreasing cash-to-cash cycle time, for example, is a strong indicator that you are successfully reducing waste and improving flow, turning lean theory into a measurable competitive advantage in your supply chain management best practices.
7. Sustainability and Green Supply Chain
Modern supply chain management best practices extend beyond mere efficiency and cost savings to include environmental and social responsibility. A sustainable or "green" supply chain integrates these considerations into every decision, from sourcing raw materials to final delivery. The focus is on reducing the carbon footprint, minimizing waste, ensuring ethical labor practices, and creating long-term value that protects the planet and enhances brand reputation.
Leading companies have turned sustainability into a core competitive advantage. Patagonia is renowned for its transparent and ethical sourcing, while Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan has driven growth by embedding eco-friendly practices across its vast operations. Similarly, IKEA’s commitment to a circular business model, using renewable materials and energy, and Walmart’s Project Gigaton, which aims to reduce one billion metric tons of greenhouse gases from its supply chain, demonstrate that profitability and sustainability can go hand in hand.
How to Implement a Green Supply Chain
Adopting a sustainable approach is a strategic journey that builds resilience and appeals to a growing base of eco-conscious consumers. The key is to start with clear, measurable actions.
Set Clear Sustainability Goals: Define specific, measurable targets for your operations, such as reducing emissions by a certain percentage, achieving zero-waste-to-landfill status, or increasing the use of recycled materials. These goals provide a clear roadmap for action and accountability.
Engage and Collaborate with Suppliers: Your supply chain's environmental impact is a shared responsibility. Work closely with your suppliers to encourage and enforce sustainable practices, offering incentives for those who meet or exceed your standards. To explore further on how to implement environmentally responsible logistics, consider adopting sustainable supply chain practices.
Embrace Circular Economy Principles: Move away from the traditional "take-make-dispose" model. Design products for longevity, repairability, and recyclability. Implement reverse logistics programs to reclaim products at the end of their life, turning waste into a valuable resource.
Key Insight: Sustainability in the supply chain is no longer a niche concern but a strategic imperative. It mitigates risk from regulations and resource scarcity, strengthens brand loyalty, and uncovers new opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
8. Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR)
True supply chain excellence extends beyond your own four walls. Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR) is a business practice that breaks down traditional silos by combining the intelligence of multiple trading partners, such as retailers and manufacturers, to fulfill customer demand. It moves beyond isolated forecasting to a shared, synchronized process for planning, forecasting, and restocking inventory across the entire supply chain.
The pioneering CPFR partnership between Walmart and Procter & Gamble set the standard, enabling P&G to directly monitor diaper sales and inventory levels at Walmart stores. This visibility allowed P&G to proactively manage replenishment, drastically reducing stockouts and inventory carrying costs for both parties. Similarly, retailers like Carrefour and West Marine have used CPFR with partners like Nestle and Kimberly-Clark to align on promotions, new product introductions, and demand forecasts, creating a more responsive and efficient supply chain.
How to Implement CPFR
Adopting a collaborative model requires trust, transparency, and a structured approach. It's about creating a partnership where shared data leads to shared success.
Start with Pilot Programs: Don't attempt a full-scale rollout at once. Select a key strategic partner and a specific product category to launch a pilot program. This allows you to test processes, refine workflows, and demonstrate value before expanding.
Establish Clear Governance: Define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority from the outset. Create a joint business plan that outlines shared goals, performance metrics (e.g., in-stock percentage, inventory turns), and a process for resolving exceptions or disagreements.
Invest in a Shared Technology Platform: Effective CPFR relies on seamless and secure data exchange. Invest in technology, such as a shared portal or EDI integration, that gives all partners a single source of truth for sales data, forecasts, and inventory levels.
Focus on Mutual Wins: Structure the collaboration so that all participants benefit. Whether it's through increased sales, lower inventory costs, or improved service levels, the value proposition must be clear and compelling for everyone involved to ensure long-term commitment.
Key Insight: CPFR transforms the supply chain from a series of independent transactions into a unified, strategic collaboration. The focus shifts from negotiating individual orders to jointly managing the flow of goods based on actual end-customer demand.
By aligning planning and execution with your key partners, you can mitigate the bullwhip effect, where small fluctuations in demand at the retail level become amplified as they move up the supply chain. This alignment is a cornerstone of modern supply chain management best practices, enabling greater agility, reduced waste, and improved profitability for all partners.
9. Agile and Responsive Supply chain
In a world of rapidly shifting consumer tastes and unpredictable market disruptions, the ability to adapt is no longer a luxury, it's a necessity. This is where an agile and responsive supply chain excels. This best practice prioritizes flexibility and speed over the traditional focus on lowest-cost production, enabling a company to react swiftly to market signals, customize products, and reconfigure operations on the fly. It is a demand-driven approach designed for high-volatility environments.
Companies like Zara have famously built their empires on this model. Their legendary two-week design-to-shelf cycle allows them to respond almost instantly to emerging fashion trends, minimizing markdowns and maximizing sales. Similarly, Dell’s pioneering build-to-order system allows for mass customization, creating products only after a customer places an order, which dramatically reduces inventory risk and waste.
How to Implement an Agile Supply Chain
Building agility requires a strategic shift in both mindset and infrastructure. The focus moves from static, long-term plans to dynamic, short-cycle execution.
Develop Strong Supplier Networks: Instead of relying on a single, low-cost supplier, cultivate a network of partners. This diversification provides flexibility and reduces risk, allowing you to quickly switch sourcing based on capacity, speed, or capability.
Implement Postponement Strategies: Postponement involves delaying the final customization of a product until the last possible moment. For example, a company might produce generic, un-dyed t-shirts and only apply colors or prints once specific regional demand becomes clear, reducing forecast error and obsolete inventory.
Focus on Information Sharing and Visibility: Agility is impossible without real-time information. Invest in technologies that provide end-to-end visibility into inventory levels, production status, and logistics. This allows all partners in the supply chain to act on the same data, synchronizing their response to changes.
Key Insight: An agile supply chain isn't about being lean for the sake of it. It's about being smart and responsive, using speed and flexibility as competitive weapons to capture market opportunities that slower, more rigid competitors will miss.
To truly build a responsive operation, you must invest in the systems and partnerships that enable quick pivots. This approach is fundamental to modern supply chain management best practices, ensuring resilience against a backdrop of constant change. By prioritizing adaptability, businesses can better serve customer needs and protect themselves from market volatility.
10. Performance Measurement and KPIs
You cannot improve what you do not measure. This principle is the essence of performance measurement, a critical best practice in supply chain management. It involves establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to monitor, evaluate, and continuously enhance every facet of your supply chain operations. This data-driven approach provides clear visibility into performance gaps, empowering you to make strategic decisions that drive efficiency and profitability.
Companies that excel in this area gain a significant competitive edge. UPS, for instance, uses its ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) system not just for routing but for meticulously tracking performance metrics like miles per gallon and delivery times. Similarly, Caterpillar implements a rigorous supplier performance measurement program, using KPIs to ensure its partners meet stringent quality and delivery standards, which is vital for its complex global operations.
How to Implement Performance Measurement
Building an effective measurement system requires a strategic approach that connects operational actions to overarching business goals. The key is to focus on metrics that truly matter and drive actionable insights.
Align Metrics with Strategy: Your KPIs should directly reflect your company's strategic objectives. If your goal is to be a low-cost leader, focus on cost-centric metrics like cost per unit shipped. If customer service is your differentiator, prioritize metrics like on-time delivery and order accuracy.
Take a Balanced Approach: Avoid focusing solely on one area, like cost, at the expense of others. A balanced scorecard should cover cost, quality, service, and increasingly, sustainability. This provides a holistic view of supply chain health. To truly master performance, it's crucial to understand key strategies for building effective performance systems with KPIs and scorecards.
Focus on Actionable Insights: Don't get lost in a sea of data. Concentrate on a manageable number of actionable KPIs that provide leading indicators of future performance, not just lagging indicators of past results. Regularly review these metrics to adjust targets and strategies as needed.
Key Insight: Effective performance measurement isn't about tracking every possible metric. It's about selecting the right KPIs that provide a clear, unambiguous signal of whether your supply chain is performing in line with your strategic business objectives.
Top 10 Supply Chain Best Practices Comparison
Supply Chain Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Demand Forecasting and Planning | High: Statistical models, data integration | High: Data quality, tech, training | Better inventory, cost reduction, improved service | Inventory planning, capacity optimization | Reduces stockouts, supports strategic decisions |
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) | Moderate-High: Governance, partnerships | High: Ongoing relationship management | Improved supplier performance, risk reduction | Strategic supplier management, innovation | Enhanced collaboration and transparency |
Inventory Optimization | Moderate-High: Mathematical modeling | Moderate: Accurate demand and lead time data | Lower carrying costs, fewer stockouts | Inventory cost control, warehouse efficiency | Cash flow improvement, optimized stock levels |
Risk Management and Resilience | Moderate-High: Risk frameworks, monitoring | Moderate-High: Diversification, contingency plans | Reduced disruptions, better recovery | Business continuity, supply disruption avoidance | Enhances resilience, regulatory compliance |
Technology Integration and Digitalization | High: Tech adoption, change management | High: Investment in IoT, AI, blockchain | Real-time visibility, automation, improved decisions | Digital transformation, process automation | Improves transparency, predictive analytics |
Lean Supply Chain Management | Moderate: Process redesign, culture change | Moderate: Supplier reliability, training | Waste reduction, efficiency increase | Efficiency improvement, waste elimination | Continuous improvement culture, reduced costs |
Sustainability and Green Supply Chain | Moderate-High: Measurement, reporting | Moderate-High: Sustainable sourcing investments | Lower environmental impact, brand enhancement | Environmental compliance, ethical sourcing | Reduced footprint, customer loyalty |
Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, Replenishment (CPFR) | High: Trust, governance, collaboration | High: Data sharing platforms, alignment | Improved forecast accuracy, reduced inventory levels | Collaborative supplier-customer partnerships | Stronger relationships, cost reduction |
Agile and Responsive Supply Chain | High: Flexibility, network coordination | High: Flexible manufacturing, info systems | Faster response, customization, reduced waste | Fast-moving markets, customized products | Speed, flexibility, customer satisfaction |
Performance Measurement and KPIs | Moderate: Data systems, metric design | Moderate: Data collection and reporting | Visibility, continuous improvement | Performance tracking, benchmarking | Data-driven decisions, accountability |
From Theory to Action: Building Your Future-Ready Supply Chain
We've explored a comprehensive landscape of modern supply chain management best practices, from the predictive power of demand forecasting to the strategic necessity of performance measurement. Each practice, whether it’s strengthening supplier relationships, optimizing inventory levels, or embedding sustainability into your core operations, represents a critical pillar in constructing a resilient and high-performing supply chain. However, the true power of these concepts is not found in isolation. They are not a checklist to be completed but a dynamic, interconnected system.
The journey from a reactive, siloed operation to a proactive, integrated one is transformative. Implementing Lean principles to eliminate waste directly enhances your agility, while robust risk management protocols fortify your resilience against unforeseen disruptions. Similarly, a commitment to digitalization and technology integration acts as the central nervous system, enabling real-time data flow for collaborative planning and precise performance tracking. The synergy created when these practices are woven together is what separates market leaders from the rest. A strong supplier relationship (SRM) becomes exponentially more valuable when supported by a shared data platform (CPFR), just as inventory optimization becomes more precise with accurate demand forecasting.
Charting Your Course for Continuous Improvement
Embarking on this journey can feel daunting, but it doesn't require a complete overhaul overnight. The most effective approach is a phased, strategic implementation focused on continuous improvement. Begin with a candid assessment of your current supply chain. Where are the most significant bottlenecks? What repetitive, manual tasks consume your team's valuable time? Identifying these pain points will illuminate the path forward.
Consider these actionable next steps to translate theory into tangible results:
Conduct a Gap Analysis: Benchmark your current processes against the ten best practices outlined in this article. Identify the 2-3 areas with the most significant gaps or those that present the biggest operational risks. This will be your starting point.
Prioritize with an Impact/Effort Matrix: For your identified gaps, map each potential initiative based on its expected impact on your business and the effort required to implement it. Focus on high-impact, low-effort "quick wins" first to build momentum and demonstrate value.
Embrace a Pilot Program: Instead of a company-wide rollout, select a single product line, region, or supplier to test a new practice. For example, implement a new inventory optimization model for your top-selling product or launch a CPFR pilot with a key strategic partner. This allows you to learn, adapt, and prove the concept on a smaller scale.
Automate the Foundation: Look for opportunities to automate foundational processes. Manual data entry, generating standard reports, and sending routine supplier communications are prime candidates. Automating these tasks frees up your team to focus on strategic analysis and relationship building, accelerating your ability to adopt more advanced practices.
The True Value of a Modernized Supply Chain
Mastering these supply chain management best practices is more than an operational upgrade; it's a fundamental competitive advantage. A resilient, efficient, and transparent supply chain directly impacts your bottom line by reducing costs, but its value extends far beyond that. It enhances customer satisfaction through reliable delivery, strengthens brand reputation through sustainable and ethical sourcing, and fosters innovation through deeper collaboration with partners.
Ultimately, building a future-ready supply chain is about creating an ecosystem that can not only withstand a volatile global landscape but thrive within it. It’s about replacing guesswork with data-driven decisions, manual labor with intelligent automation, and reactive problem-solving with proactive risk mitigation. By committing to this path of continuous improvement, you are not just optimizing logistics; you are building a more agile, profitable, and enduring business.
Ready to eliminate manual work and accelerate your adoption of these best practices? The team at Flow Genius specializes in conducting in-depth consultations to identify and automate the efficiency gaps in your supply chain workflows. Visit Flow Genius to learn how we can design and deploy custom automation solutions that empower your team to focus on strategic growth.

Comments