Distribution of Workload: Key Strategies for Success
- May 19, 2025
- 12 min read
The Evolution of Workload Distribution in Modern Organizations

Workload distribution has changed significantly. Traditional top-down hierarchical models often created bottlenecks and uneven task allocation. This rigid structure struggled to adapt to the dynamic demands of today's work environment. Organizations clearly needed a more agile approach.
This need for agility has led to the adoption of more flexible models. These new models prioritize collaboration, shared responsibility, and the ability to adapt to evolving project requirements. Some organizations are using skills-based allocation, assigning tasks based on individual expertise. This approach boosts efficiency and encourages employee growth. It reflects a growing understanding of the importance of aligning talent with tasks effectively.
The Growing Workforce and Its Impact on Workload
The changing nature of work is also influenced by a rapidly expanding global workforce. By 2025, an estimated 3.6 billion people will be employed worldwide, a significant increase from 2.23 billion in 1991. Find more detailed statistics here This growth demands sophisticated workload distribution strategies to ensure both efficiency and fairness. The rise of service-oriented jobs and flexible work arrangements further complicates effective workload management.
Addressing the Challenges of Modern Workload Distribution
Despite advancements, challenges remain. Uneven workload distribution can contribute to employee burnout, lower morale, and ultimately, reduced productivity. Organizations need to address the often-hidden costs of workload imbalance proactively.
Strategies for Effective Workload Distribution
One effective strategy is using workload visibility tools. These tools provide a clear picture of task assignments, enabling managers to identify potential overload or underutilization within their teams. This transparency facilitates proactive adjustments and prevents bottlenecks. Open communication is also essential. Regular check-ins and ongoing dialogue between managers and team members help ensure workload distribution stays fair and sustainable.
The Future of Workload Management
Effective workload distribution is no longer solely about productivity; it's about cultivating a thriving workforce. Prioritizing a balanced workload fosters a culture of engagement and well-being, leading to long-term success. For organizations to stay competitive and adaptable, effective workload distribution is essential.
Breaking the Glass Ceiling in Workload Distribution

Workload distribution isn't always equal, often reflecting broader societal biases. One key area where this imbalance shows up is between genders. This unequal distribution isn't just about fairness; it significantly impacts an organization's potential. Companies are losing out on valuable contributions and innovative ideas.
Unseen Burdens: Beyond Explicit Assignments
Gendered work allocation often goes beyond formal job descriptions. While assigned tasks might seem balanced, subtle expectations can create workload disparities. For instance, women are often expected to handle "office housekeeping," like organizing events or managing supplies.
Women also frequently carry a heavier burden of emotional labor, offering support and navigating interpersonal team dynamics. This unseen workload adds up, taking away from time and energy that could be spent on core job responsibilities.
This dynamic is linked to pay discrepancies. As of 2024, the uncontrolled gender pay gap was reported as 0.83, meaning women earned roughly 83 cents for every dollar earned by men. Explore this topic further Sectors like nursing and midwifery, with predominantly female workforces, highlight this issue, often worsening workload and pay gap problems.
Restructuring for Equity: Leading the Change
Progressive organizations are actively challenging this imbalance. They're restructuring workload systems to address pay gaps and responsibility imbalances, critically examining current practices and identifying hidden biases in task allocation.
Some companies are using blind assignment systems for projects, removing identifying information to ensure decisions are based solely on skills and experience.
Practical Strategies for Equitable Distribution
Several strategies are promoting more equitable workload distribution:
Regular Workload Audits: Regularly review task assignments to identify imbalances.
Transparent Task Allocation: Clearly define roles and responsibilities for each project to minimize ambiguity.
Skills-Based Assignments: Focus on aligning tasks with individual skills and strengths.
Rotation of Responsibilities: Distribute less desirable tasks fairly among team members.
Open Communication Channels: Encourage open discussions about workload concerns and solutions.
The Benefits of Balance: Innovation, Retention, and Performance
Organizations using these strategies are seeing positive results. A more balanced workload directly improves employee morale and increases retention. By creating a fair and supportive environment, companies foster greater innovation and better overall performance. This highlights the importance of balance for long-term success.
How Economic Shifts Reshape Distribution of Workload

Economic conditions have a significant impact on how businesses operate, influencing everything from internal processes to, importantly, how they distribute workloads. These influences can be subtle, affecting internal work patterns in ways that may not be immediately apparent to leadership. Understanding this connection is essential for businesses to adapt effectively and maintain a productive and engaged workforce.
Macroeconomic Trends and Their Impact on Work Allocation
Several macroeconomic factors contribute to shifts in workload distribution. These include changes in the labor market, inflationary pressures, and disruptions specific to certain industries. For instance, a tight labor market often leads to heavier workloads for existing employees. This then requires organizations to implement effective strategies for managing capacity and preventing burnout.
Industry disruptions also present unique challenges. These can force companies to reassess their core functions and redistribute work to adapt to new market realities. This necessitates a flexible and agile approach to workload allocation in order to remain competitive. This responsiveness is vital for navigating economic uncertainty and maintaining stability.
The global economic landscape has undergone a period of significant transformation. The World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report 2025 indicates that, despite global economic headwinds, the global unemployment rate has stabilized at 4.9%. This seemingly positive figure, however, masks significant disparities between middle and low-income countries. For a more in-depth analysis, you can Read the full research here. This nuanced understanding of the economic landscape is critical for accurately predicting workload needs and preparing for potential distribution challenges.
Reactive and Proactive Strategies for Workload Distribution
Generally, organizations adopt two primary approaches to workload distribution during periods of economic change: reactive and proactive. Reactive strategies are implemented after an economic shift, often as a necessary response to immediate challenges such as unexpected staffing shortages or a sudden surge in demand.
Proactive strategies, conversely, involve anticipating potential economic changes and adjusting workload distribution systems in advance. This forward-thinking approach allows companies to build greater resilience and minimize potential disruptions.
Building Resilient Allocation Systems
Forward-thinking organizations are leveraging economic indicators to predict future workload needs and establish more robust allocation systems. These systems are designed to withstand market fluctuations while simultaneously prioritizing employee well-being.
One key strategy is the implementation of flexible work arrangements. This provides the adaptability needed to respond to changing demand. Investing in automation tools, such as those offered by Flow Genius, is another crucial aspect. Automation helps streamline processes and improve efficiency, ultimately freeing up employee time for higher-value tasks.
By embracing a proactive approach, organizations can build workload distribution systems that are both effective and adaptable. This adaptability is crucial not just for survival, but for continued growth in a dynamic and ever-changing economic environment.
To better understand the interplay between economic conditions and workload strategies, let's examine the following table:
The table below, "Economic Impact on Workload Distribution Strategies," illustrates how different economic conditions influence approaches to workload distribution across various market segments.
Economic Condition | Typical Workload Impact | Strategic Response | Implementation Challenge | Success Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Recession | Reduced workload, potential layoffs | Consolidation of tasks, focus on core competencies | Maintaining employee morale, managing skill gaps | Improved efficiency, cost reduction |
Economic Growth | Increased workload, potential hiring surge | Expansion of teams, delegation of tasks | Finding and onboarding qualified talent quickly, managing rapid growth | Increased revenue, market share growth |
Inflation | Increased operational costs, potential budget constraints | Prioritization of tasks, automation of processes | Balancing cost-cutting measures with maintaining service quality | Controlled costs, maintained productivity |
Industry Disruption | Shift in demand, potential need for reskilling | Re-evaluation of core functions, reallocation of resources | Adapting to new technologies and processes, managing change resistance | Successful transition to new market demands |
Labor Shortage | Increased workload for existing employees | Flexible work arrangements, outsourcing | Maintaining quality control with external resources, managing potential burnout | Retention of key employees, sustained productivity |
This table highlights the interconnectedness of economic conditions and workload distribution strategies. Reacting strategically to economic shifts is paramount for maintaining productivity and achieving desired business outcomes. By understanding the typical workload impacts and strategic responses outlined above, businesses can proactively prepare for various economic scenarios and build more resilient operations.
Actionable Frameworks for Balanced Workload Distribution
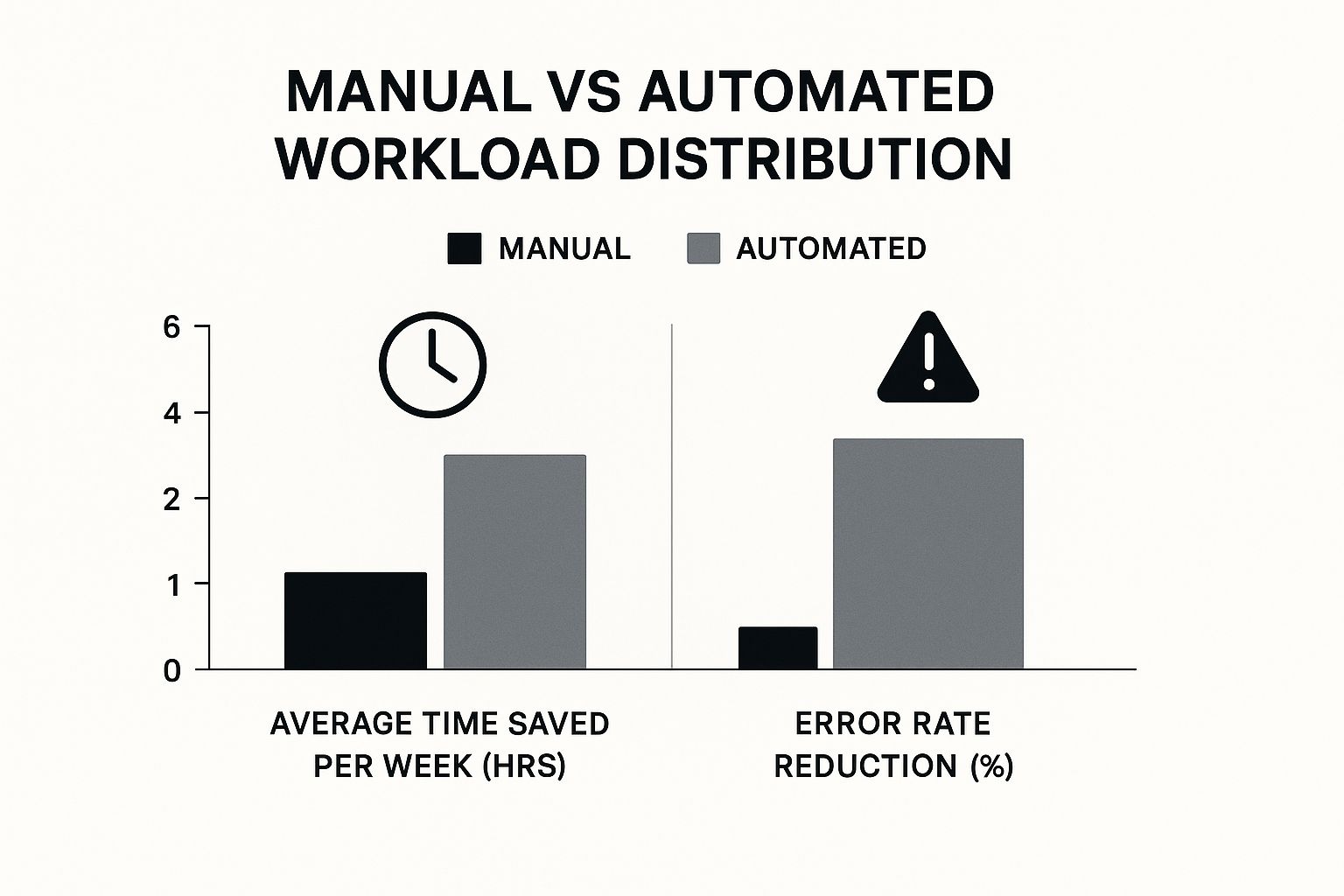
This infographic illustrates the positive impact of automating workload distribution. It compares the average time saved per week and error rate reduction between manual and automated approaches. The data clearly shows automation can save several hours per week and significantly reduce errors, leading to greater accuracy and efficiency. For a deeper dive into optimizing projects with automation, check out our guide on How automation can streamline your project management.
Implementing Skills-Based Allocation
Distributing workloads effectively relies heavily on understanding each team member's strengths. Skills-based allocation goes beyond simple task assignment. It focuses on aligning individuals with projects that best suit their expertise.
This approach ensures projects benefit from specialized knowledge. It also fosters professional growth by allowing team members to utilize and develop their skills.
Capacity Planning: Predicting and Managing Workload
Capacity planning is essential for maintaining a balanced workload. It involves forecasting future project demands and adjusting resource allocation accordingly. By anticipating busy and slow periods, teams can address potential bottlenecks before they impact project timelines.
This proactive approach prevents individuals from becoming overloaded, contributing to a healthier work environment.
Workload Visibility Tools: Transparency and Accountability
Workload visibility tools offer invaluable transparency. They provide a clear overview of current tasks and assignments, allowing managers to easily spot imbalances and potential conflicts.
This transparency enables quick adjustments and proactive problem-solving. It also encourages accountability among team members, promoting efficient task management.
Human-Centered Management Practices: Balancing Technology With Empathy
Technology plays a vital role, but human-centered management remains critical for effective workload distribution. Regular check-ins with team members create opportunities to discuss workload concerns and ensure everyone feels supported.
These conversations also help identify potential burnout risks early on, fostering a healthier and more productive team. Open communication builds trust and strengthens team collaboration.
Practical Strategies for Workload Assessment and Rebalancing
Regularly assessing workload is key to identifying areas that need adjustment. Implementing a system for tracking tasks and time spent provides data-driven insights for rebalancing workloads.
When imbalances arise, focus on immediate solutions and long-term structural adjustments. This may involve re-prioritizing tasks, delegating, or providing additional support to overloaded team members. Effective rebalancing creates a sustainable and equitable workload distribution.
Fostering Transparency and Open Communication
Open communication is essential for successful workload management. Create channels for team members to express workload concerns. This could include regular team meetings, individual check-ins, or anonymous feedback systems.
Addressing these concerns proactively shows a commitment to employee well-being and builds trust. Transparency around workload distribution cultivates a sense of fairness and shared responsibility.
The following table summarizes key differences and similarities between common workload distribution methods:
Workload Distribution Methods Comparison
This comprehensive comparison examines different approaches to distributing work, helping you identify the right model for your organizational context
Distribution Method | Core Benefits | Implementation Challenges | Best Organizational Fit | Technology Requirements | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Skills-Based | Optimized resource utilization, improved project quality, employee development | Identifying and tracking individual skills, potential for skill gaps | Organizations with diverse skill sets and project requirements | Skills management software, project management tools | Project completion rates, employee satisfaction, skill development |
Capacity-Based | Proactive resource allocation, reduced bottlenecks, improved forecasting | Accurate workload prediction, potential for overestimation or underestimation | Organizations with predictable workloads and well-defined project scopes | Capacity planning software, resource management tools | Resource utilization rates, project delivery timelines, budget adherence |
Rotation-Based | Skill diversification, increased flexibility, reduced burnout | Potential for decreased efficiency during initial training, difficulty in maintaining specialized expertise | Organizations with standardized tasks and a focus on cross-training | Project management tools, communication platforms | Employee engagement, task completion rates, skill versatility |
First-Come, First-Served | Simple to implement, transparent process | Potential for uneven workload distribution, may not prioritize urgent tasks | Organizations with relatively stable workloads and clear task prioritization guidelines | Task management software, communication platforms | Task completion rates, response times, employee satisfaction |
This table highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each method, allowing you to choose the best fit for your organization’s specific needs and resources. Consider your team's structure, project types, and available technology when making your decision.
Technology's Transformative Role in Workload Distribution
Technology is changing how we distribute workloads, offering tools to boost efficiency and promote balance. From AI-powered systems to sophisticated capacity planning platforms, technology offers unparalleled insight into workload patterns. This allows organizations to identify and address potential burnout risks before they become serious problems.
AI-Powered Allocation and Capacity Planning
AI-driven systems can analyze large datasets to pinpoint the best workload distribution strategies. These systems account for factors like individual skills, project needs, and team capacity to ensure tasks are assigned effectively. This data-driven method improves efficiency and lowers the chance of individual team members becoming overloaded.
For a more balanced task distribution, consider the Auto Assign Round Robin technique: Auto Assign Round Robin. This helps ensure fairer task distribution and prevents individuals from consistently being overburdened.
Sophisticated capacity planning platforms, such as Jira, forecast future workload demands and proactively adjust resource allocation. By anticipating busy periods and potential bottlenecks, organizations can optimize resource use and maintain steady productivity. This forward-thinking approach is essential for minimizing disruptions and keeping projects on track.
Real-World Implementation and Benefits
Many organizations are already benefiting from technology-driven workload distribution. These technologies let businesses go beyond assigning tasks based on proximity or familiarity and instead focus on skills and capacity. This makes sure projects are staffed with the most suitable people, resulting in higher quality work and better project success rates. Learn more about optimizing workflow with technology in our guide: streamlining operations and boosting efficiency.
These tools also give real-time insights into workload patterns, allowing managers to make informed decisions about task allocation and resource management. This transparency promotes accountability within teams and enables proactive workload adjustments as project needs change.
Addressing Potential Pitfalls
While technology offers many advantages, it’s important to consider possible drawbacks. Concerns about surveillance, algorithmic bias, and digital equity need proactive solutions. Systems should be implemented in a way that improves, not hinders, the employee experience. Transparency in how these systems function and incorporating employee feedback are key to building trust and a positive work environment.
Balancing technological solutions with human oversight is crucial. While AI can automate many parts of workload distribution, human judgment and empathy are still needed to ensure fairness and address individual circumstances. Open communication and regular check-ins with team members are essential for a sustainable and supportive work environment, even with advanced tools. By thoughtfully addressing these factors, organizations can unlock technology's full potential to create a more efficient and equitable way to manage workloads.
Measuring What Matters in Distribution of Workload
Effective workload distribution isn't something you can set up once and then forget about. It requires consistent monitoring and measurement to ensure your systems remain balanced and productive. This means looking beyond basic metrics and delving into data that truly reflects how work is allocated. Building a solid measurement framework is essential for long-term success.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Choosing the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is the first step. While metrics like tasks completed per week might seem informative at first glance, they can hide underlying imbalances. For example, a team might appear highly productive overall, while individual members could be overloaded.
More insightful metrics include:
Time Spent on Tasks: Tracking the actual time spent on tasks offers a more accurate view of individual workload.
Work Distribution Evenness: This metric assesses how balanced the distribution of tasks is across the team.
Employee Feedback: Regular surveys or individual check-ins provide valuable qualitative insights into team members' workload experiences.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Assessment
Both qualitative and quantitative data are necessary for a thorough understanding of workload distribution. While utilization tracking offers concrete data on task allocation, employee feedback adds important context. Feedback highlights potential problems that might not be apparent in quantitative data alone. This combination allows for a comprehensive analysis of workload distribution.
Building a Measurement System That Works
Setting up an effective measurement system doesn’t have to increase administrative overhead. Integrating measurement within existing workflows, such as your project management software, can streamline the process. Technology plays a vital role in modern distribution models, and automation is key. Resources like articles on automating HR processes can help further streamline administrative tasks. You may even find valuable information on improving other processes, such as document management and contract approvals.
Consider these strategies:
Automated Time Tracking: Implement tools that automatically record the time spent on various tasks.
Regular Workload Reviews: Schedule consistent check-ins to discuss workload distribution with the team.
Anonymous Feedback Surveys: Offer a safe space for team members to share their experiences confidentially.
Interpreting Data Patterns and Identifying Early Warning Signs
Understanding how to interpret workload data patterns is essential. Look for trends that could indicate emerging imbalances. For instance, consistently high time spent on tasks by certain individuals may be a sign of potential burnout.
Other early warning signs to watch for include:
Missed Deadlines: While not always related to workload, frequent missed deadlines can sometimes indicate capacity issues.
Decreased Quality of Work: Team members struggling with excessive workloads may find it difficult to maintain quality.
Increased Stress and Complaints: Pay attention to shifts in team morale and address concerns promptly.
Continuous Improvement Through Targeted Interventions
Measuring workload isn't simply about identifying problems—it’s about driving ongoing improvements. Use the data you collect to implement focused interventions. This could involve re-assigning tasks, offering additional training, or adjusting project deadlines. By addressing these issues proactively, teams can operate at peak performance while maintaining a healthy work environment. Regularly evaluating your measurement system is also important. Ensure your KPIs remain relevant and accurately reflect the current state of workload distribution. As team dynamics and project needs evolve, your approach to measurement should adapt as well. This flexibility is vital for sustained success. Flow Genius offers expert automation consultancy and implementation services to optimize your workflows and resource allocation.