Top Business Process Automation Examples to Boost Efficiency
- Matthew Amann

- May 30, 2025
- 20 min read
Unlocking Efficiency: The Power of Automation
Want to streamline operations and boost productivity? This listicle provides seven practical business process automation examples to inspire your automation journey. Discover how automating tasks like invoice processing, customer onboarding, and email marketing can free up your team and unlock new levels of efficiency. From HR and finance to marketing and customer service, explore how these business process automation examples can transform your organization.
1. Invoice Processing Automation
Invoice processing automation stands as a prime example of business process automation, transforming the often tedious and error-prone accounts payable workflow into a streamlined, efficient operation. This automation eliminates manual data entry and leverages technology to accelerate the entire invoice lifecycle, from receipt to payment. It's a crucial automation strategy for any business looking to optimize financial operations, improve accuracy, and free up valuable employee time for more strategic tasks. This approach is particularly relevant to infrastructure project managers, technology companies, logistics directors, and any organization dealing with a high volume of invoices. For those using workflow automation platforms like Zapier, Make.com, or N8n, integrating invoice processing automation can significantly enhance their existing automated ecosystems.
Invoice processing automation works by employing several key technologies. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) extracts invoice data like vendor information, invoice number, date, and line items, eliminating manual keying. This extracted data is then validated against corresponding purchase orders and receipts using three-way matching, ensuring accuracy and preventing discrepancies. Automated approval workflows route invoices to the appropriate individuals based on predefined rules, minimizing delays and bottlenecks. The system also handles exceptions, flagging discrepancies for manual review and resolution. Finally, integration with existing ERP systems allows for seamless data transfer and automated payment processing.
Features of a robust invoice processing automation system include:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Extracts data from invoices.
Three-way matching: Validates invoice data against purchase orders and receipts.
Automated approval workflows: Routes invoices for approval based on predefined rules.
Exception handling: Flags discrepancies for review and resolution.
Integration with ERP systems: Enables seamless data transfer and automated payment processing.
Digital audit trails: Provides a complete record of all transactions for compliance and audit purposes.
The benefits of implementing this form of business process automation are numerous:
Reduces processing time: Studies show a potential reduction of 70-80% in invoice processing time.
Eliminates manual errors: Automating data entry drastically reduces the risk of human error.
Improves vendor relationships: Faster payments lead to stronger vendor relationships.
Provides real-time visibility into cash flow: Offers a clear overview of outstanding and processed invoices.
Ensures compliance with tax regulations: Digital audit trails facilitate compliance.
However, like any system, it comes with potential drawbacks:
High initial setup costs: Implementing the software and integrating it with existing systems can be expensive.
Requires quality invoice formats for accurate OCR: The system's effectiveness depends on the quality and consistency of invoice formats.
May struggle with non-standard invoice layouts: OCR may have difficulty processing invoices with unusual layouts.
Needs integration with existing financial systems: Integration can be complex and time-consuming.
Several companies have seen significant success with invoice processing automation. Siemens reduced their invoice processing time from 30 days to a mere 5 days, while Coca-Cola processes over 1 million invoices annually with 99% accuracy. Microsoft also automated 80% of their invoice approvals, freeing up significant resources.
To ensure a successful implementation, consider these tips:
Start with high-volume, standard invoice formats: Begin by automating invoices with consistent layouts to maximize OCR accuracy.
Establish clear approval hierarchies: Define clear approval workflows to minimize delays.
Train OCR systems with historical invoice data: Improve OCR accuracy by training the system on your specific invoice formats.
Implement gradual rollout by department: Start with a pilot program in one department and gradually expand to other areas.
The following infographic illustrates the core workflow of automated invoice processing:
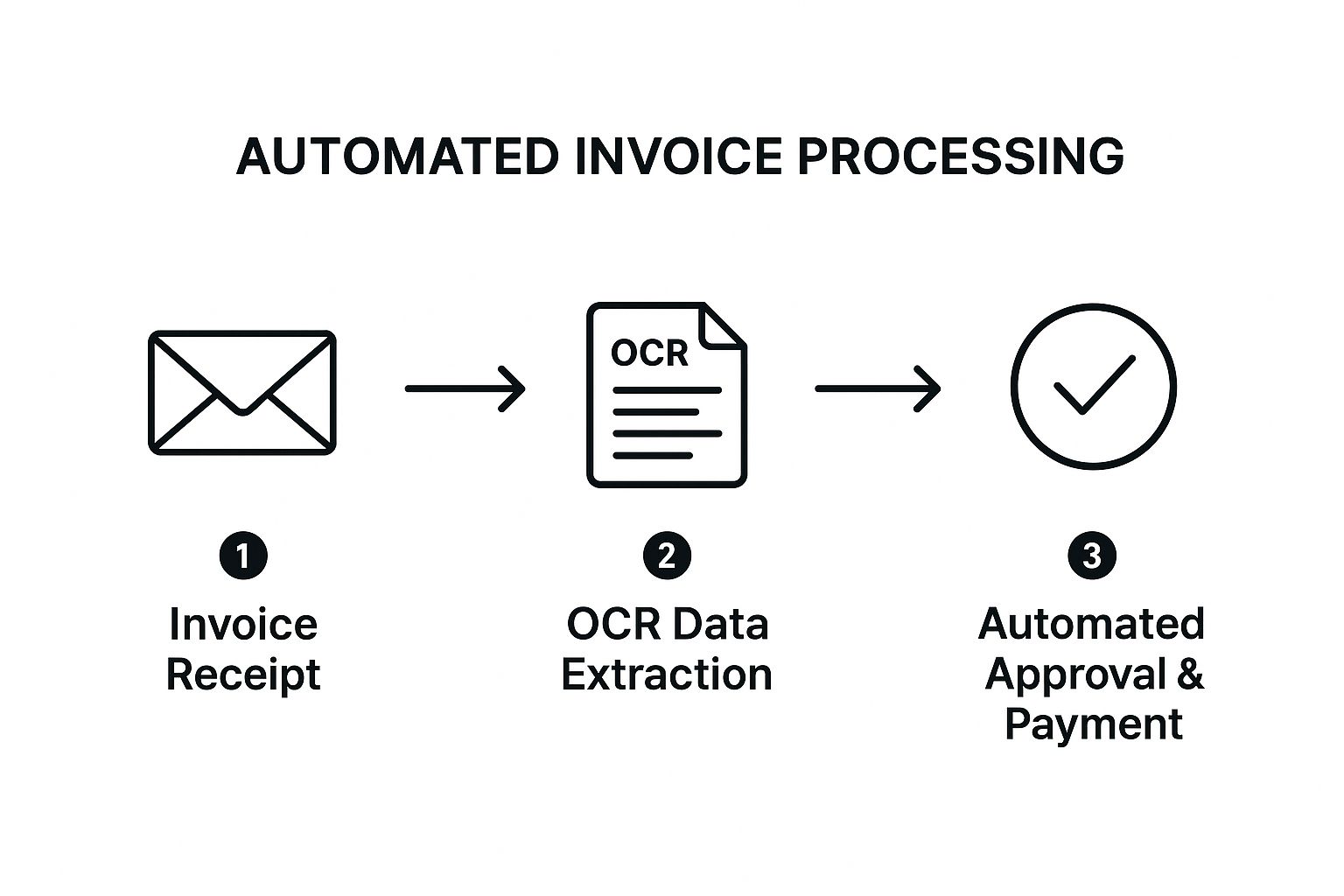
This simplified process flow demonstrates the three key steps: invoice receipt, OCR data extraction, and automated approval and payment. The sequential nature of the process highlights the efficiency gains achieved through automation.
Popularized by platforms like SAP Ariba, Oracle NetSuite, QuickBooks, and Sage Intacct, invoice processing automation is a powerful tool for businesses seeking to optimize their financial operations. Learn more about Invoice Processing Automation and discover how it can benefit your organization. This example deserves its place on the list of business process automation examples due to its widespread applicability, significant ROI, and the tangible improvements it delivers to financial processes.
2. Customer Onboarding Automation
Customer onboarding automation is a prime example of business process automation that streamlines the often tedious and repetitive process of welcoming new customers. It leverages predefined workflows to automate key steps, including account setup, document collection, verification, and initial product or service delivery. This approach ensures a consistent and efficient customer experience while significantly reducing manual administrative work, freeing up valuable employee time for more strategic tasks. This makes it a highly effective method for businesses across various sectors, from technology companies integrating software ecosystems to commercial cleaning businesses automating scheduling.

This automation relies on several key features. Digital document collection and verification simplifies the often cumbersome paperwork involved in onboarding. Automated welcome email sequences ensure consistent communication and provide new customers with essential information. Account provisioning and setup happens automatically in the background, eliminating delays and manual errors. Progress tracking dashboards provide real-time visibility into the onboarding process for both the customer and the business. Integration with CRM systems allows for seamless data flow and personalized communication. Finally, built-in compliance checking and Know Your Customer (KYC) processes help businesses adhere to regulatory requirements.
The benefits of automated customer onboarding are numerous. Studies have shown it can reduce onboarding time by 60-70%, dramatically accelerating the time it takes for customers to realize value. This efficiency also translates to improved customer satisfaction scores as clients appreciate a smooth and streamlined experience. By freeing up staff from repetitive administrative tasks, businesses can redirect resources towards building stronger customer relationships, providing personalized support, and ultimately driving revenue growth. Furthermore, the data collected during the automated onboarding process provides valuable analytics on bottlenecks and areas for improvement, enabling continuous optimization.
However, automated customer onboarding is not without its potential drawbacks. For high-value customers, a fully automated approach may feel impersonal, lacking the human touch they expect. The system requires careful design and testing to handle edge cases and exceptions, ensuring a seamless experience for all customers. The initial setup and configuration can be complex, requiring technical expertise and careful planning. Finally, while automation handles the majority of tasks, human intervention may still be necessary for complex scenarios or specific customer requests.
Numerous companies have demonstrated the power of customer onboarding automation. Stripe, a popular payment processing platform, reduced customer onboarding from days to minutes, significantly improving the user experience and accelerating business growth. Salesforce automated 90% of their trial-to-customer conversion process, showcasing the scalability and efficiency of this approach. Even financial giants like PayPal leverage automation to process millions of new accounts with minimal manual intervention.
For businesses considering implementing customer onboarding automation, several tips are crucial for success. First, map your current onboarding journey to identify pain points and opportunities for automation. Include progress indicators for customers to keep them informed and engaged throughout the process. Build in escalation paths for complex cases that require human intervention. Regularly update workflows based on customer feedback and data analysis to continuously optimize the experience. Platforms like HubSpot, Salesforce, Zendesk, and Intercom are popular choices for building and managing automated onboarding workflows.
Whether you are an infrastructure project manager seeking synchronized logistics, a roofing contractor aiming for streamlined scheduling, or a real estate broker looking to automate client communication, customer onboarding automation offers a powerful solution for improving efficiency and enhancing customer experience. Its place in the list of essential business process automation examples is well-deserved, as it addresses a critical touchpoint in the customer lifecycle and offers significant benefits for businesses of all sizes and industries. This automation is particularly beneficial for users of workflow automation tools like Make.com, Zapier, and n8n, empowering them to create seamless and efficient onboarding experiences.
3. HR Recruitment and Screening
HR recruitment and screening is a prime example of how business process automation (BPA) can revolutionize core business operations. Traditionally, recruitment involved a laborious manual process of sifting through resumes, scheduling interviews, and communicating with candidates. This approach was not only time-consuming and resource-intensive but also prone to human error and bias. Automating these processes allows HR departments to focus on strategic initiatives like employer branding and candidate experience enhancement. This form of BPA dramatically streamlines the entire hiring pipeline, from initial job posting to final offer, making it faster, more efficient, and more data-driven. It achieves this by leveraging technology, particularly AI and machine learning, to automate repetitive tasks and improve decision-making.

Automated recruitment systems handle a wide range of tasks. These include multi-platform job posting distribution, ensuring your open positions reach a wider audience. Resume parsing and keyword matching automatically extract relevant information from resumes and compare it against predefined job requirements. Automated candidate scoring algorithms rank applicants based on their skills, experience, and other criteria, allowing recruiters to quickly identify top contenders. The system also integrates interview scheduling tools, simplifying the logistics of coordinating interviews with multiple candidates. Background check integration automates the verification of candidate credentials. Finally, automated candidate communication workflows ensure consistent and timely communication throughout the hiring process.
This automation provides significant benefits. It reduces time-to-hire, some organizations reporting improvements of 40-50%, saving valuable time and resources. By automating initial screening, it eliminates unconscious bias, promoting a more diverse and inclusive workforce. These systems efficiently handle high volumes of applications, particularly crucial for large organizations or during peak hiring seasons. Automation also provides a more consistent candidate experience, ensuring every applicant receives timely updates and feedback. Finally, these systems generate recruitment analytics, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of hiring strategies.
However, there are potential drawbacks. Automated systems may inadvertently miss qualified candidates with non-traditional backgrounds whose resumes don’t align with predefined keywords or algorithms. This necessitates regular algorithm updates and fine-tuning to ensure the system remains effective and unbiased. Over-reliance on automation can also create an impersonal candidate experience, so it's essential to maintain strategic human touchpoints throughout the process. Finally, the initial setup requires extensive job requirement definition to ensure the system accurately identifies and ranks suitable candidates.
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented automated recruitment systems. Unilever, for instance, screens a staggering 1.8 million job applications annually using AI. Hilton reduced its hiring time from 42 days to a mere 5 days through automation. IBM's Watson Recruitment improved quality of hire by 50%. These examples highlight the transformative potential of BPA in HR.
For organizations considering implementing automated recruitment systems, these tips are crucial. Clearly define job requirements and success criteria for each role. Regularly audit the system for bias in automated decisions. Maintain human touchpoints in the process, such as personalized emails or phone calls, to enhance the candidate experience. Use A/B testing to optimize screening criteria and improve the system's effectiveness.
This approach is particularly relevant for organizations dealing with high-volume recruitment, those seeking to reduce time-to-hire and improve quality of hire, and companies aiming to minimize bias and promote diversity in their workforce. Whether you’re a multinational corporation like Unilever or a growing tech startup, automating HR recruitment and screening can offer significant advantages. Popular platforms like Workday, BambooHR, Greenhouse, and Lever provide comprehensive solutions for automating various aspects of the recruitment process. By leveraging these tools and best practices, businesses can transform their HR departments into efficient, data-driven engines of talent acquisition.
4. Email Marketing Automation
Email marketing remains a cornerstone of successful business strategies, but manual email campaigns are time-consuming and often inefficient. This is where email marketing automation, a prime example of business process automation, comes into play. It transforms the way businesses communicate with their customers, enabling personalized, trigger-based campaigns that respond to individual behaviors, preferences, and lifecycle stages. This approach moves beyond generic email blasts and fosters meaningful customer engagement, leading to increased conversions and stronger brand loyalty. Email marketing automation deserves its place on this list due to its proven ability to significantly enhance marketing ROI and streamline communication processes.
This form of business process automation works by integrating software platforms with customer relationship management (CRM) and e-commerce systems. These platforms allow businesses to segment their audience based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchase history, website activity, and email engagement. Once segmented, automated systems deliver tailored email content triggered by specific actions or pre-defined schedules. For example, a welcome email series can be automatically sent to new subscribers, while an abandoned cart email can be triggered when a customer adds items to their online shopping cart but doesn't complete the purchase. The system automatically personalizes the content, optimizes send times based on individual engagement patterns, and tracks key metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and conversions.
The benefits of email marketing automation are substantial. Studies have shown that automated email campaigns can increase engagement by 50-100% and generate 320% more revenue compared to non-automated emails. This boost stems from the ability to deliver the right message to the right person at the right time, nurturing leads 24/7 and scaling personalization efforts previously unattainable with manual campaigns. Automated systems also improve customer retention by delivering targeted content that keeps customers engaged and informed throughout their lifecycle. For example, Amazon's personalized product recommendations, a form of email marketing automation, are credited with driving 35% of their revenue. Similarly, Netflix leverages behavioral triggers to send personalized recommendations, reducing churn by 25%. Even something as simple as Airbnb's automated booking confirmations contributes significantly to a positive guest experience.
While the advantages are compelling, there are some potential drawbacks to consider. Over-automation can lead to a spammy feel if not carefully managed, requiring constant content creation to keep messages fresh and relevant. Deliverability challenges can also arise if best practices aren't followed, impacting sender reputation and inbox placement. Finally, setting up complex workflows for advanced automation can be initially challenging, requiring technical expertise and careful planning. However, most platforms offer user-friendly interfaces and pre-built templates to simplify the process.
For those managing complex projects or overseeing software ecosystems, streamlining workflows is crucial. Even seemingly unrelated tasks, like managing pull request automation, can free up valuable time and resources that can then be focused on optimizing your email marketing strategies. Tools that automate code review and merge processes, like those offered by Mergify, can significantly enhance team efficiency, allowing for better allocation of resources to other critical areas, such as content creation for email campaigns.
To effectively implement email marketing automation as a business process automation example, start with simple workflows like welcome series and abandoned cart emails. Gradually segment your audience based on behavior and preferences, testing different send times and subject lines to optimize engagement. Regularly monitor deliverability and sender reputation to ensure your messages reach the intended recipients.
Popular platforms like Mailchimp, HubSpot, Marketo, and Constant Contact offer a range of features and pricing plans to suit various business needs. These platforms provide intuitive interfaces for designing email templates, segmenting audiences, setting up automated workflows, and tracking campaign performance. By leveraging these tools and adhering to best practices, businesses can harness the power of email marketing automation to drive significant improvements in customer engagement, revenue generation, and overall marketing ROI. This form of business process automation is particularly relevant to a wide range of industries, from logistics and supply chain management to real estate and software development, offering a scalable and effective way to personalize communication and optimize marketing efforts.
5. Inventory Management and Reordering
Inventory management is a crucial aspect of any business dealing with physical goods. Inefficient inventory management can lead to stockouts, lost sales, increased carrying costs, and ultimately, a hit to the bottom line. This is where automating inventory management and reordering processes becomes a powerful example of business process automation, offering substantial benefits across various industries. This automated approach streamlines the entire inventory lifecycle, from tracking stock levels to generating purchase orders, thus optimizing resource allocation and improving overall operational efficiency. This makes it a highly relevant business process automation example, especially for infrastructure project managers, technology companies, energy sector operations, logistics directors, and even smaller businesses like commercial cleaning services or roofing contractors who need to maintain optimal stock levels of supplies.
Automated inventory management systems leverage technology to monitor stock levels in real-time, predict demand patterns, and automatically generate purchase orders when inventory reaches predetermined thresholds. These systems integrate seamlessly with various parts of the business, including suppliers, warehouses, and sales channels, providing a holistic view of inventory status and facilitating efficient decision-making. This integration is particularly valuable for technology companies aiming to automate their software ecosystems and energy sector operations teams focused on optimizing resource management.
Here's how it works:
Real-time Tracking: The system continuously monitors inventory levels using barcode scanners, RFID tags, or other tracking technologies. This provides an accurate, up-to-the-minute picture of stock on hand across multiple locations, a critical feature for businesses with complex supply chains, like those managed by logistics and supply chain directors. This real-time visibility is also beneficial for infrastructure project managers who need to ensure materials are available on site when needed.
Demand Forecasting: Sophisticated algorithms analyze historical sales data, seasonality, market trends, and other factors to predict future demand. This allows businesses to anticipate inventory needs proactively, minimizing the risk of stockouts and overstocking. This feature is especially relevant for fast-moving industries, like those served by Zara, and helps commercial cleaning businesses or roofing contractors anticipate supply needs based on projected jobs.
Automated Reordering: The system automatically generates purchase orders when inventory levels fall below predefined reorder points. These reorder points are dynamically calculated based on lead times, demand forecasts, and safety stock levels. This automation eliminates manual data entry and reduces the risk of human error, particularly beneficial for real estate or business brokers who may handle a large volume of transactions.
Supplier Integration: Many systems integrate directly with supplier systems via Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) or other methods, facilitating seamless communication and automated order processing. This streamlines the procurement process and ensures timely delivery of goods, a key advantage for businesses using platforms like Make.com, Zapier, or n8n to connect different parts of their operations.
Features of Automated Inventory Management Systems:
Real-time inventory tracking
Demand forecasting algorithms
Automatic reorder point calculations
Supplier integration and EDI
Multi-location inventory sync
Seasonal demand adjustments
Pros:
Reduces stockouts by up to 80%
Decreases carrying costs by 20-30%
Improves cash flow management
Eliminates manual counting errors
Provides valuable demand insights
Cons:
Requires accurate historical data for reliable forecasting
May over-order during unexpected demand fluctuations
High implementation costs for complex systems
Needs regular algorithm calibration
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Walmart's automated replenishment system manages millions of items efficiently.
Zara's fast fashion model relies heavily on automated inventory optimization.
Amazon's anticipatory shipping leverages predictive analytics to reduce delivery times.
Tips for Implementing Automated Inventory Management:
Start with high-velocity, predictable items.
Set safety stock levels based on supplier lead times and demand variability.
Regularly review and adjust reorder parameters.
Integrate with sales forecasting systems for improved accuracy.
Popularized By:
Oracle WMS
SAP Extended Warehouse Management
Manhattan Associates
Blue Yonder
Automating inventory management and reordering offers a compelling business process automation example. By leveraging technology to streamline inventory processes, businesses can significantly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge in today's dynamic market. Whether you're a large enterprise or a small business, the benefits of this type of automation can be substantial, offering a powerful solution for optimizing inventory control and driving growth.
6. Financial Reporting and Analytics
Financial reporting and analytics is a prime example of the transformative power of business process automation. In today's fast-paced business environment, access to accurate and timely financial data is critical for making informed decisions. Manual reporting processes are often slow, prone to errors, and consume valuable time that finance teams could spend on higher-value tasks like analysis and strategic planning. Automating these processes not only streamlines operations but also provides a more comprehensive and reliable view of a company’s financial health, making this a powerful business process automation example.
This automation involves using software solutions to collect financial data from various sources, perform calculations, generate standardized reports, and distribute them to stakeholders on predetermined schedules. Think of it as a sophisticated, automated assembly line for financial data. Instead of manually gathering data, performing calculations on spreadsheets, and creating reports piecemeal, the system handles everything seamlessly. This ensures accuracy, compliance, and the timely delivery of critical financial information, enabling businesses to react quickly to market changes and make data-driven decisions.
How it Works:
Automated financial reporting systems typically integrate with various data sources, including ERP systems, CRM platforms, and accounting software. This multi-source data integration ensures a holistic view of the company’s finances. The system then uses automated calculation engines to perform complex calculations, eliminating the risk of human error that often plagues manual processes. Compliance templates and frameworks are built into the system to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements. Scheduled report generation ensures that reports are delivered automatically to relevant stakeholders at predefined intervals (daily, weekly, monthly, etc.). Many systems also include interactive dashboards that provide real-time insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) and enable users to drill down into specific data points. Furthermore, variance analysis and alert features automatically flag significant deviations from budget or forecast, enabling proactive intervention.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several large organizations have demonstrated the substantial benefits of automating their financial reporting processes. JPMorgan Chase, for instance, automated 90% of its regulatory reporting, significantly reducing compliance risks and freeing up staff for other tasks. General Electric reduced its month-end close process from eight days to two, drastically improving efficiency. Procter & Gamble automated its consolidation processes across 180 countries, streamlining a complex global operation and providing a unified view of its financial performance. These business process automation examples highlight the potential for significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and compliance.
Benefits and Drawbacks:
Pros:
Reduces report preparation time significantly (up to 75%): This frees up valuable time for finance teams to focus on strategic analysis and decision-making.
Eliminates calculation errors: Automating calculations ensures accuracy and improves the reliability of financial reports.
Ensures regulatory compliance: Built-in compliance templates and frameworks help organizations meet regulatory requirements.
Provides real-time financial insights: Interactive dashboards and reporting tools provide up-to-the-minute information on key performance indicators.
Frees finance teams for analysis: Automation eliminates tedious manual tasks, allowing finance professionals to focus on higher-value activities.
Cons:
Requires robust data governance: Accurate and consistent data is crucial for the system to function effectively.
Initial setup can be complex: Integrating various data sources and configuring the system can be a challenging undertaking.
May need customization for unique requirements: Out-of-the-box solutions may not always meet the specific needs of every organization.
Dependent on data quality from source systems: The accuracy of the reports is directly dependent on the quality of the data input into the system.
Tips for Implementation:
Start with standard reports before customization: Begin by automating the generation of standard reports before tackling more complex or customized reports.
Establish data validation checkpoints: Implement data quality checks throughout the process to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Create clear approval workflows: Define clear roles and responsibilities for report generation and distribution.
Regular reconciliation with source systems: Reconcile the data in the automated reporting system with source systems regularly to identify and address any discrepancies.
Popular Platforms:
Several software solutions facilitate automated financial reporting and analytics, including SAP BPC, Oracle Hyperion, IBM Cognos, and Microsoft Power BI. These platforms offer a range of features and capabilities to suit the needs of businesses of all sizes.
When and Why to Use this Approach:
Automating financial reporting and analytics is particularly beneficial for organizations that:
Spend significant time on manual report preparation.
Struggle to meet regulatory reporting requirements.
Require real-time access to financial data for decision-making.
Seek to improve the accuracy and reliability of their financial reporting.
This business process automation example offers a clear path towards more efficient, accurate, and insightful financial reporting. By automating tedious tasks and providing real-time access to critical data, organizations can empower their finance teams to focus on strategic initiatives and drive business growth.
7. Customer Support Ticketing Systems
Customer support ticketing systems represent a powerful example of business process automation, streamlining how companies handle customer inquiries, issues, and requests. This automation significantly enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of customer support operations, making it a crucial tool for businesses of all sizes. For infrastructure project managers juggling complex logistics, technology companies integrating software ecosystems, or even commercial cleaning businesses managing schedules, automated ticketing systems offer a centralized and organized approach to customer service. This approach aligns perfectly with the needs of diverse industries, from energy sector operations optimizing resource management to real estate brokers seeking efficient communication channels.
Essentially, a customer support ticketing system acts as a central hub for all incoming customer communications. Whether a customer reaches out via email, phone, live chat, or social media, their interaction is automatically converted into a "ticket." This ticket contains all relevant information about the customer's issue, including contact details, a description of the problem, and any supporting documentation. From there, predefined workflows take over, routing the ticket to the appropriate agent or department based on factors like issue type, product line, or customer priority.
This automation eliminates manual sorting and distribution of inquiries, drastically reducing response times and ensuring that no customer request falls through the cracks. Priority scoring algorithms further optimize this process by automatically assigning a priority level to each ticket based on pre-defined criteria like severity, customer value, or impact on business operations. This allows support teams to address the most urgent issues first, maximizing customer satisfaction and minimizing potential damage. SLA (Service Level Agreement) monitoring and escalation features ensure that tickets are resolved within agreed-upon timeframes, automatically escalating unresolved issues to higher-level support staff if necessary.
The benefits of automated ticketing systems are substantial. Companies like Spotify, which handles over 100,000 support tickets daily with 90% automation, demonstrate the scalability and efficiency of these systems. Shopify, another successful example, reduced its average response time from 24 hours to a mere 2 hours after implementing an automated ticketing system. Overall, businesses using such systems often see a 60% reduction in response time and a significant improvement in first-call resolution rates. These efficiencies free up valuable agent time, allowing them to focus on more complex issues and provide higher-quality customer service. Furthermore, the comprehensive case histories maintained by these systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior and common issues, enabling businesses to proactively address recurring problems and improve their products or services. Learn more about Customer Support Ticketing Systems
However, implementing a customer support ticketing system does come with certain challenges. Complex or unique issues might be misrouted by automated rules, requiring manual intervention. The initial setup of categorization and routing rules can be time-consuming, and these rules need ongoing maintenance to ensure accuracy. Furthermore, some customers may perceive automated responses as impersonal, necessitating careful consideration of the customer experience.
To maximize the effectiveness of your customer support ticketing system, consider these tips:
Define clear escalation criteria and timelines: This ensures that urgent issues are addressed promptly and prevents customer frustration.
Regularly review routing rules and accuracy: As your business evolves, your routing rules need to adapt to maintain optimal efficiency.
Integrate with a knowledge base for self-service: Empowering customers to find solutions themselves through a readily accessible knowledge base can significantly reduce ticket volume and improve customer satisfaction.
Train agents on when to override automation: While automation is powerful, human intervention is sometimes crucial for handling complex or sensitive issues.
For businesses looking to automate their workflows – whether it's CRM management, outbound communication, or even intricate logistics for infrastructure projects – customer support ticketing systems exemplify the power of business process automation examples. Popular platforms like Zendesk, ServiceNow, Freshdesk, and Jira Service Management offer robust solutions tailored to various business needs. By carefully considering the pros and cons and implementing best practices, businesses can leverage these systems to transform their customer support operations, achieving higher efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and valuable business insights. For users of automation platforms like Zapier, Make.com, or n8n, integrating a customer support ticketing system can further enhance workflow automation across the entire organization, from marketing and sales to operations and customer service.
7 Key Automation Examples Compared
Automation Type | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | 🖥️💡 Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Invoice Processing Automation | High initial setup; integration with ERP needed | OCR tech, AI models, ERP integration | 70-80% processing time reduction; 99% accuracy | High-volume invoicing in manufacturing, retail | Reduces errors, improves cash flow, compliance |
Customer Onboarding Automation | Moderate complexity; workflow design critical | CRM integration, verification tools | 60-70% onboarding time reduction; better satisfaction | New customer acquisition across industries | Consistent experience, frees staff, bottleneck insights |
HR Recruitment and Screening | Complex job setup and algorithm tuning required | AI-driven resume parsing, multi-platform posting | 40-50% time-to-hire reduction; bias reduction | High-volume hiring, unbiased candidate screening | Speeds hiring, reduces bias, analytics insights |
Email Marketing Automation | Moderate to complex for advanced workflows | CRM & e-commerce integration, content creation | 50-100% engagement increase; 4,200% ROI | Customer engagement, lead nurturing, retention | Personalization at scale, revenue boost, 24/7 nurturing |
Inventory Management & Reordering | High for complex predictions & integrations | Demand forecasting, supplier & warehouse integration | 80% fewer stockouts; 25% carrying cost reduction | Retail, manufacturing, multi-location inventory control | Optimizes stock, reduces costs, improves accuracy |
Financial Reporting & Analytics | Complex setup; requires strong data governance | Multi-source data integration and compliance tools | 75% time saved; 5x faster decision-making | Finance departments, regulatory reporting | Ensures compliance, real-time insights, error-free reports |
Customer Support Ticketing | Moderate complexity with ongoing rule maintenance | Multi-channel integration, SLA monitoring | 60% faster response; 25% CSAT improvement | High-volume customer support across industries | Improves resolution rates, avoids lost tickets, analytics |
Embrace the Automation Advantage with Flow Genius
From automating invoice processing and customer onboarding to streamlining HR tasks and optimizing inventory management, the business process automation examples explored in this article highlight the transformative potential of automation across diverse industries. Whether you're an infrastructure project manager seeking synchronized logistics, a tech company integrating software ecosystems, or a logistics director aiming for seamless tracking, mastering these automation concepts empowers you to optimize resources, improve decision-making, and boost overall efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, you free up valuable time and resources to focus on strategic initiatives, innovation, and ultimately, achieving significant business growth. These improvements are not just incremental gains; they represent a fundamental shift towards a more agile, responsive, and successful operational model.
The key takeaway? Embracing automation isn't just about doing things faster; it's about working smarter. From CRM workflows and marketing automation to complex integrations with platforms like Make.com, Zapier, and n8n, the possibilities are vast. By automating strategically, businesses of all sizes – from commercial cleaning companies and roofing contractors to real estate brokers and enterprise-level corporations – can unlock unprecedented levels of productivity and achieve a competitive edge.
Ready to transform your business operations and experience the power of automation firsthand? Flow Genius specializes in creating custom automation solutions tailored to your specific needs, providing expert guidance and implementation for all your business process automation examples. Visit Flow Genius today to schedule a consultation and discover how we can help you streamline your workflows, optimize your resources, and achieve sustainable growth.

Comments