Vendor Relationship Management Best Practices to Optimize Your Supply Chain
- Matthew Amann

- Jun 26, 2025
- 17 min read
In the complex web of modern business operations, vendors are more than just suppliers; they are integral partners in your success. Treating these relationships as purely transactional is a missed opportunity. Effective vendor relationship management transforms a simple supply chain into a strategic asset, driving innovation, mitigating risk, and unlocking significant value that goes far beyond cost savings. It’s the difference between a vendor who simply meets contractual obligations and one who proactively suggests process improvements, offers preferential terms, and collaborates on solutions to your biggest challenges.
This article moves past generic advice to provide a comprehensive guide to actionable vendor relationship management best practices. We will detail specific strategies you can implement immediately to build a more resilient and collaborative vendor ecosystem. You will learn how to segment vendors for focused engagement, create data-driven performance scorecards, and establish a structured communication framework that prevents costly misunderstandings. We'll also explore how to optimize contract lifecycles and leverage technology to automate and streamline your workflows.
From infrastructure project managers synchronizing logistics to technology companies integrating software ecosystems, these principles are universally applicable. Each best practice is designed to be a practical tool, complete with examples of how to use automation platforms like Zapier, Make.com, or custom scripts to embed these strategies directly into your daily operations. By implementing these tactics, you can forge powerful, long-term partnerships that provide a distinct competitive advantage, ensuring your key suppliers are actively contributing to your bottom line and strategic goals.
1. Strategic Vendor Segmentation and Tiering
Not all vendors are created equal, and treating them as such is a common pitfall in vendor relationship management. A far more effective approach is to implement strategic vendor segmentation. This practice involves systematically categorizing your suppliers into tiers based on their strategic importance, spend volume, risk profile, and overall business impact. By doing so, you can allocate your time, resources, and management attention proportionally, focusing your most intensive efforts where they will yield the greatest return.
This tiered system allows you to move beyond a one-size-fits-all strategy. For example, a supplier providing critical, proprietary technology that directly impacts your product innovation is vastly different from a vendor supplying standard office supplies. The former requires a deep, collaborative partnership, while the latter can be managed with a more transactional, efficiency-focused approach.
Implementing a Tiered Framework
Creating a successful segmentation model requires a blend of quantitative data and qualitative assessment.
Quantitative Metrics: Analyze hard data such as annual spend, volume of transactions, and the vendor's direct impact on revenue or cost savings.
Qualitative Factors: Evaluate aspects like the vendor’s innovation capabilities, their alignment with your company's strategic goals, the level of risk associated with their service (e.g., data security, supply chain vulnerability), and the ease of replacing them.
This hierarchy diagram illustrates a common three-level vendor segmentation model, where each tier dictates a different level of engagement and strategic focus.
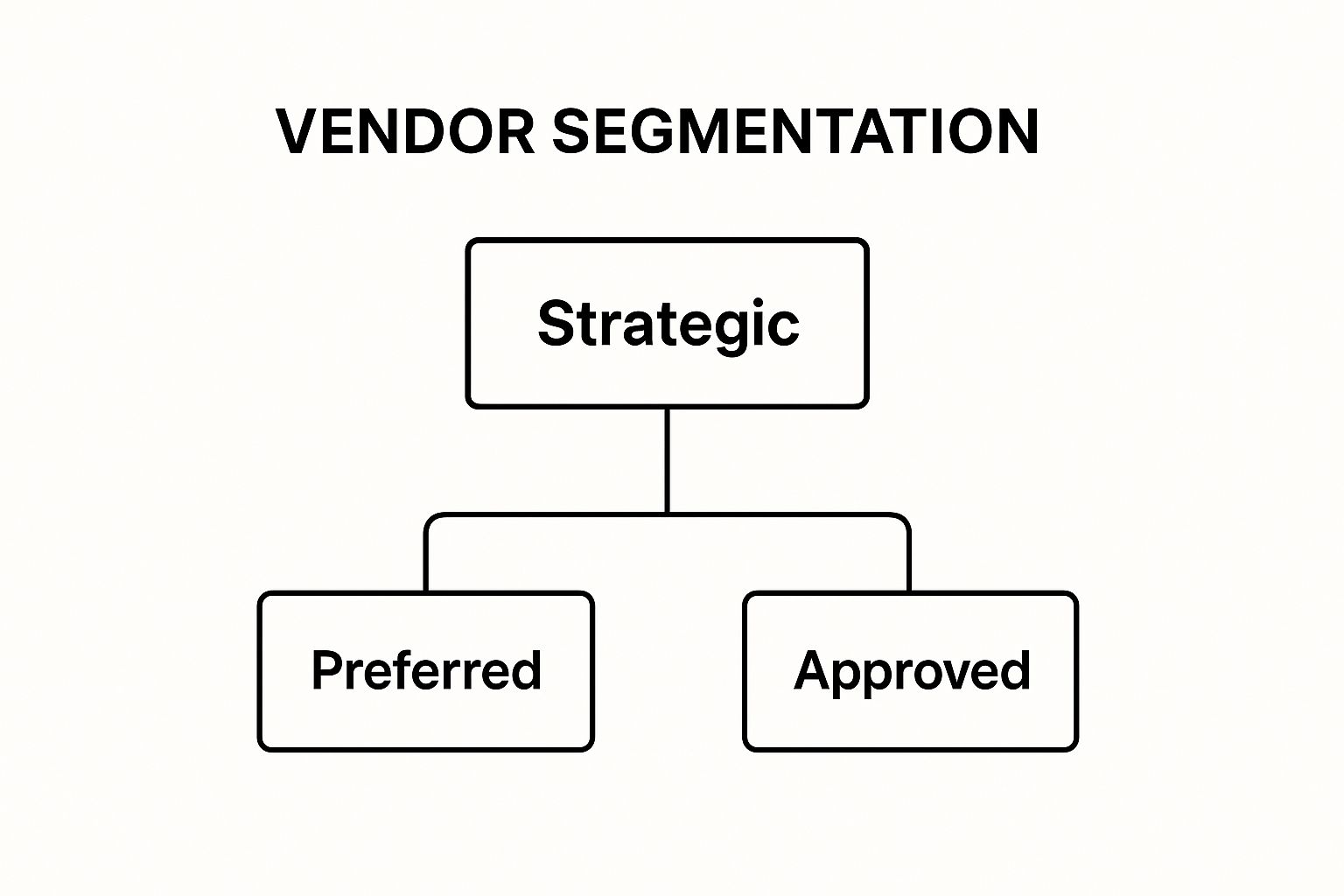
The visualization clearly shows that 'Strategic' partners sit at the pinnacle of the hierarchy, representing the smallest group but receiving the most significant investment in relationship management.
Actionable Tips for Segmentation
To make this one of the most effective vendor relationship management best practices in your playbook, consider these steps:
Establish Clear Criteria: Define and document the specific metrics that determine a vendor's placement in a tier. This ensures consistency and transparency in your evaluation process.
Communicate with Vendors: Inform your vendors of their tier status and what it means. Clearly outline your expectations for performance, collaboration, and communication for each level.
Define Tier Mobility: Create a clear pathway for vendors to move between tiers. A high-performing "Preferred" vendor might graduate to "Strategic" status by demonstrating exceptional innovation and reliability.
Conduct Regular Reviews: Your business needs and the vendor landscape are constantly changing. Review and adjust your vendor segmentation annually or in response to major events like a merger, acquisition, or significant market shift.
2. Comprehensive Vendor Performance Management and Scorecards
Beyond simply segmenting vendors, you must actively manage their performance to ensure they consistently deliver value. This is where a structured vendor performance management system comes into play. It establishes a formal process for continuously monitoring, measuring, and improving vendor performance using standardized metrics, regular reviews, and transparent performance scorecards. This practice moves relationships from subjective assessments to objective, data-driven evaluations, ensuring accountability and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
The core idea, popularized by frameworks like the Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) model, is that you can't improve what you don't measure. By defining what "good" looks like with clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), you create a shared understanding of success. For instance, Walmart's renowned Supplier Scorecard program tracks metrics on sustainability, logistics, and sales, providing suppliers with clear data to improve their performance and strengthen their partnership with the retail giant.
Implementing a Performance Scorecard System
Building an effective scorecard system requires collaboration and a focus on what truly matters to your business. It's not about tracking every possible metric but about identifying the ones that directly correlate with value and strategic goals.
Metric Definition: Work with stakeholders from relevant departments (e.g., finance, operations, IT) and even the vendors themselves to define a balanced set of KPIs. This ensures the metrics are meaningful, achievable, and fair.
Data Collection and Automation: Establish a reliable process for collecting performance data. This can be manual initially but should ideally be automated by integrating your vendor management system with operational platforms (e.g., ERP, accounting software) to pull data on delivery times, invoice accuracy, and service quality.
This structured approach transforms vendor reviews from anecdotal conversations into productive, data-backed strategic discussions, ultimately strengthening the partnership.
Actionable Tips for Performance Management
To ensure this becomes one of your most impactful vendor relationship management best practices, focus on creating a collaborative and forward-looking process:
Balance Leading and Lagging Indicators: Don't just track historical results like on-time delivery (lagging). Also, measure proactive indicators like the vendor's participation in innovation workshops or their process improvement suggestions (leading).
Involve Vendors in Goal Setting: Collaboratively set performance targets with your vendors. This co-ownership fosters buy-in and makes them active partners in achieving shared objectives.
Use Data for Recognition, Not Just Correction: Highlight and reward top-performing vendors. Public recognition or inclusion in strategic projects can be a powerful motivator that goes beyond contractual obligations.
Implement Frequent Reviews: Ditch the annual-only review. Conduct formal performance reviews on a monthly or quarterly basis to address issues quickly and adapt to changing business needs, preventing small problems from escalating.
3. Risk-Based Vendor Assessment and Monitoring
A proactive approach to vendor management extends beyond performance metrics and into the critical domain of risk. Ignoring potential vendor-related risks is a direct path to operational disruption, financial loss, and reputational damage. Risk-based vendor assessment is the practice of systematically identifying, evaluating, and continuously monitoring the spectrum of risks your vendors introduce, including financial, operational, cybersecurity, compliance, and reputational threats.
This methodology, heavily influenced by frameworks like COSO and ISO 31000, ensures that your diligence and monitoring efforts are proportional to the risk a vendor represents. For instance, a cloud hosting provider holding sensitive customer data requires a far more rigorous and frequent assessment than a local catering service. This focus allows you to channel resources effectively, building robust defenses where you are most vulnerable.

The image above highlights the cyclical nature of this process, emphasizing that risk management is not a one-time check but an ongoing commitment to vigilance and adaptation.
Implementing a Risk-Based Framework
A successful risk management program requires a structured, data-driven approach. It starts with comprehensive due diligence during the onboarding process and evolves into continuous monitoring throughout the vendor lifecycle. When conducting thorough assessments of potential vendors, it's crucial to understand how to approach the process effectively. For a deeper dive into assessing potential collaborators, you can explore a guide on evaluating fulfillment partners.
Financial Viability: Assess the vendor's financial health to ensure they won't unexpectedly cease operations. This can involve reviewing financial statements or using third-party financial risk monitoring services.
Cybersecurity Posture: Evaluate their security controls, data protection policies, and incident response plans, especially if they handle your data. This became a critical focus for companies like Target after its infamous 2013 data breach, which originated through a third-party HVAC vendor.
Compliance and Legal: Verify that the vendor adheres to relevant laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards.
Operational Resilience: Analyze their business continuity and disaster recovery plans to understand how they would manage disruptions that could impact your supply chain.
Actionable Tips for Risk Management
To embed this as one of your core vendor relationship management best practices, implement these targeted strategies:
Establish Risk Tiers: Just as you tier vendors for strategic importance, tier them for risk. High-risk vendors should undergo more frequent and in-depth assessments.
Define Risk Tolerance: Clearly document your organization's risk appetite and create thresholds that trigger specific actions or escalation procedures when crossed.
Automate Monitoring: Use tools that automatically monitor vendors for negative news, sanctions list changes, credit score drops, or cybersecurity vulnerabilities. This provides real-time alerts instead of relying on periodic reviews.
Incorporate Right-to-Audit Clauses: Ensure your contracts include clauses that give you the right to audit the vendor's controls and security practices, providing a crucial verification mechanism.
4. Structured Communication and Governance Framework
Even the best-laid plans can falter without clear, consistent communication. Establishing a formal communication and governance framework is the backbone of effective vendor relationship management. This practice moves beyond ad-hoc emails and phone calls, creating a predictable, structured system for interaction, issue resolution, and strategic alignment between your organization and your vendors.
This framework defines who talks to whom, about what, and how often. It includes everything from executive sponsor check-ins to operational business reviews and clear escalation paths for problems. For instance, Amazon's Vendor Central provides a highly structured communication platform, while Toyota's supplier development model relies on deeply embedded, regular communication to drive continuous improvement. A robust framework ensures that small operational issues don’t spiral into major disruptions and that strategic goals remain aligned.
Implementing a Communication Framework
A successful governance structure formalizes the relationship and sets clear expectations for engagement.
Operational Touchpoints: Schedule regular, frequent meetings (daily or weekly) for operational teams to discuss day-to-day performance, order fulfillment, and immediate challenges.
Strategic Reviews: Implement quarterly or bi-annual business reviews (QBRs/SBRs) with senior leadership from both sides. These sessions should focus on long-term goals, innovation opportunities, relationship health, and performance against strategic KPIs.
Executive Sponsorship: Assign executive sponsors on both sides for your most strategic vendors. Their role is to champion the partnership, resolve high-level conflicts, and ensure continued alignment at the highest levels of the organization.
The goal is to create a rhythm of communication that matches the vendor's strategic importance. This structured approach is a cornerstone of the best vendor relationship management best practices, preventing misunderstandings and fostering a proactive, collaborative environment.
Actionable Tips for Governance
To build a framework that enhances rather than hinders your partnerships, follow these steps:
Match Cadence to Tier: High-frequency, detailed communication is vital for strategic partners. For transactional vendors, a less frequent, exception-based approach may be sufficient.
Define Clear Agendas: Ensure every meeting has a purpose. Circulate agendas beforehand that cover both operational performance and strategic topics to keep discussions focused and productive.
Document and Track Actions: Meticulously record meeting minutes, decisions, and action items. Assign owners and deadlines to all action items and review their status at the start of the next meeting. This creates accountability.
Establish Escalation Paths: Create a documented, multi-level escalation procedure. This ensures that problems are addressed by the right people at the right time, preventing delays and frustration. You can learn more about how to structure these types of plans by reviewing this guide to project communication planning.
5. Contract Lifecycle Management and Optimization
A vendor relationship is legally and operationally defined by its contract. Simply signing an agreement and filing it away is a missed opportunity and a potential risk. Effective contract lifecycle management (CLM) is a systematic process for managing contracts from initial creation and negotiation through execution, performance, renewal, and eventual termination. This holistic approach ensures that the terms agreed upon are realized in practice, risks are mitigated, and value is maximized over the duration of the partnership.
Adopting a CLM framework transforms contracts from static legal documents into dynamic management tools. It provides visibility into obligations, deadlines, and performance metrics for both your organization and the vendor. For instance, companies like Siemens have leveraged global contract standardization to streamline operations, reduce negotiation times, and ensure consistent compliance across thousands of supplier agreements, showcasing the power of a centralized approach.
Implementing a CLM Framework
A successful CLM strategy integrates technology, process, and people to oversee every stage of a contract's journey.
Standardization and Creation: Develop standardized templates with pre-approved legal clauses for different vendor tiers and risk levels. This speeds up the creation process and reduces legal review cycles.
Automation and Workflow: Implement automated workflows for internal reviews and approvals. This eliminates manual handoffs and bottlenecks, ensuring contracts move efficiently from draft to signature.
Active Monitoring and Compliance: Use a centralized repository to track key dates, obligations, and performance metrics. This proactive monitoring prevents missed renewals and ensures vendors adhere to agreed-upon service levels. For complex agreements, particularly in the EU, it's crucial to maîtriser la sous-traitance et la conformité RGPD to ensure all partnerships are secure and compliant with data protection regulations.
Automating these stages is key. You can explore how to revolutionize your document management and contract approvals to create a more efficient system.
Actionable Tips for Optimization
To turn CLM into one of your most valuable vendor relationship management best practices, focus on these actionable steps:
Implement Automated Alerts: Use contract management software or simple automation tools to set up alerts for key milestones like expiration dates, renewal windows, and performance review deadlines. This prevents auto-renewals of underperforming contracts.
Use Data Analytics: Analyze data from your contract portfolio to identify trends, pinpoint sources of value leakage, and find opportunities for cost savings or performance improvements during renegotiations.
Standardize with Flexibility: While using standard templates is efficient, allow for flexibility to negotiate bespoke terms with your most strategic partners to foster innovation and collaboration.
Include Performance-Based Clauses: Tie vendor compensation directly to the achievement of specific, measurable key performance indicators (KPIs). This aligns the vendor’s goals with your own and incentivizes top performance.
6. Vendor Development and Capability Building
Moving beyond a purely transactional relationship to one of mutual growth is a hallmark of advanced vendor management. Vendor development and capability building is a proactive strategy focused on collaboratively improving a supplier’s performance, processes, and overall value. Instead of simply penalizing poor performance or switching suppliers, this approach treats key vendors as strategic partners whose success is intertwined with your own. It involves investing in them through training, knowledge sharing, and joint improvement initiatives.
This long-term perspective, famously pioneered within the Toyota Production System, builds a more resilient and innovative supply chain. When you help your vendors improve their efficiency, quality, or technological capabilities, you directly benefit from lower costs, higher-quality inputs, and access to new innovations. It transforms the vendor relationship from a cost center into a value-creation engine.
Implementing a Collaborative Growth Framework
A successful development program is a partnership, not a mandate. It requires a shared commitment to continuous improvement and a clear understanding of mutual benefits.
Quantitative Metrics: Track improvements in key performance indicators like on-time delivery rates, defect reductions, cost savings from process efficiencies, and cycle time reductions.
Qualitative Factors: Assess the vendor’s engagement level, their willingness to adopt new technologies or processes, improvements in communication, and their contribution to joint innovation projects.
This approach is particularly powerful for strategic and high-potential vendors whose capabilities have a direct impact on your product or service quality. For instance, Honda’s supplier development program is renowned for sending its own engineers to help suppliers implement lean manufacturing, resulting in a highly efficient and integrated supply chain.
Actionable Tips for Vendor Development
To make this one of the most impactful vendor relationship management best practices for your organization, consider these strategic steps:
Focus Your Efforts: Concentrate development initiatives on the strategic and high-potential vendors identified in your segmentation process. Your investment will yield the highest return with partners who are critical to your success.
Set Clear Joint Goals: Work with the vendor to establish clear, measurable objectives for the development program. Define what success looks like for both parties, whether it's achieving a specific quality certification or reducing production lead times by a certain percentage.
Foster Two-Way Knowledge Sharing: Create forums for open dialogue, such as joint business reviews or technology showcases. This allows you to share your strategic goals and challenges while learning about your vendor's capabilities and constraints.
Involve Vendors in the Design: Collaborate with your vendors when designing development initiatives. Their firsthand insight into their own operations is invaluable for creating programs that are practical, relevant, and more likely to succeed.
7. Technology-Enabled Vendor Management Platforms
Relying on spreadsheets, disparate email threads, and manual tracking is a significant barrier to effective vendor management in the modern business landscape. The most sophisticated organizations leverage technology-enabled vendor management platforms to centralize, automate, and optimize the entire vendor lifecycle. These integrated systems provide a single source of truth, offering unparalleled visibility and control over everything from onboarding and performance tracking to risk assessment and payment processing.
Adopting such a platform transforms vendor management from a series of disjointed, administrative tasks into a cohesive, strategic function. For instance, platforms like SAP Ariba or Coupa allow businesses to automate routine activities, freeing up procurement and vendor management teams to focus on building strategic relationships, mitigating risks, and driving innovation with key partners. This shift is a cornerstone of advanced vendor relationship management best practices.
Implementing a Centralized Platform
Successfully deploying a vendor management system requires careful planning and a strategic approach, not just a technology purchase.
Process Automation: These platforms excel at automating workflows. Vendor onboarding, for example, can be standardized with digital forms, automated compliance checks, and system-guided approvals, drastically reducing manual effort and ensuring consistency.
Data Centralization: All vendor information, including contracts, performance scorecards, risk profiles, and communication history, is stored in one accessible location. This provides a 360-degree view of each vendor relationship, enabling more informed decision-making.
The goal is to create a unified ecosystem where data flows seamlessly between your internal systems (like ERP and finance) and the vendor platform, creating end-to-end efficiency. Many of these platforms are core to wider digital transformation initiatives, functioning as essential business process automation solutions.
Actionable Tips for Platform Adoption
To ensure your technology investment delivers maximum value, consider these implementation steps:
Start with a Pilot: Begin with a pilot implementation for a specific, critical vendor category. This allows you to refine processes, identify integration challenges, and demonstrate value before a full-scale rollout.
Prioritize Integration: Ensure the chosen platform can integrate smoothly with your existing business systems (e.g., ERP, accounting software). A lack of integration creates data silos, defeating the purpose of a centralized system.
Provide Comprehensive Training: Your internal teams and your vendors must be comfortable using the new platform. Develop robust training programs and support materials to drive adoption and ensure everyone understands the new workflows and expectations.
Leverage Analytics: Use the platform’s built-in analytics and reporting capabilities to monitor key performance indicators, identify trends, and uncover opportunities for continuous improvement in your vendor management strategy.
8. Value-Based Vendor Relationship Strategy
Shifting from a purely cost-centric model to a value-based strategy represents a fundamental evolution in vendor management. This approach reframes the relationship from a transactional negotiation over price to a strategic alliance focused on creating mutual, long-term value. Instead of simply asking "How much does this cost?", leading organizations ask, "How can we work together to achieve shared objectives and drive innovation?"
This strategy recognizes that the true worth of a vendor partnership often extends far beyond the initial price tag. It encompasses innovation, risk mitigation, improved speed-to-market, and enhanced brand reputation. For instance, Boeing’s partnership with key suppliers on the 787 Dreamliner development involved deep collaboration to co-create a groundbreaking aircraft, a feat impossible with a traditional, cost-focused procurement model. Similarly, Starbucks' relationships with coffee growers incorporate sustainability initiatives that create value for the farmers, the environment, and the Starbucks brand.
Building a Value-Driven Framework
Implementing a value-based strategy requires a cultural shift and a new set of engagement rules. It's about aligning vendor success directly with your own organizational objectives to forge a true competitive advantage.
Joint Value Creation: Move beyond negotiating terms to co-developing solutions. This could involve joint research and development, shared process improvements, or collaborative market entry strategies.
Shared Risk and Reward: Structure agreements where both parties have skin in the game. This might include performance-based incentives, gain-sharing models, or joint investments in new technology.
This approach transforms vendors from interchangeable suppliers into indispensable partners who are actively invested in your success. The focus becomes a collaborative effort to grow the entire pie, rather than just fighting over how to slice it.
Actionable Tips for Value-Based Relationships
To make this one of the most impactful vendor relationship management best practices you can adopt, focus on these implementation steps:
Select Partners on Strategic Alignment: During sourcing, evaluate potential vendors not just on price but on their cultural fit, innovation capabilities, and alignment with your long-term strategic vision.
Develop Joint Success Metrics: Work with your strategic partners to define and agree upon a shared set of KPIs that reflect mutual value. These metrics should go beyond cost and delivery times to include innovation contributions, customer satisfaction, or market share growth.
Establish a Governance Structure: Create a formal framework for the partnership, including executive sponsorship, regular strategic review meetings, and clear communication channels to guide collaboration and resolve issues.
Invest in Relationship Building: Foster connections at multiple levels of both organizations, from operational teams to the C-suite. This builds trust and facilitates the open, honest communication necessary for a true partnership.
Best Practices Comparison of 8 Vendor Management Strategies
Approach | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Strategic Vendor Segmentation and Tiering | Medium to High | Moderate | Optimized resource allocation and improved negotiation | Managing diverse vendor portfolios with risk and spend variance | Focused relationship investment, risk prioritization |
Comprehensive Vendor Performance Management and Scorecards | Medium | Moderate to High | Continuous performance improvement and accountability | Vendor performance tracking and benchmarking | Objective evaluation, early issue detection |
Risk-Based Vendor Assessment and Monitoring | High | High | Enhanced risk mitigation and compliance | High-risk vendor environments needing proactive controls | Prevents disruptions, ensures regulatory compliance |
Structured Communication and Governance Framework | Medium | Moderate | Improved transparency, faster issue resolution | Complex, strategic vendor relationships | Builds trust, enables collaboration |
Contract Lifecycle Management and Optimization | Medium to High | High | Reduced legal risks and faster contract cycles | Organizations with extensive contractual dealings | Increased visibility, standardized terms |
Vendor Development and Capability Building | Medium to High | High | Improved vendor capabilities and innovation | Strategic partnerships aiming for mutual growth | Drives innovation, builds strong partnerships |
Technology-Enabled Vendor Management Platforms | High | High | Automated processes, real-time insights | Organizations seeking scalable, tech-driven vendor management | Increased efficiency, centralized control |
Value-Based Vendor Relationship Strategy | High | High | Sustainable competitive advantage and mutual growth | Long-term strategic partnerships focusing on value sharing | Drives innovation, creates resilient supply chains |
From Best Practices to Business as Usual: Automating Your Vendor Ecosystem
Navigating the complex landscape of vendor relationships requires more than just a handshake and a signed contract. As we've explored, transforming your vendor interactions from simple transactions into strategic partnerships is a multifaceted endeavor, grounded in structure, communication, and technology. The journey from good intentions to exceptional outcomes is paved with deliberate, actionable strategies that, when implemented consistently, become the very fabric of your operational excellence.
This article has detailed a comprehensive toolkit of vendor relationship management best practices, moving beyond abstract theories to provide concrete, automatable workflows. We've seen how strategic segmentation allows you to focus your energy where it matters most, and how data-driven performance scorecards turn subjective feelings into objective, actionable insights. The key is to stop viewing these as isolated tasks and instead see them as interconnected components of a single, powerful system: your vendor ecosystem.
Synthesizing the Core Principles
The true power of these best practices is realized when they work in concert. A robust communication framework is essential, but it becomes exponentially more effective when supported by a solid contract lifecycle management process. Similarly, a value-based relationship strategy is only possible when you have a clear, risk-assessed understanding of each vendor’s capabilities and performance.
Let's distill the most critical takeaways:
Structure Precedes Success: A formalized approach is non-negotiable. Whether it's tiering vendors, establishing governance protocols, or creating performance scorecards, structure provides the clarity and consistency needed to manage relationships at scale. Without it, you’re relying on individual effort and institutional memory, which are notoriously unreliable.
Data, Not Drama, Drives Decisions: The shift from anecdotal evidence to empirical data is a cornerstone of modern vendor management. Implementing performance metrics, tracking contract milestones, and conducting risk assessments provide the objective information necessary to have productive, forward-looking conversations with your partners.
Automation is the Ultimate Accelerator: Manually managing dozens or hundreds of vendor touchpoints is a recipe for inefficiency and human error. As demonstrated with examples using Zapier, Make.com, and custom scripts, automation is the key to embedding these best practices into your daily operations. It ensures that scorecards are updated, communications are logged, and risks are flagged without constant manual intervention.
Your Actionable Roadmap to Vendor Excellence
Mastering these concepts is not an academic exercise; it's a direct investment in your company's resilience, efficiency, and competitive advantage. A well-managed vendor ecosystem translates into lower costs, reduced risk, greater innovation, and superior end-product quality for your customers. Your supply chain becomes a source of strength, not a point of vulnerability.
To begin this transformation, here are your immediate next steps:
Conduct a Vendor Audit: Start by applying the principles of Strategic Vendor Segmentation. Categorize your current vendors into tiers (e.g., Strategic, Preferred, Transactional) to understand where your focus should be.
Pick One Process to Digitize: Don't try to boil the ocean. Select a single, high-impact process to improve first. This could be creating a simple automated performance scorecard in a spreadsheet, setting up automated reminders for contract renewals, or establishing a dedicated Slack channel for a strategic partner.
Implement a Pilot Automation: Choose a low-risk, high-reward workflow to automate. A perfect starting point is creating a Zap that logs all email communications with a Tier 1 vendor into a central database or CRM. This small win will demonstrate the value and build momentum for more complex integrations.
Ultimately, the goal is to weave these vendor relationship management best practices so deeply into your company's DNA that they become "business as usual." When your processes are automated and your strategies are clear, you free up your team to focus on what truly matters: fostering genuine, value-driven partnerships that propel your business forward. The future of vendor management is not about more paperwork; it's about smarter, more connected, and highly automated systems that empower human relationships.
Ready to move from manual processes to a fully automated vendor management workflow? The team at Flow Genius specializes in designing and implementing the exact kind of custom automation solutions discussed in this article, using platforms like Zapier, Make, and GoHighLevel to build a seamless operational backbone for your business. Visit Flow Genius to learn how we can help you turn best practices into powerful, automated realities.

Comments