Top Resource Allocation Strategies for 2025 Success
- Matthew Amann
- Jul 11, 2025
- 16 min read
In any business, from technology firms integrating software to roofing contractors managing job sites, the difference between stagnation and growth often comes down to one critical factor: how you manage your resources. Effective resource allocation isn't just about managing budgets; it's the strategic deployment of your most valuable assets, including time, talent, and technology, to achieve maximum impact. Getting this right means projects are completed on time, teams are productive and engaged, and financial investments yield the highest possible returns. Poor resource management, however, leads to burnout, budget overruns, and missed opportunities.
This article cuts through the noise to deliver a comprehensive guide to the top ten resource allocation strategies that modern businesses are using to gain a competitive edge. We will explore a diverse range of models, from the financial discipline of Zero-Based Budgeting to the flexibility of Agile and Dynamic allocation. For industries managing physical assets, like logistics or commercial cleaning, understanding financial impact is key. To truly unlock peak performance and ensure optimal resource utilization, organizations can benefit from understanding and leveraging tools like utilizing a fleet ROI calculator to make data-driven investment decisions.
You will learn not just what these strategies are, but how to implement them with practical steps, automation examples (using tools like Zapier, Make.com, or N8n), and clear benefits for different operational needs. Get ready to transform how you assign, manage, and optimize your resources for peak performance.
1. Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB)
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) is a rigorous resource allocation strategy that requires every expense to be justified from scratch for each new budget period. Unlike traditional budgeting that builds upon the previous period's numbers, ZBB starts from a "zero base," forcing managers to analyze and validate every dollar spent. This approach scrutinizes all functions and activities for their necessity and cost-effectiveness, promoting a culture of accountability and deliberate spending.
How ZBB Drives Efficiency
Pioneered at Texas Instruments and later popularized by firms like 3G Capital, ZBB is highly effective for organizations aiming to eliminate wasteful spending and realign resources with strategic priorities. By resetting budgets annually or periodically, it prevents incremental budget creep and ensures funds are directed only to activities that deliver clear value. Companies like Unilever and Mondelez International have successfully implemented ZBB to achieve significant cost savings and reallocate capital toward growth-oriented initiatives.
Key Insight: ZBB shifts the conversation from "What did we spend last year?" to "What value does this expense create, and is it essential for our goals this year?" This fundamental change in perspective is what makes it one of the most powerful resource allocation strategies available.
The following infographic summarizes the core principles of the ZBB process.
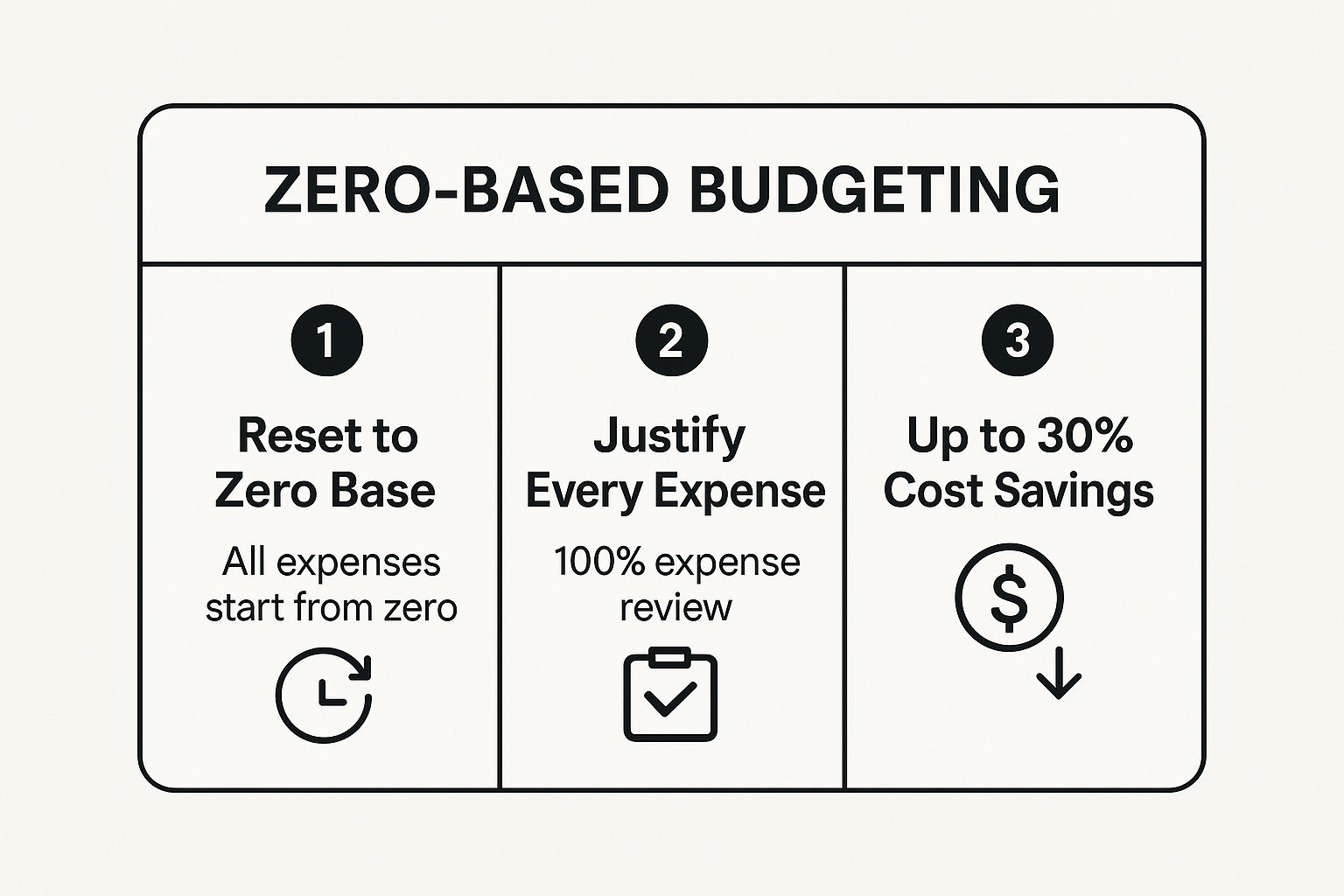
This visual highlights how resetting the budget to zero and requiring justification for every expense can lead to substantial cost reductions, often up to 30%.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Implementing ZBB requires a structured approach and strong organizational commitment.
Start with a Pilot: Begin with a single department or business unit to refine the process before a company-wide rollout.
Leverage Technology: Use financial planning and analysis (FP&A) software to automate data collection and streamline the justification process.
Prioritize High-Impact Areas: Focus initial efforts on departments with the largest or most discretionary budgets to secure early wins.
Balance Cuts with Growth: Ensure the process doesn't just cut costs but also identifies opportunities to re-invest savings into innovation and strategic growth.
2. Portfolio-Based Resource Allocation
Portfolio-Based Resource Allocation is a strategic approach that treats an organization's various business units, projects, and investments as a portfolio of assets. Resources are distributed based on each component's strategic importance, risk-return profile, and contribution to overall organizational goals. This method helps balance investments across different categories, such as sustaining the core business, funding growth initiatives, and placing bets on transformational ventures.
How Portfolio Management Drives Strategic Alignment
Popularized by consulting firms like McKinsey & Company and famously practiced by leaders like Jack Welch at General Electric, this strategy ensures capital flows to the areas with the highest potential for value creation. It forces organizations to think like investors, constantly evaluating which parts of their portfolio are delivering and which are underperforming. For example, Alphabet Inc. manages its diverse ventures, from Google Search to Waymo, as a portfolio, allowing it to allocate resources effectively to both mature profit centers and high-risk, high-reward "other bets."
Key Insight: This strategy shifts the focus from departmental budget battles to a holistic view of value creation. It answers the question, "Where can we best invest our next dollar to maximize our long-term strategic advantage?"
The following diagram illustrates how a portfolio approach can balance different types of investments, from core operations to innovative new ventures.

This visual shows how resources can be balanced across sustaining core business, fueling growth, and exploring transformational opportunities.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Implementing a portfolio-based approach requires clear governance and a data-driven mindset.
Define Strategic Categories: Classify investments into clear buckets like core, growth, and exploratory. Establish distinct criteria and KPIs for each.
Establish a Governance Process: Create a dedicated committee or review board to regularly assess portfolio performance and make reallocation decisions.
Use Data for Performance Tracking: Implement analytics tools to monitor the performance of each portfolio component against its strategic and financial targets.
Maintain Flexibility: The portfolio is not static. Be prepared to shift resources away from underperforming assets and double down on successful ones based on real-world results.
3. Agile Resource Allocation
Agile Resource Allocation is a dynamic, iterative approach that prioritizes flexibility, rapid response to change, and continuous adjustment. Instead of locking in resources for long periods, this strategy allocates them in short cycles, or sprints, with frequent reassessment. This allows organizations to pivot quickly based on real-time feedback, performance data, and evolving market conditions, ensuring capital and talent are always directed toward the most valuable initiatives.

How Agile Allocation Drives Adaptability
Pioneered by tech giants like Spotify with its squad-based model and Amazon with its "two-pizza teams," agile resource allocation strategies are ideal for industries facing high uncertainty and rapid change. By empowering small, autonomous teams with the resources they need to execute specific tasks, companies can foster innovation and accelerate project delivery. For teams new to this concept, understanding the core principles of Agile Methodology for Small Teams is a crucial first step toward successful adoption.
Key Insight: Agile Resource Allocation treats resources like a dynamic portfolio, constantly rebalancing investments to maximize returns rather than sticking to a static, preconceived plan. The focus is on progress over perfection and adaptability over rigid adherence to budgets.
This method excels at breaking down silos and improving workflow efficiency, leading to faster product launches and more responsive customer service. Learn more about boosting productivity with agile workflows.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Adopting agile resource allocation requires a cultural shift towards empowerment and data-driven decision-making.
Establish Clear Frameworks: Create lightweight governance structures for rapid decision-making, such as quarterly business reviews, to reallocate funds between teams.
Invest in Real-Time Data: Use dashboards and analytics tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, providing the data needed for quick adjustments.
Train Teams in Agile Methodologies: Equip your workforce with training in Scrum, Kanban, or other agile frameworks to ensure they can operate effectively within the new structure.
Create Psychological Safety: Foster an environment where teams feel safe to experiment, fail fast, and learn without fear of reprisal.
Balance Agility with Strategy: While being flexible, ensure all short-term resource shifts remain aligned with the organization's long-term strategic goals.
4. Activity-Based Resource Allocation
Activity-Based Resource Allocation is a sophisticated method that links resource allocation directly to the specific activities that drive costs and create value. Instead of allocating funds based on broad departmental categories, this strategy identifies the true cost drivers behind products and services, assigning resources with surgical precision to the activities that deliver the highest return. It moves beyond traditional accounting to provide a granular view of how resources are truly consumed.
How Activity-Based Allocation Drives Efficiency
Popularized by academics like Robert Kaplan and Robin Cooper, Activity-Based Resource Allocation provides deep operational insights. It allows managers to understand the real cost of serving a specific customer or producing a particular product line. Companies like Chrysler and John Deere have used this model to optimize manufacturing costs and streamline operations, while American Express applied it to analyze service costs and enhance profitability by focusing resources on high-value customer interactions.
Key Insight: This strategy reframes the allocation question from "How much does this department need?" to "What activities create value, and what resources do those specific activities require?" This pinpoints inefficiencies and directly links spending to strategic outcomes.
By focusing on the "why" behind costs, organizations can make more informed decisions, eliminate non-value-added activities, and improve overall process efficiency.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Successfully implementing this strategy requires a meticulous, data-driven approach.
Start with High-Impact Activities: Begin your analysis on processes that are either very costly or critical to customer value to demonstrate clear ROI.
Invest in Data Collection: Robust systems are needed to accurately track how time, materials, and overhead are consumed by different activities.
Train Your Team: Ensure staff understand activity-based principles to help identify cost drivers and support the new allocation model.
Prioritize Customer Value: Focus resources on activities that directly enhance the customer experience or product quality, as this is a core component of business process improvement techniques.
5. Strategic Resource Allocation (SRA)
Strategic Resource Allocation (SRA) is a top-down approach where all resource decisions are explicitly tied to an organization's long-term strategic objectives. Instead of focusing solely on departmental budgets or historical spending, SRA prioritizes investments in initiatives that strengthen competitive advantages and drive future growth. This method ensures that capital, talent, and time are channeled toward activities with the highest strategic value.
How SRA Drives Efficiency
Championed by thinkers like Michael Porter and Jim Collins, SRA aligns operational spending with high-level strategy. It forces leadership to define what is truly important for long-term success and allocate resources accordingly. For example, Apple's relentless focus on premium product R&D and Tesla's heavy investment in battery technology are classic examples of SRA in action. By linking every dollar to a strategic goal, companies can avoid spreading resources too thin and instead concentrate their power on areas that create sustainable value.
Key Insight: SRA moves resource management from a tactical, short-term exercise to a strategic, forward-looking discipline. The core question shifts from "How do we fund this department?" to "Which investments will best advance our strategic mission over the next five years?"
This proactive alignment makes SRA one of the most impactful resource allocation strategies for organizations focused on long-term market leadership.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Successfully implementing SRA requires discipline and a clear vision from leadership.
Establish Clear Strategic Priorities: Define and quantify your most critical long-term goals. Use metrics to track progress and guide allocation decisions.
Create Cross-Functional Planning Teams: Involve leaders from different departments to ensure resource plans are integrated and support the entire organization's strategy.
Conduct Regular Strategic Reviews: The market changes, so your strategy must adapt. Schedule quarterly or biannual reviews to reassess priorities and adjust resource allocations as needed.
Balance Strategic Bets with Operational Needs: While funding future growth is crucial, ensure core business operations remain well-supported to maintain stability.
6. Dynamic Resource Allocation
Dynamic Resource Allocation is an agile and data-driven strategy that continuously adjusts resource distribution in response to real-time performance metrics, shifting market conditions, and evolving business priorities. Unlike static annual plans, this approach uses advanced analytics and machine learning to optimize the deployment of capital, talent, and technology on the fly, enabling organizations to pivot swiftly toward opportunities and away from threats. This is one of the most responsive resource allocation strategies available.
How Dynamic Allocation Drives Efficiency
Popularized by tech giants like Amazon and Google, dynamic allocation excels in volatile environments. Amazon's algorithms dynamically adjust inventory and pricing based on demand, while Uber's surge pricing model reallocates drivers to high-demand areas in real time. These systems ensure that resources are always deployed where they can generate the highest impact, maximizing efficiency and profitability. This model is ideal for businesses that operate in fast-paced markets and need to make instant, data-backed decisions.
Key Insight: Dynamic Resource Allocation transforms resource management from a periodic, manual task into a continuous, automated process. The focus shifts from "what should we plan for?" to "how can we react optimally right now?"
The system's ability to learn and adapt makes it a cornerstone of modern operational excellence. You can learn more about resource allocation optimization on flowgenius.ai to see how automation powers these models.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Successfully implementing a dynamic system requires a solid technological and cultural foundation.
Invest in Robust Data Infrastructure: A clean, centralized, and accessible data pipeline is non-negotiable for feeding the algorithms that power dynamic allocation.
Establish Clear Performance Metrics: Define the key performance indicators (KPIs) the system will optimize for, such as customer lifetime value, conversion rates, or operational uptime.
Start with Pilot Programs: Test the model in a controlled environment, like a single product line or marketing campaign, to refine algorithms before a wider rollout.
Maintain Human Oversight: Use the system as a powerful decision-support tool, but retain human oversight to manage exceptions, provide strategic context, and prevent algorithmic bias.
7. Constraint-Based Resource Allocation
Constraint-Based Resource Allocation is a strategic approach derived from the Theory of Constraints (TOC), which posits that every complex system has at least one factor limiting its performance. This method focuses on identifying and managing these bottlenecks, directing resources to alleviate the constraint and thereby elevate the performance of the entire system. Instead of optimizing individual departments, this strategy prioritizes maximizing the throughput of the whole organization.
How Constraint-Based Allocation Drives Efficiency
Popularized by Eliyahu Goldratt, this approach is foundational to highly efficient operations like Toyota's lean manufacturing system and Southwest Airlines' rapid gate turnarounds. The core idea is that strengthening any part of a chain except its weakest link is a waste of resources. By allocating capital, personnel, and attention to fixing the primary bottleneck, companies can achieve disproportionate gains in overall productivity and output. Zara, for example, uses this to optimize its fast-fashion supply chain, ensuring production bottlenecks don't delay getting new styles to stores.
Key Insight: This strategy fundamentally shifts focus from local efficiencies to system-wide throughput. The question becomes not "Is this department efficient?" but "Is this department's activity helping or hindering our primary constraint?" This perspective aligns all resource decisions with what truly drives organizational success.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Implementing constraint-based resource allocation strategies requires a disciplined, system-wide view.
Identify and Validate Constraints: Regularly use data analysis and operational feedback to pinpoint the single most significant bottleneck in your workflow.
Focus on Constraint Utilization: Allocate resources to ensure the constraint is operating at maximum capacity and is never starved for work.
Avoid Over-Optimizing Non-Constraints: Improving non-bottleneck processes beyond the capacity of the main constraint creates excess inventory and waste.
Implement Continuous Improvement: Once a constraint is elevated, another part of the system will become the new bottleneck. Continuously repeat the identification and elevation process.
8. Risk-Adjusted Resource Allocation
Risk-Adjusted Resource Allocation is a sophisticated strategy that integrates risk assessment directly into investment decisions. Instead of focusing solely on potential returns, this approach uses quantitative methods to balance expected gains against potential downsides. Resources are directed toward initiatives based on their risk-adjusted returns, ensuring the portfolio is diversified and that higher-risk projects justify their funding with proportionally higher potential rewards.
How Risk-Adjusted Allocation Drives Efficiency
Popularized by financial theorists like Harry Markowitz and practiced by investment giants like Berkshire Hathaway, this strategy prevents over-investment in high-risk, low-probability ventures. It forces a disciplined evaluation of uncertainty. For instance, pharmaceutical firms use it to manage R&D portfolios, balancing high-risk, high-reward drug development with lower-risk projects. Similarly, oil companies apply it to exploration investments, weighing geological uncertainties against potential yields.
Key Insight: This strategy moves the focus from "How much can we make?" to "Is the potential reward worth the risk we are taking?" This critical shift ensures that capital is not just productive but also protected.
This analytical rigor is a hallmark of the most effective resource allocation strategies, creating a resilient and strategically sound portfolio of initiatives.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Successfully implementing a risk-adjusted framework requires a robust analytical foundation and a culture that respects data-driven decision-making.
Develop Risk Assessment Frameworks: Create clear, standardized models to quantify and score risks like market volatility, operational failures, and competitive threats.
Use Multiple Risk Metrics: Rely on a combination of metrics such as Sharpe ratio, Value at Risk (VaR), and scenario analysis to get a comprehensive view.
Regularly Validate Models: Continuously test and refine your risk models against actual outcomes to ensure they remain accurate and relevant.
Balance Quantitative and Qualitative Factors: While data is crucial, supplement it with expert judgment and qualitative insights to account for risks that are difficult to model.
9. Outcome-Based Resource Allocation
Outcome-Based Resource Allocation is a results-focused strategy where funds and personnel are directed to initiatives that achieve specific, measurable results. Instead of funding activities or inputs, this approach ties resource allocation directly to the successful delivery of predefined outcomes, fostering a culture of performance, accountability, and continuous improvement. It forces organizations to define what success looks like before committing capital.
How Outcome-Based Allocation Drives Efficiency
Popularized by public sector reform movements and the social impact investing community, this method ensures resources flow to programs demonstrating the best results relative to strategic goals. For example, the UK government’s "Payment by Results" programs and Social Impact Bonds only release full funding once specific societal outcomes, like reduced reoffending rates, are met. Similarly, performance-based healthcare models reimburse providers based on patient health outcomes rather than the number of services performed.
Key Insight: This strategy fundamentally shifts the focus from "How much are we doing?" to "What are we achieving?" By linking funding to demonstrated success, it ensures that resources are not just spent but are actively working to deliver tangible value.
This results-driven model incentivizes innovation and efficiency, as teams are motivated to find the most effective ways to achieve their targets.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Successfully implementing outcome-based resource allocation strategies requires a clear framework for measuring success.
Define Clear, Measurable Outcomes: Vague goals are incompatible with this model. Outcomes must be specific, quantifiable, and directly tied to strategic objectives (e.g., "reduce customer churn by 15% in 6 months").
Establish Baseline Measurements: Before launching an initiative, you must know your starting point. Baseline data is crucial for accurately measuring progress and proving impact.
Create Balanced Scorecards: Use scorecards to track performance against a mix of financial and non-financial outcomes, ensuring a holistic view of success.
Align Incentives with Desired Outcomes: Structure team and individual incentives to reward the achievement of the defined outcomes, creating powerful motivation and alignment.
10. Lean Resource Allocation
Lean Resource Allocation is a strategy derived from lean manufacturing principles that prioritizes maximizing value while relentlessly eliminating waste. It extends beyond the factory floor to guide how organizations deploy capital, time, and talent. This approach focuses on optimizing the entire value stream, ensuring that resources are only committed to activities that directly contribute to customer value.
How Lean Resource Allocation Drives Efficiency
Popularized through the Toyota Production System and adapted for various industries by thinkers like Eric Ries in "The Lean Startup," this methodology builds operational excellence. It encourages continuous improvement and just-in-time resource deployment, preventing the over-commitment of funds to unproven projects. Companies like General Electric and Nike use lean principles to streamline supply chains and product development, ensuring resource allocation strategies remain agile and customer-focused.
Key Insight: Lean Resource Allocation redefines waste as anything that doesn't add value for the end customer. This shifts decision-making from departmental budgets to a holistic view of the value creation process, making every resource investment purposeful.
By focusing on small, incremental improvements and empowering teams to identify inefficiencies, organizations can achieve significant long-term gains without disruptive, large-scale overhauls.
Actionable Implementation Tips
Adopting a lean approach requires a cultural shift toward continuous improvement and waste reduction.
Start with Value Stream Mapping: Visually map your current process from start to finish to identify bottlenecks, delays, and non-value-adding activities.
Implement Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Foster a culture where employees are encouraged to make small, ongoing improvements to processes and resource use.
Focus on Customer Value: Before allocating resources, ask: "How does this activity create value for our customer?" If the answer isn't clear, reconsider the investment.
Train Staff in Lean Principles: Equip teams with the knowledge and tools needed to identify and eliminate the eight forms of waste (e.g., defects, overproduction, waiting).
Resource Allocation Strategies Comparison Matrix
Resource Allocation Method | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) | High - Detailed justification needed | High - Intensive time, training & analysis | Cost reduction up to 30%, cost visibility | Organizations aiming to eliminate budget bloat and increase cost discipline | Eliminates unnecessary spending; promotes efficiency |
Portfolio-Based Resource Allocation | High - Requires analytical & governance frameworks | High - Analytical capabilities & oversight | Balanced risk-return, strategic flexibility | Large diversified organizations managing multiple business units or projects | Balances risk & return; supports strategic agility |
Agile Resource Allocation | Medium to High - Cultural change & rapid cycles | Medium - Requires agile teams and data tools | Faster time-to-market, high adaptability | Fast-moving industries needing quick response to changing priorities | Enhances innovation; rapid adjustment to market changes |
Activity-Based Resource Allocation | High - Detailed data collection & analysis | High - Specialized expertise & data systems | Accurate cost info; improved operational efficiency | Organizations focused on cost drivers and process improvements | Provides precise cost information; supports value-based decisions |
Strategic Resource Allocation (SRA) | Medium to High - Requires strategic planning capabilities | Medium - Cross-functional coordination and analysis | Long-term value creation; strategic alignment | Firms prioritizing competitive positioning and sustained growth | Aligns resources with strategy; maximizes long-term value |
Dynamic Resource Allocation | High - Advanced tech and real-time data integration | High - Technology infrastructure and analytics | Optimal resource use; rapid response to changing conditions | Data-driven companies needing real-time optimization | Maximizes efficiency; reduces bias in allocation |
Constraint-Based Resource Allocation | Medium - Requires systems thinking and continuous monitoring | Medium - Focused on bottleneck resources | Maximized system throughput; waste reduction | Operations with clear bottlenecks, e.g., manufacturing or supply chains | Focuses on highest-impact constraints; system-wide optimization |
Risk-Adjusted Resource Allocation | High - Sophisticated quantitative methods | High - Specialized expertise & analytics | Balanced risk-return profiles; reduced unexpected losses | Investment-heavy or risk-sensitive industries | Improved risk management; optimized risk-return balance |
Outcome-Based Resource Allocation | Medium - Needs robust measurement systems | Medium - Measurement and monitoring tools | Results-driven resource optimization; improved accountability | Organizations focused on performance and measurable impact | Encourages accountability; focuses on measurable outcomes |
Lean Resource Allocation | Medium - Cultural shift and continuous improvement | Medium - Training and ongoing management | Waste reduction; improved efficiency and responsiveness | Manufacturing and operations aiming to eliminate waste and optimize flows | Eliminates waste; promotes continuous improvement |
From Strategy to Action: Automating Your Path to Efficiency
Mastering the art of resource allocation is no longer a strategic advantage; it's a fundamental requirement for survival and growth in today's competitive landscape. We've explored ten powerful resource allocation strategies, from the granular justification of Zero-Based Budgeting to the flexible, sprint-based approach of Agile Resource Allocation. Each method offers a unique lens through which to view your most valuable assets: your people, your capital, and your time.
The common thread weaving through these modern strategies is a decisive shift from static, annual planning to dynamic, data-driven decision-making. Whether you're a roofing contractor using Constraint-Based Allocation to manage crew availability and material lead times, or a tech company leveraging Dynamic Allocation to pivot development teams toward emerging market opportunities, the goal is the same: to place the right resources on the right tasks at the right time for maximum impact.
Key Takeaways and Your Next Steps
The theoretical knowledge of these frameworks is only the first step. True transformation happens when these strategies are embedded into your daily operations, and automation is the engine that drives this integration.
Your immediate path forward should focus on these actionable steps:
Audit Your Current Process: Before implementing a new strategy, you must first understand your existing one. Identify current bottlenecks, resource conflicts, and areas where allocation decisions are based on gut feelings rather than data. Is your team consistently over-allocated? Are high-value projects frequently delayed due to a lack of personnel?
Select the Right Strategic Mix: You don’t have to choose just one strategy. A powerful approach often involves blending models. For example, you might use Strategic Resource Allocation (SRA) for high-level yearly planning, complemented by Agile principles for quarterly project execution and Dynamic Allocation for weekly adjustments.
Embrace Automation Tools: The secret to making these complex strategies work without creating an administrative nightmare is automation. Modern workflow automation platforms and resource management software can handle the heavy lifting. A critical component of achieving efficiency and optimizing resource utilization through automation involves learning how to automate repetitive tasks, which frees up project managers to focus on strategic oversight rather than manual data entry and scheduling.
Ultimately, effective resource allocation strategies are about creating a resilient, efficient, and forward-thinking organization. By moving from abstract plans to automated, actionable workflows, you empower your teams to do their best work, ensuring that every dollar spent and every hour worked pushes your business closer to its most important goals.
Ready to turn your resource allocation strategy into a seamless, automated reality? Flow Genius connects all your tools, from CRMs to project management software, creating powerful workflows that execute your allocation decisions automatically. Visit Flow Genius to see how our no-code platform can eliminate manual work and put your resource strategy on autopilot.