- Oct 14, 2025
- 18 min read
Business automation consulting is all about bringing in an expert to analyze, redesign, and set up automated workflows that make a company run better and save money. Think of it as hiring a professional organizer for your company's digital house, swapping out cluttered manual tasks for clean, smart systems that practically run themselves.
What Does Business Automation Consulting Actually Do

Let's cut through the jargon. A business automation consultant is like an architect for your company’s daily grind. While your team is heads-down in their day-to-day work, a consultant steps back to look at the entire operational blueprint. Their main job is to find the hidden traffic jams—those repetitive, manual tasks that secretly bleed time and money from your bottom line.
It’s a bit like a Formula 1 pit crew chief. The driver is focused on the track, but the chief is analyzing every part of the car and the team's process to find ways to shave precious seconds off lap times. A consultant does the same for your business. They don’t just tell your team to work faster; they re-engineer the engine.
The Diagnostic and Design Process
It all starts with a deep dive into how you work right now. A consultant's first task is to play detective, mapping out how tasks flow through different departments. They’re looking for the weak spots by asking tough questions.
Which tasks are eating up the most staff hours?
Where are data entry errors most likely to creep in?
What communication gaps are causing delays between teams?
This detailed analysis becomes the foundation for a strategic automation roadmap. To get a feel for this phase, it’s helpful to start by understanding workflow automation and how it directly affects a business’s performance.
A consultant’s value isn't just in knowing which software to use, but in knowing why and how to use it to solve a specific business problem. Their strategy connects technology directly to your most important growth goals.
From Blueprint to Reality
Once the roadmap is clear, the consultant gets to work building. This means choosing the right tools for the job—whether it’s software like Zapier, Make.com, or even custom scripts—and weaving them into your current systems without causing disruption.
They build, test, and tweak these new automated workflows until they run perfectly. But the job isn't done yet. The final, and maybe most important, step is guiding your team through the change. This involves training and support to make sure everyone is comfortable with the new, simpler way of doing things. The real goal is to leave your organization running with more precision, speed, and a whole lot more room to focus on what really matters: growth.
Why Smart Companies Hire Automation Consultants
Trying to automate your business on your own can feel like navigating a maze without a map. It seems simple enough at first, but a few wrong turns quickly lead to wasted time, mounting frustration, and expensive dead ends. This is exactly why even the most capable companies turn to business automation consulting experts.
The DIY route is tempting, but it’s riddled with hidden traps. You might pour money into powerful software that just doesn't fit your unique workflow, accidentally creating more manual workarounds than you eliminate. Or, you could build a system your team finds so confusing that nobody uses it, leaving you with zero return on your investment.
An automation consultant is your strategic partner. They bring an objective, experienced perspective that immediately de-risks the entire project because they've already navigated this maze hundreds of times.
Sidestepping Costly DIY Pitfalls
One of the biggest hurdles in any automation project is the sheer number of choices. With thousands of software tools all claiming to be the best, it's easy to get stuck in "analysis paralysis" or, worse, commit to a platform that isn't a good long-term fit.
Consultants cut right through that noise. Their job is to be technology-agnostic, focusing only on what your business truly needs to recommend and set up the right tools—not just the trendiest ones. This expertise helps you steer clear of common pitfalls, such as:
Software Mismatch: Buying expensive tools that are either too complex for your team or not powerful enough for your goals.
Siloed Systems: Building automated processes that don't talk to each other, which leads to fragmented data and brand-new inefficiencies.
Scope Creep: Starting with a simple goal but ending up with an over-engineered "science project" that never delivers real value.
This kind of guidance is critical because automation projects are far from a sure thing. In fact, about 70% of digital transformation projects fail to meet their objectives, which really underscores the need for a skilled guide. On the flip side, when it's done right, companies see an average 22% reduction in operating costs and over 90% of employees report a boost in productivity.
Accelerating Your Return on Investment
Beyond just avoiding mistakes, the main reason to hire a consultant is speed. They use proven frameworks to get from analysis to a working solution much faster than an internal team that's learning as they go. This faster timeline means you start seeing the benefits—and the savings—that much sooner.
Smart companies look to automation consulting to achieve clear financial gains. To get a better sense of why, you can explore the ROI of adopting AI-powered analytics tools, which breaks down how these projects drive tangible results.
A consultant’s focus is always on creating value. They’ll prioritize the "quick wins" that deliver an immediate impact while building a solid foundation for bigger, more ambitious projects down the line.
An experienced consultant doesn’t just install software. They install a new, more efficient operating system for your entire business, ensuring it's built to scale and adapt for the future.
Ensuring Team Adoption and Long-Term Success
Getting the technology right is only half the battle. The other, often more challenging, half is getting your people on board. A great automation consultant also acts as a change management expert, making sure your team understands, embraces, and actually uses the new systems effectively. You can learn more in our guide on the 8 key benefits of automation in business for 2025.
They make this happen by:
Inclusive Design: Involving key team members in the process from day one to build buy-in.
Clear Training: Providing hands-on, role-specific training so everyone feels confident with the new tools.
Ongoing Optimization: Watching how the system performs after launch and making tweaks based on real-world feedback to ensure it keeps delivering value.
Ultimately, hiring an automation consultant turns a high-risk, high-effort gamble into a strategic, well-managed initiative. They provide the map, the tools, and the expert guidance to make sure your journey through the automation maze ends in powerful, sustainable growth.
Where Automation Delivers the Biggest Wins
You can’t just wave a magic wand and automate your entire company. The real power of automation comes from applying it strategically, like acupuncture for your business. Instead of guesswork, a business automation consulting expert finds the exact operational pressure points where a small, automated fix can solve a major headache and unlock serious growth.
Some areas are just begging for this kind of treatment. We're talking about the departments buried under mountains of repetitive, rule-based tasks. These are the low-hanging fruit where you'll see an immediate and measurable boost in both efficiency and team morale.
This infographic breaks down how automated workflows in key departments can claw back a surprising amount of time each week.
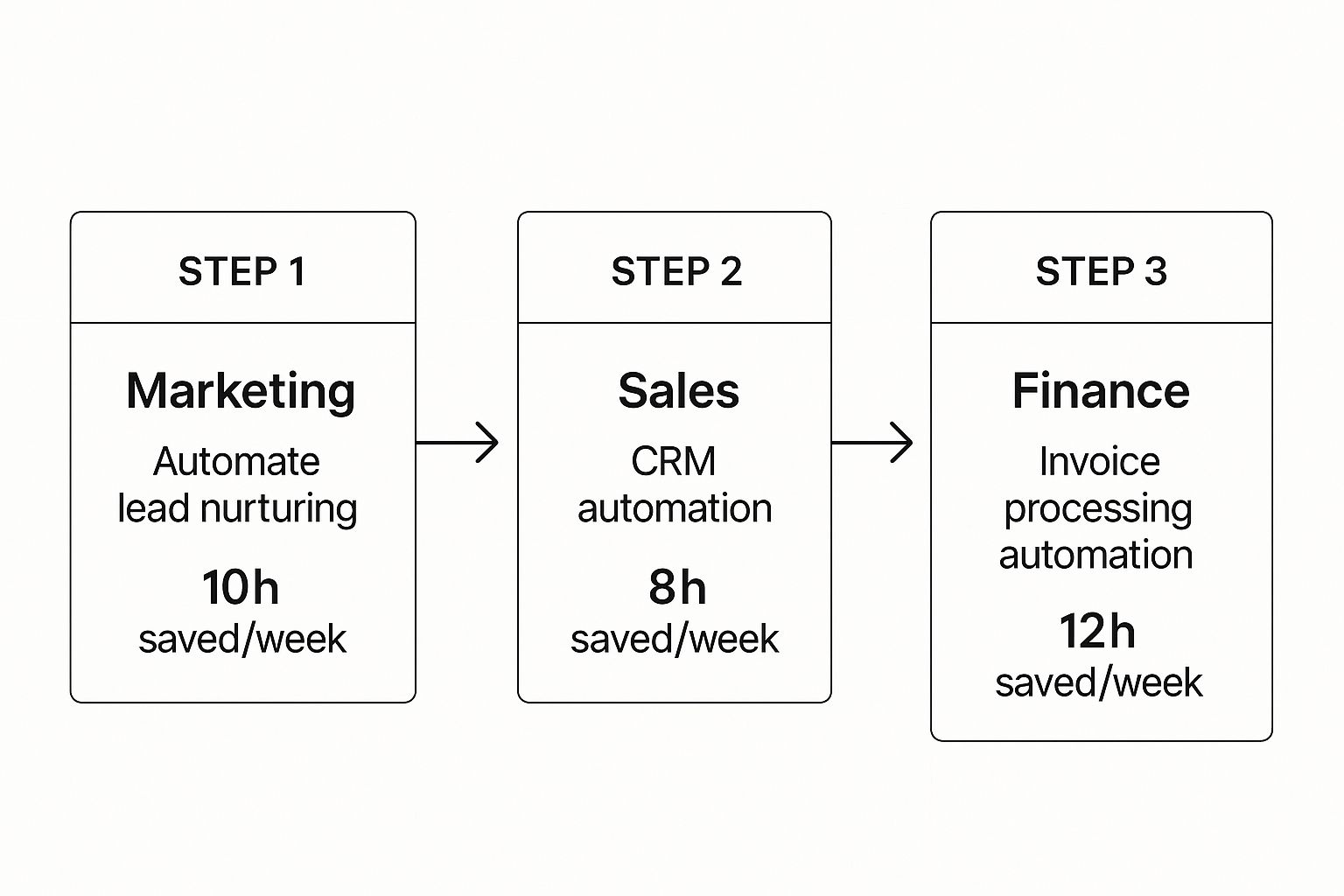
As you can see, tackling processes in marketing, sales, and finance creates a ripple effect. It frees up dozens of hours that can be poured back into the kind of high-value, strategic work that actually moves the needle.
To get a clearer picture, let's look at the primary domains where automation really shines and what makes each one a prime candidate for improvement.
Key Business Automation Areas at a Glance
Automation Area | Primary Goal | Example Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
Marketing | Nurture leads at scale and ensure timely follow-up. | A new subscriber downloads an ebook and is automatically added to a tailored email sequence. | Warmer, more engaged leads are handed off to the sales team. |
Sales | Free up reps from admin work to focus on selling. | Automatically log calls and emails in the CRM and send follow-up reminders. | More time spent building relationships and closing deals. |
Finance | Increase accuracy and speed in financial transactions. | Scan an emailed invoice, extract the data, and route it for approval without manual entry. | Faster payments, fewer errors, and improved compliance. |
Human Resources | Create a smooth and consistent employee experience. | A new hire signs their offer, triggering automatic IT setup and onboarding tasks. | New team members feel welcomed and productive from day one. |
Each of these areas solves a different business problem, but they all share a common thread: they take repetitive, manual work off your team's plate so they can focus on what humans do best.
Marketing and Lead Nurturing
Your marketing team's job is to attract and engage potential customers, not get stuck doing manual data entry or sending the same follow-up emails over and over. This is where automation acts as a perfect sidekick, making sure no lead ever slips through the cracks.
Think about it. A potential customer downloads a whitepaper from your site. An automated workflow can instantly pop their info into your CRM, tag them based on their interest, and kick off a personalized email journey. This keeps the conversation going at the perfect time, with zero manual effort.
Task Eliminated: Manually sending welcome emails and follow-up content.
Time Saved: Your team can focus on creating killer campaigns instead of managing contact lists.
Result: A steady pipeline of warm, engaged leads ready to talk to sales.
Sales and CRM Management
A salesperson's most valuable currency is time. Every minute spent on admin is a minute not spent building relationships and closing deals. The problem is, many reps are drowning in tasks like updating the CRM, logging calls, and pulling reports.
Sales automation gets all that essential-but-draining work done behind the scenes. It can automatically log every email and call to the right contact, set reminders for follow-ups, and even generate sales quotes from a template. This gives your reps the freedom to do what they were hired for: sell.
By automating the administrative backbone of the sales process, you empower your team to operate at peak performance, turning their full attention toward strategy and customer engagement.
Finance and Invoice Processing
The finance department is the operational heart of the company, but it's often slowed down by manual, error-prone tasks like processing invoices and approving expenses. A single typo during data entry can cause payment delays and create a cascade of compliance issues.
Automation brings much-needed precision and speed to finance. Imagine a system where an invoice arrives by email, is automatically scanned, has its data pulled and entered into your accounting software, and is then sent to the right manager for approval—all in a matter of minutes.
This isn't just a nice-to-have; it's becoming the standard. The business process automation (BPA) market is expected to jump from $14.87 billion in 2024 to $16.32 billion in 2025. Why the boom? Because automation can slash process errors by up to 70%, and over 90% of IT pros agree it frees up employees for more meaningful work. You can read the full research about business process automation to dig into the data.
Human Resources and Employee Onboarding
Bringing a new person onto the team should feel exciting and welcoming. Too often, it’s a chaotic scramble of paperwork, IT requests, and manual pings to different departments.
HR automation turns that messy process into a smooth, professional, and structured journey. Once a candidate accepts an offer, a single click can trigger a chain reaction:
IT Department: Instantly gets a ticket to set up the new hire's email, software access, and laptop.
Hiring Manager: Receives a notification with a first-week checklist and goals for their new report.
New Hire: Gets a welcome email with all the necessary forms and info for their first day.
This simple workflow ensures nothing gets missed. More importantly, it makes your new team member feel organized and supported from the very beginning, setting a positive tone for their entire career with your company.
The Automation Consulting Journey From Start To Finish

Bringing in a business automation consulting firm is nothing like buying a piece of software off the shelf. Think of it as a deep, collaborative partnership—a project designed to fundamentally upgrade how your company operates. The process is methodical and structured, with each step building on the last to create a solution that feels like it was born inside your business.
This partnership is all about turning complex technology into tangible results. It typically unfolds across four distinct phases, guiding you from understanding your current headaches to implementing a lasting, efficient system. Let's walk through what that journey actually looks like.
Phase 1: Discovery and Diagnosis
Everything kicks off with a deep dive into your current operations. A consultant's first job is to get an expert-level understanding of your business, but with a critical outsider's perspective. They’re not just looking at what you do, but digging into the nitty-gritty of how you do it.
This phase is hands-on and involves a few key activities:
Stakeholder Interviews: They'll talk directly to the people on the front lines—the ones doing the work day in and day out—to understand their frustrations and uncover those hidden, time-sucking bottlenecks.
Process Mapping: Your workflows get drawn out, step-by-step, creating a visual map that shows exactly where things flow smoothly and, more importantly, where they get stuck.
Technology Audit: They’ll take a hard look at your existing software stack. Are there tools you’re paying for but not using? Or are certain platforms actually part of the problem?
The goal here is pure, unadulterated understanding. It's like a doctor diagnosing an illness before even thinking about a prescription. The consultant is on the hunt for those repetitive, manual, and error-prone tasks that are practically begging to be automated.
Phase 2: Strategy and Roadmap Design
Once the diagnosis is clear, the focus shifts from analysis to action. This is where the consultant translates all those findings into a concrete automation roadmap. And this isn't some vague wish list; it's a detailed blueprint that spells out what will be automated, how it will happen, and what results you can expect.
This roadmap becomes your north star for the entire project. It prioritizes the best opportunities based on a mix of high impact and low difficulty, often starting with a few "quick wins" to build momentum and show immediate value.
A great automation strategy isn't just about the tech. It maps out a clear path from where you are today to where you want to be, making sure every automated process directly serves a bigger business goal, like slashing operational costs or speeding up customer response times.
The final roadmap will have all the essentials: specific technology recommendations, project timelines, clear metrics for success, and a transparent budget. This gets everyone on the same page before a single line of code is written.
Phase 3: Implementation and Integration
Now it’s time to build. In this phase, the strategic plan is brought to life. The consultant typically takes the lead, managing the project and handling all the technical heavy lifting so your team can stay focused on their day jobs.
The real work here involves a few key steps:
Tool Configuration: This means setting up and customizing software—whether it's a platform like Zapier or Make.com, or a more specialized CRM—to run the new workflows.
System Integration: They’ll build bridges between your different apps (like connecting your marketing platform to your sales CRM) so data can finally move between them seamlessly, without anyone having to copy and paste.
Rigorous Testing: Before anything goes live, the new automations are put through their paces. They’re tested against all sorts of scenarios to iron out any bugs and ensure a smooth, hiccup-free rollout.
The name of the game is seamless integration. The new automated systems should feel like a natural extension of your existing operations, enhancing what you already do instead of forcing a massive, disruptive change.
Phase 4: Adoption and Optimization
Here's a truth many people miss: the project isn't over when the tech is launched. The final—and arguably most important—phase is making sure your team actually uses the new tools and processes. A shiny new automation is useless if nobody adopts it.
A good consultant will provide thorough training and crystal-clear documentation to get your staff comfortable and confident. They’ll work alongside your team, showing them how these new systems make their jobs easier, not more complex. This human side of change is critical, and our guide on organizational change management offers a much deeper look into getting it right.
Finally, the journey concludes with ongoing optimization. The consultant will monitor how the automations are performing, gather feedback, and analyze the data to make final tweaks. This ensures the solution doesn't just work on day one, but continues to deliver more and more value long after the initial project is complete.
How to Choose the Right Automation Consulting Partner
Picking a partner for your automation journey is one of the most critical decisions you'll make. This choice directly impacts the project's success, how well your team adapts to new processes, and, ultimately, your return on investment. You're not just looking for a vendor; you need a strategic partner who gets the unique DNA of your business.
This isn't just about finding someone who knows the latest software. It's about finding an expert who can diagnose your real-world challenges, design a practical solution, and guide your team through the change. A great consultant doesn't just install tools—they help install a new, more efficient way of working.
The market for this expertise is growing fast. Workflow automation is projected to explode from over $21.17 billion in 2025 to more than $80.57 billion by 2035. This boom is fueled by companies chasing efficiency and savings, especially as remote work becomes standard. And with 74% of employees reporting they work faster with automation, choosing the right business automation consulting firm is your ticket to getting those benefits. To see more on this trend, you can explore the global workflow automation market report on Research Nester.
Look Beyond the Technical Checklist
It’s easy to get fixated on a consultant's list of technical skills or the fancy logos on their website. While technical ability is a must, it’s just the starting point. The best partners bring a mix of deep industry knowledge, a solid philosophy on technology, and a real understanding of the human side of business change.
Think about it: a consultant who has already automated processes for another logistics company will speak your language from day one. They already know your specific pain points and regulatory headaches, which dramatically shortens the learning curve and leads to a much better solution.
Their approach to technology also matters immensely. Are they locked into a single software platform, or are they technology-agnostic? An agnostic consultant will recommend the absolute best tool for your specific problem, not just the one they happen to sell. This ensures the solution is built around your needs, not their partnerships.
Assess Their Strategic and Cultural Fit
Often, the most crucial factor has nothing to do with technology: it's all about strategic and cultural alignment. An automation project touches multiple parts of your organization, so the right partner must be able to navigate your company culture with skill and empathy. They need to be more than a technician; they need to be a change leader.
This is where you need to ask tough, insightful questions during the vetting process. You have to understand their methodology, how they define success, and what they do when things go sideways. Their answers will tell you far more about their suitability than any case study or client list ever could.
A consultant's true value is revealed when things don't go according to plan. Their ability to communicate clearly, solve problems collaboratively, and keep the project moving forward under pressure is what separates a good partner from a great one.
To help you get started, our guide on how to find a business automation consultant to boost efficiency offers more practical steps and insights.
Critical Questions to Ask Every Potential Partner
Before you sign anything, sit down with potential consultants and treat it like you're hiring for a key leadership role. Their responses will give you a clear sense of their approach and whether they’ll click with your team.
Here are a few essential questions to guide that conversation:
How do you define and measure success for an automation project? Look for answers that go beyond technical metrics. They should be talking about business outcomes like cost savings, time reclaimed, or error reduction.
Can you walk me through your process for understanding our current workflows and pain points? A good answer will detail a discovery phase that includes interviewing your team and mapping out processes, not just sending over a quick questionnaire.
Tell me about a time a project didn't go as planned. What happened, and how did you handle it? This question tests their honesty, problem-solving skills, and commitment to their clients.
What’s your approach to training our team and making sure people actually use the new system? The best consultants have a clear change management plan to make sure the new systems are embraced, not ignored.
This checklist can help you systematically evaluate your options as you interview different firms. It provides a structured way to compare partners and spot potential issues before they become real problems.
Consultant Evaluation Checklist
Evaluation Criterion | What to Look For | Red Flags to Avoid |
|---|---|---|
Industry Experience | Demonstrable success with businesses like yours. They can provide specific, relevant examples. | Generic case studies that lack detail or feel disconnected from your industry's reality. |
Tech Philosophy | An agnostic approach focused on finding the best tool for the job, not just the tool they know. | Pushing a single software solution for every problem, regardless of your unique needs. |
Change Management | A clear plan for training, communication, and ongoing support to ensure user adoption. | The focus is entirely on the technology, with little or no mention of the people who will use it. |
Success Metrics | A focus on measurable business impact (ROI, efficiency gains, error rates) with clear KPIs. | Vague promises of "improvement" or "optimization" without any way to actually measure it. |
Choosing the right business automation consulting partner lays the foundation for your entire initiative. By focusing on strategic fit, asking the right questions, and looking beyond the technical brochure, you can find a partner who will not only build great automations but also empower your business to achieve lasting success.
Got Questions About Business Automation Consulting? You're Not Alone.
Jumping into the world of automation is a big step, and it’s smart to have questions about the investment, timelines, and how it will all affect your team. Before you bring a consultant on board, you need straight answers to feel confident you're making the right move.
Let's cut through the noise and tackle the most common questions we hear. We'll break down everything from typical costs to what’s expected of your team, so you can see the full picture.
What's the Real Cost of Business Automation Consulting?
This is always the first question, and the honest answer is: it depends. The price tag for consulting is tied directly to the size and complexity of your project. Think of it like this: a simple kitchen remodel doesn’t cost the same as building a brand-new house from the ground up.
Consulting firms typically use a few different pricing structures:
By the Hour: Rates often range from $150 to over $400 per hour, based on the consultant's experience and how technical the work is.
Flat Project Fee: This is a fixed price for the entire project. It’s perfect for projects with a clear, defined scope, like automating one specific workflow.
Monthly Retainer: This model is great for long-term partnerships that involve ongoing support, tweaks, and rolling out changes in phases.
A small project, like mapping out a single process, might only be a few thousand dollars. A full-blown, company-wide overhaul, on the other hand, can easily run into the six figures.
The key is to stop thinking about cost and start thinking about value. A good consultant won't just hand you a bill; they'll show you a detailed proposal that connects their fees directly to your return on investment—things like time saved, fewer errors, and new opportunities for growth.
How Long Until We Actually See a Return on Our Investment?
The good news is you won't be waiting years to see results. The timeline is tied to your project's complexity, but a well-designed plan delivers value in stages.
Some automations are what we call "quick wins" and can make an impact almost immediately. For example, getting a tedious data entry task off someone's plate could start saving your team hours every single week, often within the first month. These early successes are fantastic for building momentum and showing everyone the real-world power of automation.
Bigger, more fundamental projects—like rolling out a new CRM or completely reimagining your finance department's workflow—will naturally take longer. You might be looking at 6 to 12 months for those to be fully built, tested, and adopted by the whole team.
A huge part of a consultant's job is creating a phased roadmap. This approach ensures you see real benefits and improvements at every milestone, long before the project is officially "done." Most businesses start seeing a significant ROI within the first year as their operations get faster and costly manual mistakes fade away.
How Much Time Will This Take from My Team?
Your team's involvement is non-negotiable. While the consultant does the heavy lifting on the technical side, the project can't succeed in a vacuum. Their insights are what make the final solution a perfect fit for your business.
The time commitment changes depending on where you are in the project:
Discovery: This is the most hands-on phase for your team. We'll need to talk to your key people—the ones who live and breathe these processes every day—to map out how things work now and find the real bottlenecks.
Implementation: You’ll need a point person from your company to be the main contact. Other team members will be asked to give feedback and help test things as they’re built.
Adoption: Your team will need time for training to get comfortable with the new tools and workflows.
A great consultant is an expert at minimizing disruption. They’ll lay out a clear schedule and keep communication lines open. As a rule of thumb, plan for key team members to set aside a few hours per week, especially during the early stages.
How Do You Handle Our Data Security and Compliance?
Data security isn't just a feature; it's the foundation of everything. Any consultant worth their salt will treat your business data with the utmost seriousness and follow strict security protocols from day one.
Before any work kicks off, a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) should be signed to legally protect your information. From there, every new tool or connection they build will be configured with security best practices in mind.
This always includes:
Strict User Access Controls: People should only be able to see and touch the data they absolutely need for their job.
Data Encryption: Protecting your information whether it’s sitting on a server or moving between different applications.
Regulatory Compliance: Making sure everything is built to meet standards like GDPR or HIPAA if they apply to your industry.
Don't be shy about this. Ask a potential consultant to walk you through their data handling policies and their experience with sensitive information. They should be able to confidently explain exactly how they'll keep your business safe.
Ready to stop wasting time on manual tasks and start scaling your business with intelligent automation? At Flow Genius, we design and build custom workflows that give you back your most valuable resource: time. Book a free discovery call with us today and find out what your business can achieve.



