- Sep 9, 2025
- 20 min read
In today's fast-paced business world, making the right call can be the difference between stagnation and growth. While intuition has its place, relying on it alone is a gamble, especially when managing complex logistics, integrating software ecosystems, or optimizing resource management. The most successful leaders and organizations leverage structured systems to navigate complexity and uncertainty. This guide explores several powerful decision making frameworks designed to bring clarity, objectivity, and strategic foresight to your most critical choices.
These structured methods move you beyond simple pros and cons, offering a systematic way to deconstruct challenges and evaluate potential outcomes. For a broader exploration of different structured approaches, you can delve into this guide on 10 powerful decision making frameworks that offer additional perspectives for making better choices. By incorporating these models, you can minimize bias, manage risk, and ensure your entire team is aligned on a well-reasoned path forward.
From time-tested models like SWOT analysis for strategic planning to agile loops like Build-Measure-Learn for product development, these frameworks provide a versatile toolkit for dissecting problems, evaluating options, and committing to a course of action with confidence. Whether you are a project manager synchronizing logistics, a business owner automating workflows in Zapier or Make.com, or a director planning for market shifts, mastering these approaches is essential. This article will provide a comprehensive breakdown of each framework, including its core principles, ideal use cases, and actionable steps for implementation. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of how to transform ambiguity into a decisive path forward, ensuring your choices are not just quick, but also sound, strategic, and aligned with your long-term goals.
1. SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a foundational strategic planning and decision-making framework used to evaluate a project or business venture. It organizes key factors into four distinct quadrants: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Strengths and Weaknesses are internal factors that you can control, while Opportunities and Threats are external factors beyond your direct influence.
This matrix-based approach provides a comprehensive, at-a-glance overview of the internal and external landscape affecting your decision. By systematically mapping these elements, you gain clarity on strategic advantages to leverage and potential pitfalls to mitigate, making it one of the most versatile decision making frameworks available.

How It Works & When to Use It
The primary goal is to match your internal strengths with external opportunities while converting weaknesses or defending against threats. For instance, Netflix used a SWOT analysis to transition from DVDs to streaming. They identified their strong brand (Strength) and the rise of high-speed internet (Opportunity) to pivot, while recognizing their dependence on physical mail (Weakness) and emerging digital competitors (Threats).
Use SWOT when you need to:
Evaluate a new business idea or project: Assess the viability and potential risks of a new venture, such as a roofing contractor considering expansion into a new city.
Formulate strategic plans: Determine where to focus resources for maximum impact, like a technology company deciding which product feature to develop next.
Assess a changing environment: Understand the implications of market shifts, like a university adapting to the threat of declining enrollment by creating online learning opportunities.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To get the most out of your SWOT analysis, move beyond simple brainstorming.
Be Specific and Factual: Instead of listing "good marketing" as a strength, specify "a highly engaged email list of 50,000 subscribers with a 35% open rate."
Involve Diverse Stakeholders: Include team members from different departments (sales, operations, marketing) to gain a 360-degree perspective and avoid blind spots.
Prioritize with Weighting: Assign a score (e.g., 1-10) for both the importance and magnitude of each item. This helps you focus on what truly matters rather than treating every point as equal.
Develop Action Items: Your analysis is a starting point. Match Strengths to Opportunities to create "attack" strategies and match Weaknesses to Threats to formulate "defensive" strategies.
2. Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA)
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) is a systematic and quantitative approach to decision-making. It involves summing the total expected benefits of an action and subtracting the total expected costs. By expressing both sides of the equation in monetary terms, CBA provides a clear, data-driven basis for determining if a potential decision is financially sound.
This framework moves beyond intuition by assigning a tangible value to both the positive and negative consequences of a choice. The core principle is simple: if the total benefits outweigh the total costs, the project is worth pursuing. This makes CBA one of the most powerful decision making frameworks for evaluating investments and comparing multiple, competing alternatives on a like-for-like basis.
How It Works & When to Use It
The primary goal of a CBA is to produce a net benefit value, enabling objective comparisons. For example, a city government considering a new subway line would quantify costs like construction, land acquisition, and maintenance, and weigh them against benefits like reduced traffic congestion, lower pollution levels, and increased property values. To conduct a thorough Cost-Benefit Analysis, it is essential to understand key metrics like Return on Investment (ROI).
Use CBA when you need to:
Justify major capital expenditures: Decide if a corporate investment in a new IT system or manufacturing plant is financially viable.
Evaluate public policy or projects: Assess government infrastructure projects or environmental regulations where a clear social and economic rationale is required.
Choose between competing options: Select the most financially advantageous project when resources are limited, such as a company deciding which of three potential software tools to purchase.
Actionable Implementation Tips
A robust CBA requires meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive view of all impacts.
Quantify Everything Possible: Go beyond direct costs. Include indirect and intangible factors by assigning them a monetary value. For instance, the "cost" of poor employee morale could be monetized as increased turnover and recruitment expenses.
Apply a Discount Rate: Future costs and benefits are worth less than present ones. Use a discount rate to calculate the present value of all future cash flows, ensuring a more accurate comparison.
Use Sensitivity Analysis: Your analysis is built on assumptions. Test these assumptions by running the numbers with different variables (e.g., higher costs, lower benefits) to see how sensitive your conclusion is to change.
Document Assumptions Clearly: Be transparent about how you arrived at your figures, which intangibles were included, and what discount rate was used. This builds credibility and allows for informed debate. Learn more about how to improve your business efficiency with these kinds of frameworks.
3. Decision Matrix Analysis (Weighted Scoring)
Decision Matrix Analysis is a quantitative framework for evaluating multiple options against a set of predefined criteria. It brings structure and objectivity to complex choices by assigning numerical scores to alternatives based on how well they meet the criteria, which are weighted according to their importance.
This method transforms a subjective decision into a more logical process. By calculating a total weighted score for each option, you can systematically identify the most suitable choice, making it an indispensable tool among decision making frameworks for choices with multiple competing variables.
How It Works & When to Use It
The core principle is to break down a decision into its key components, score each option against those components, and then tally the scores for a clear winner. For example, a company selecting new CRM software would list criteria like "Cost," "Ease of Use," and "Integration Capabilities." They would assign a weight to each (e.g., Integration is most important), score each vendor's software against the criteria, and calculate the total weighted score to find the best fit.
Use a Decision Matrix when you need to:
Select a vendor or supplier: Compare multiple proposals objectively for a major purchase, such as enterprise software or manufacturing equipment.
Prioritize projects or features: Decide which initiatives to fund or which product features to develop next based on criteria like potential ROI, resource cost, and strategic alignment.
Make hiring or promotion decisions: Evaluate candidates against a consistent set of job-related criteria like experience, technical skills, and cultural fit to reduce bias.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To ensure your Decision Matrix is effective, focus on the setup and execution.
Involve Stakeholders in Criteria & Weighting: Collaborate with key team members to define the evaluation criteria and agree on their respective weights. This builds consensus and ensures the model reflects collective priorities.
Use a Consistent Scoring Scale: Whether you use a 1-5 or 1-10 scale, apply it uniformly across all criteria to maintain mathematical integrity. Clearly define what each number on the scale represents (e.g., 1 = Poor, 5 = Excellent).
Conduct a Sensitivity Analysis: After calculating the initial results, test them by slightly adjusting the weights of the most important criteria. If the winning option remains the same, it confirms a robust decision. If it changes, further discussion is needed.
Combine with Qualitative Discussion: The final score is a guide, not a mandate. Use the results to facilitate a final discussion, considering any intangible factors the matrix couldn't capture.
4. Decision Trees
A Decision Tree is a visual, flowchart-like framework that maps out every potential outcome of a decision. It organizes choices, chance events, and their consequences into a tree-like model, with each branch representing a different path. This allows you to quantitatively compare different options by calculating the "expected value" of each path, making it an indispensable tool for navigating uncertainty.
This structured approach transforms complex problems into a clear visual map, making it one of the most powerful quantitative decision making frameworks for strategic planning. It forces you to consider various possibilities and their probabilities, providing a logical basis for your final choice. For more on creating effective visual aids, check out these data visualization best practices.

How It Works & When to Use It
The primary goal of a Decision Tree is to identify the strategy that maximizes the expected value or outcome. For example, a technology company can use a decision tree to decide whether to build a new feature in-house or acquire a smaller company that already has it. The tree would map out costs, probabilities of success, and potential revenue for each path, guiding them to the most profitable choice.
Use Decision Trees when you need to:
Make financial investment choices: Evaluate different investment strategies by mapping out potential returns, risks, and market condition probabilities.
Plan a product launch: Decide on the optimal timing for a product release by weighing development costs against potential market share gains and competitor actions.
Develop emergency response plans: Map out potential disaster scenarios and the most effective sequence of actions for logistics or energy sector operations teams.
Formulate complex medical or legal strategies: Systematically chart treatment protocols or litigation paths based on probable outcomes and consequences.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To ensure your Decision Tree is a reliable guide, focus on the quality of your inputs and structure.
Start with Major Decisions: Begin by mapping the most critical decision points and branches. You can add more granular detail and secondary choices progressively to avoid overcomplicating the initial structure.
Use Data for Probabilities: Instead of guessing, use historical data, market research, or industry benchmarks to assign realistic probabilities to chance events and outcomes.
Validate with Domain Experts: Share your tree with stakeholders or subject matter experts. They can help validate the logic, identify missing variables, and refine probability estimates.
Perform Sensitivity Analysis: Test how changes in key variables, like market demand or costs, impact the final outcome. This reveals how robust your chosen strategy is under different conditions.
5. Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats, developed by Edward de Bono, is a parallel thinking framework designed to improve team decision-making by separating thinking into six distinct modes. Participants metaphorically "wear" different colored hats, each representing a specific perspective: White (facts and data), Red (emotions and intuition), Black (risks and caution), Yellow (optimism and benefits), Green (creativity and new ideas), and Blue (process and control).
This method prevents the common pitfalls of group discussions, such as adversarial debate or premature conclusions. By having everyone focus on the same type of thinking simultaneously, it ensures a comprehensive and collaborative exploration of an issue. This structured approach makes it one of the most effective decision making frameworks for fostering innovation and achieving consensus.
How It Works & When to Use It
The goal is to systematically analyze a problem from all angles without personal bias interfering. For instance, in a product development session at 3M, the team might use the Green Hat to brainstorm new features, switch to the Black Hat to identify potential flaws, and then use the Red Hat to gauge the emotional response to a proposed design. This prevents a "devil's advocate" from shutting down creative ideas prematurely.
Use Six Thinking Hats when you need to:
Solve complex problems collaboratively: Facilitate a structured discussion where all viewpoints are heard, such as a leadership team at IBM deciding on a major strategic shift.
Foster creative solutions: Encourage out-of-the-box thinking without immediate criticism, ideal for marketing teams brainstorming a new campaign.
Overcome analysis paralysis: Guide a team through a decision by systematically covering all necessary perspectives, like a healthcare organization handling a crisis.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To maximize the effectiveness of the Six Thinking Hats framework, move beyond simply assigning colors.
Appoint a Facilitator (Blue Hat): Designate one person to manage the process, keep time, and guide the group through the hat sequence. This person wears the Blue Hat throughout the meeting.
Use a Planned Sequence: Don't just jump between hats randomly. A common sequence is Blue (define), White (facts), Green (ideas), Yellow (benefits), Black (risks), Red (feelings), and Blue (summary/decision).
Enforce Parallel Thinking: When a hat is active, all participants must stick to that mode of thinking. Gently redirect anyone who strays, for instance, by saying, "That's a great point for the Black Hat, let's save it for then."
Document Everything: Keep a visible record of the key points generated under each hat. This creates a comprehensive map of the discussion that can be referenced when making the final decision.
6. OODA Loop
The OODA Loop is a high-speed decision-making cycle created by military strategist Colonel John Boyd to gain an advantage in fast-paced, competitive environments. It breaks down the decision process into four stages: Observe, Orient, Decide, and Act. The core principle is to continuously and rapidly cycle through this loop, adapting to new information faster than an opponent or a changing situation.
Unlike more static models, the OODA Loop is a dynamic framework designed for agility and continuous learning. By shortening your decision cycle, you can effectively disrupt your competitor's process, forcing them to react to a situation you have already moved past. This makes it one of the most powerful decision making frameworks for volatile and uncertain conditions where speed is a critical advantage.
How It Works & When to Use It
The goal of the OODA Loop is to "get inside" your opponent's decision cycle. By observing, orienting, deciding, and acting more quickly, you can seize the initiative. For example, in cybersecurity, an incident response team uses this loop: they Observe an anomaly (unusual network traffic), Orient by analyzing its source and potential threat, Decide on a containment strategy (e.g., isolating a server), and Act by executing the plan, immediately observing the results to start the next cycle.
Use the OODA Loop when you need to:
Respond to crises or emergencies: An emergency medical team arriving at an accident scene must quickly observe injuries, orient themselves to the situation, decide on treatment priorities, and act.
Navigate competitive markets: A startup can outmaneuver a larger, slower competitor by rapidly observing customer feedback, orienting to market needs, deciding on a product pivot, and acting to deploy it.
Manage high-stakes, real-time scenarios: Financial traders use this framework to react to market fluctuations, observing price movements and news, orienting their strategy, and deciding to buy or sell in seconds.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement the OODA Loop, focus on accelerating each stage of the cycle.
Establish Clear Information Channels (Observe): Set up real-time data feeds, monitoring dashboards, and direct customer feedback channels so you get accurate information as quickly as possible.
Develop Shared Mental Models (Orient): Train your team to analyze situations using a common framework. This shared understanding of goals and context allows for faster and more coherent orientation.
Empower Decentralized Decisions (Decide): Grant autonomy to frontline team members to make decisions without waiting for layers of approval. This drastically shortens the Decide phase.
Create Tight Feedback Loops (Act): After acting, ensure a process is in place to immediately gather data on the outcome. This data feeds directly back into the Observe stage of the next loop, fueling continuous improvement.
7. Cynefin Framework
The Cynefin Framework, developed by Dave Snowden, is a sense-making tool that helps leaders categorize problems into one of five domains to guide their response. It moves beyond a one-size-fits-all approach, recognizing that different situations require fundamentally different decision-making strategies. The domains are Simple, Complicated, Complex, Chaotic, and Disorder (a state of confusion about which domain applies).
This framework is not about placing situations into rigid boxes but about understanding the nature of the cause-and-effect relationships at play. By correctly identifying the context, leaders can avoid applying simple solutions to complex problems or over-analyzing a crisis that demands immediate action. It’s one of the most sophisticated decision making frameworks for navigating uncertainty.
The infographic below illustrates the distinct action patterns required for the three most common operational domains: Simple, Complicated, and Complex.
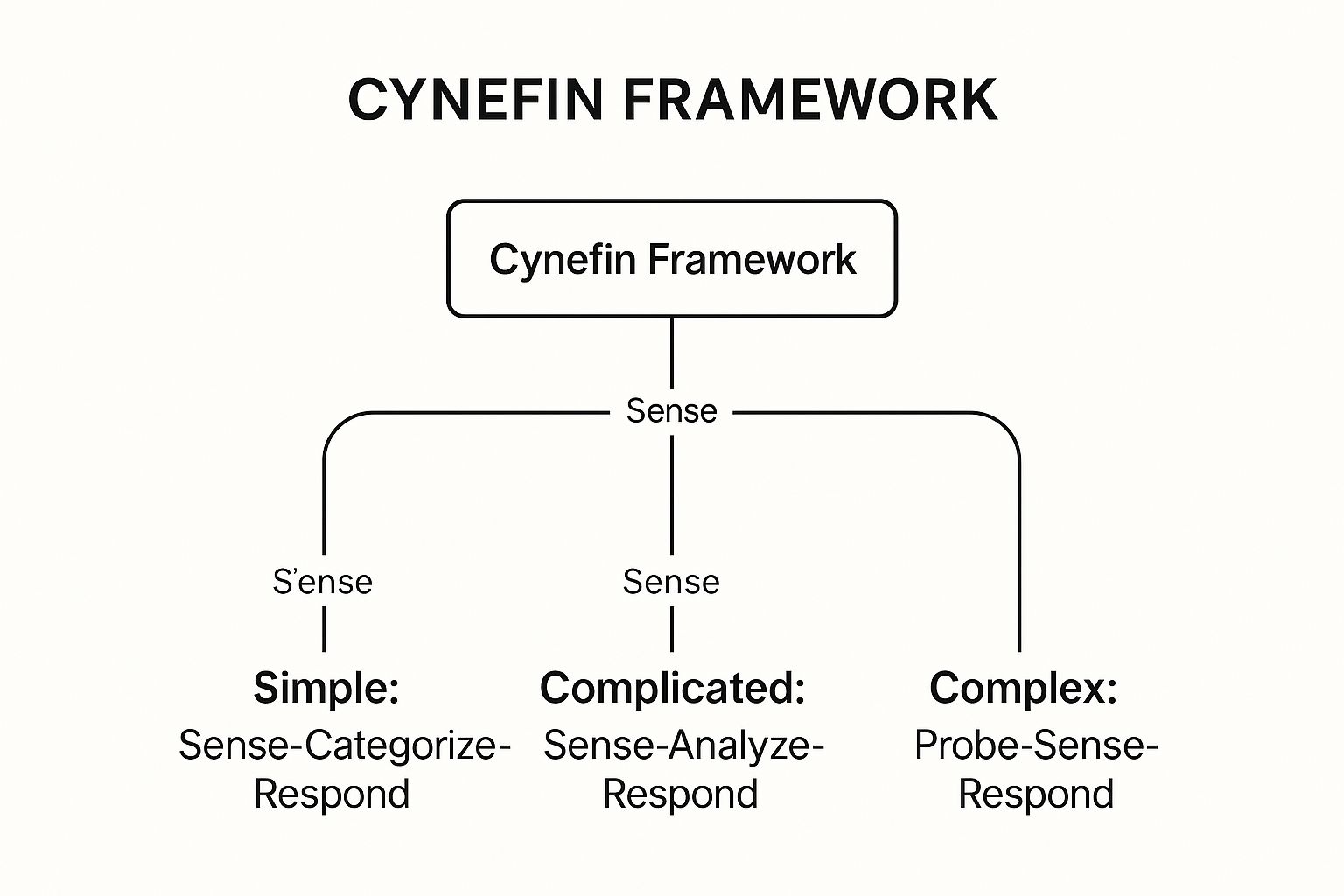
This visualization highlights how the appropriate response shifts from applying best practices in Simple domains to experimenting and adapting in Complex ones.
How It Works & When to Use It
The core idea is to first "sense" the environment to determine which domain you are in, and then act accordingly. For instance, a manufacturing plant optimizing a known production line operates in the Complicated domain: there are knowable unknowns, and experts can analyze the situation to find the right answer. In contrast, managing a public health response during a novel pandemic falls into the Complex domain, where cause and effect are only clear in hindsight, requiring leaders to probe, sense, and respond with emergent strategies.
Use the Cynefin Framework when you need to:
Lead in uncertain conditions: Differentiate between complicated but solvable problems and truly complex, unpredictable challenges.
Manage organizational change: Understand why imposing a "best practice" (Simple) solution on a cultural issue (Complex) is likely to fail.
Develop robust strategies: Create plans that are adaptable enough to handle shifts between domains, such as a crisis (Chaotic) stabilizing into a solvable problem (Complicated).
Actionable Implementation Tips
To apply the Cynefin Framework effectively, focus on situational awareness and adaptability.
Sense First, Act Second: Resist the urge to immediately jump to a solution. First, gather information and perspectives to accurately diagnose which domain your problem resides in.
Use Diverse Perspectives: When classifying a situation, involve people with different roles and expertise. A problem that seems Complicated to an engineer may appear Complex to a marketer.
Develop Domain-Appropriate Capabilities: Build teams skilled in analysis for Complicated issues, experimentation for Complex challenges, and decisive action for Chaotic events. This aligns with many process improvement methodologies.
Be Prepared to Shift: Contexts are dynamic. A Complex market innovation can become a Complicated industry standard over time. Regularly re-evaluate your position on the framework and be ready to change your approach.
8. Kepner-Tregoe Decision Analysis
Kepner-Tregoe Decision Analysis is a structured methodology for gathering, organizing, and evaluating information to make a logical choice. Developed by Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe, this framework deconstructs complex decisions into rational components: defining objectives, weighing them by importance, generating alternatives, and assessing risks. Its strength lies in its systematic, step-by-step process that minimizes emotional bias and ensures all critical factors are considered.
This model forces a clear separation between the "what" (the desired outcomes) and the "how" (the potential solutions). By focusing first on objectives, teams create a clear, agreed-upon standard against which all alternatives are measured, making it one of the most rigorous decision making frameworks for high-stakes situations where a defendable, transparent choice is crucial.
How It Works & When to Use It
The core of the Kepner-Tregoe method involves classifying objectives into two categories: Musts (mandatory, non-negotiable criteria) and Wants (desirable but not essential criteria). Alternatives that fail to meet a "Must" are immediately eliminated. The remaining options are then scored against the "Wants" to identify the best overall fit, followed by a final risk assessment. For example, when selecting a new CRM platform, a "Must" might be "integrates with our existing accounting software," while a "Want" could be "has a mobile app."
Use Kepner-Tregoe when you need to:
Make major capital investment decisions: Systematically compare large equipment purchases or facility upgrades against a clear set of financial and operational objectives.
Select critical suppliers or partners: Choose a new logistics provider by evaluating them against non-negotiable delivery times ("Musts") and desirable cost structures ("Wants").
Choose a technology platform: Decide on a new software system where functionality, security, and integration requirements are complex and non-negotiable.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To apply this framework effectively, precision is key. A vague process will yield a vague outcome.
Clearly Distinguish 'Musts' and 'Wants': This is the most critical step. A "Must" must be measurable and absolute. Ask, "If an option doesn't have this, would we still consider it?" If the answer is yes, it's a "Want."
Use Factual Data for Scoring: When evaluating alternatives against "Wants," use concrete data and performance metrics, not just opinions. Instead of "good support," use "24/7 phone support with an average resolution time of under 4 hours."
Involve Cross-Functional Stakeholders: Engage representatives from every department affected by the decision (e.g., IT, finance, operations) to define objectives and ensure all critical needs are captured.
Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment: For your top one or two choices, analyze potential negative consequences. What could go wrong with this option? How likely is it, and what would be the impact? This final check protects against unforeseen problems.
9. Scenario Planning
Scenario Planning is a strategic foresight method used to make robust decisions in the face of uncertainty. Instead of trying to predict a single future, this framework helps organizations explore several different plausible futures, or "scenarios." By doing so, decision-makers can develop strategies that are resilient and adaptable, regardless of how events unfold.
Popularized by strategists at Royal Dutch Shell, this approach acknowledges that the future is shaped by complex and unpredictable forces. By creating narratives around different potential outcomes, you can test your plans and identify blind spots. This makes it one of the most powerful decision making frameworks for long-range planning and navigating volatile environments.
How It Works & When to Use It
The core of Scenario Planning involves identifying key driving forces and critical uncertainties that could shape the future. For example, Shell famously used this method in the 1970s to prepare for a potential oil crisis. By envisioning a future where oil-producing nations restricted supply, they developed contingency plans that allowed them to thrive when the 1973 oil shock occurred, while competitors were caught off guard.
Use Scenario Planning when you need to:
Navigate high-stakes uncertainty: Prepare for major market shifts, geopolitical risks, or technological disruptions, like a financial firm planning for different economic recession outcomes.
Develop long-term corporate strategy: Create flexible 5-10 year plans that can adapt to changing industry landscapes, such as a utility company planning for various climate change and regulatory futures.
Test the resilience of a major decision: Evaluate how a significant investment, like building a new factory, would fare under different political, economic, or environmental conditions.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To make Scenario Planning effective, go beyond vague future-gazing and build structured, logical narratives.
Develop 3-4 Distinct Scenarios: Avoid simple best-case, worst-case, and base-case thinking. Instead, create stories that are fundamentally different from one another, each based on a plausible combination of driving forces. For example, "Green Revolution" vs. "Fossil Fuel Resurgence."
Focus on Key Uncertainties: Identify the two or three most critical, unpredictable factors that will have the biggest impact on your organization (e.g., consumer adoption of AI, future government regulations). These will form the axes of your scenario matrix.
Involve Diverse Stakeholders: Bring in experts from different fields, as well as internal team members from various departments, to challenge assumptions and build richer, more imaginative scenarios.
Stress-Test Your Strategies: For each scenario, ask: "If this future came to pass, would our current strategy succeed?" Identify which strategies are robust across all or most scenarios and which are brittle. Develop contingency plans for high-risk, high-impact scenarios.
10. Lean Startup Decision Framework (Build-Measure-Learn)
Popularized by Eric Ries, the Lean Startup Decision Framework is an iterative cycle designed for making decisions under conditions of extreme uncertainty. It reframes product development around rapid experimentation and validated learning, moving away from rigid, long-term planning. The core of this framework is a simple feedback loop: Build, Measure, and Learn.
Instead of investing heavily in a final product based on assumptions, you build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to test a core hypothesis. You then measure customer behavior and feedback, and finally, learn whether to persevere with the current strategy or pivot. This makes it one of the most agile decision making frameworks for innovation and market validation.

How It Works & When to Use It
The primary goal is to minimize wasted time and resources by learning what customers actually want as quickly as possible. For example, Dropbox famously used this approach by creating a simple video demonstrating their file-syncing concept (the MVP) before writing a single line of code. The overwhelming positive response validated their core idea and guided their decision to build the full product.
Use the Build-Measure-Learn framework when you need to:
Launch a new product or service: Test market demand for a novel idea, like how Zappos initially posted photos of shoes from local stores to see if people would buy them online.
Enter a new market: Validate if your existing offering resonates with a new customer segment before committing to a full-scale launch.
Develop innovative features: Quickly test user interest in a new feature without over-investing in development, similar to how Buffer used a simple landing page to gauge interest.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively use the Build-Measure-Learn cycle, focus on the speed and quality of your learning.
Define a Falsifiable Hypothesis: Before you build, state a clear, testable assumption. For example, "We believe that 15% of visitors to our landing page will sign up for early access if we offer a 20% discount."
Focus on Actionable Metrics: Avoid vanity metrics like total sign-ups. Instead, track metrics that inform specific decisions, such as conversion rates, user engagement levels, or customer acquisition cost.
Be Prepared to Pivot: The goal is learning, not just confirming your initial idea. If the data shows your hypothesis is wrong, be ready to make a significant change (a pivot) to your strategy based on what you've learned.
Gather Qualitative Feedback: The "Learn" phase isn't just about numbers. Implementing effective customer feedback strategies is crucial for understanding the "why" behind user behavior.
Decision Making Frameworks Comparison
Decision Framework | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
SWOT Analysis | Low - simple matrix setup | Low - minimal data gathering | Broad situational awareness, qualitative insights | Initial strategic planning, group brainstorming | Easy to use, fosters group consensus, cost-effective |
Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA) | Medium - requires quantitative data | Medium to High - data & forecasting | Objective financial evaluation, numeric comparison | Financial investments, policy evaluation | Quantifies costs and benefits, supports stakeholder justification |
Decision Matrix Analysis | Medium to High - criteria & weights | Medium - requires scoring inputs | Prioritized alternatives via weighted scores | Vendor selection, project prioritization | Reduces bias, transparent, handles multiple criteria |
Decision Trees | High - probability and outcome mapping | High - reliable probability data required | Quantitative risk-based decisions, expected values | Sequential decisions under uncertainty | Visualizes complex decisions, incorporates risk explicitly |
Six Thinking Hats | Medium - requires training/facilitation | Low to Medium - group sessions | Comprehensive perspective, structured thinking | Creative brainstorming, conflict reduction | Encourages collaboration, increases creativity |
OODA Loop | Medium - rapid iterative process | Medium - organizational discipline | Fast, adaptive decision cycles | Military, emergencies, startups | Promotes speed & adaptability, prevents paralysis |
Cynefin Framework | High - requires deep understanding | Medium to High - domain analysis | Context-appropriate decision strategies | Complex environments, leadership decisions | Adaptive to context, handles complexity explicitly |
Kepner-Tregoe Decision Analysis | High - multi-phase, structured process | High - training & data intensive | Thorough, risk-aware decisions | Complex investment or supplier selections | Systematic, reduces bias, integrates risk analysis |
Scenario Planning | High - multiple future scenarios | High - scenario development effort | Robust strategies accommodating uncertainty | Long-term strategic planning, risk exploration | Prepares for multiple futures, improves adaptability |
Lean Startup (Build-Measure-Learn) | Medium - iterative cycles | Medium - MVP development & testing | Rapid validated learning and market fit iteration | Startups, innovation projects | Reduces risk, maximizes learning, cost-effective |
Putting Frameworks into Action with Smart Automation
Throughout this guide, we've explored ten powerful decision making frameworks, each offering a unique lens through which to view your most critical challenges. From the strategic foresight of a SWOT Analysis to the rapid, iterative cycles of the OODA Loop, these models provide the structured thinking needed to navigate uncertainty and make choices with confidence. We've seen how a Decision Matrix can bring mathematical clarity to complex options and how the Six Thinking Hats can unlock holistic, creative problem-solving by separating perspectives.
The common thread connecting all these methodologies is the transformation of ambiguity into actionable insight. Instead of relying on gut feelings or incomplete information, these frameworks compel you to gather data, weigh variables, consider consequences, and collaborate effectively. They are not rigid rules but flexible guides designed to elevate your strategic thinking, whether you're an infrastructure project manager coordinating logistics or a technology leader pioneering a new software ecosystem.
From Theory to Execution: The Automation Advantage
Choosing the right framework is a crucial first step, but the true value is realized in its consistent and efficient application. This is where many organizations falter. Manually gathering data for a Cost-Benefit Analysis, collecting diverse feedback for a Six Thinking Hats session, or tracking metrics for a Lean Startup loop can be slow, prone to error, and resource-intensive. These manual bottlenecks often lead to frameworks being used sporadically or abandoned altogether.
This is precisely where intelligent automation becomes a game-changer. Imagine your CRM automatically populating a Decision Matrix with client data and deal values, or a system that triggers a Kepner-Tregoe analysis when a critical operational threshold is breached. Automation bridges the gap between knowing what to do and actually doing it consistently and at scale.
By automating the routine, data-intensive components of these frameworks, you free up your team’s most valuable resource: their cognitive capacity. Instead of spending hours compiling spreadsheets, they can focus on high-level analysis, strategic debate, and creative problem-solving, which is the true purpose of these decision making frameworks.
Creating an Ecosystem for Smarter Decisions
Implementing automation isn't just about speeding up a single task; it's about creating a responsive, data-driven ecosystem that supports better decision-making across your entire organization. For logistics directors, this could mean automated workflows that provide the real-time tracking data needed for Scenario Planning. For business brokers or roofing contractors, it could involve automating outreach and follow-up, then using the resulting data to refine their approach via a Build-Measure-Learn cycle.
Consider the practical applications:
Automated Data Feeds for SWOT: Integrate your CRM, financial software, and project management tools to automatically pull real-time data on Strengths (e.g., high-performing sales channels), Weaknesses (e.g., project delays), Opportunities (e.g., emerging market segments), and Threats (e.g., customer churn rates).
Streamlined OODA Loops: Create automated dashboards that Observe key metrics, Orient you with contextual data, and trigger alerts for key personnel to Decide and Act, dramatically shortening the loop's cycle time.
Enhanced Decision Trees: Use automation to run simulations, feeding historical data into your decision tree models to calculate probabilities and expected outcomes with greater accuracy and speed.
By embedding these processes into your daily operations using tools like Zapier, Make.com, or custom integrations, you transform decision-making from a periodic, high-effort event into a continuous, low-friction habit. This disciplined, system-driven approach ensures that every choice, from the daily operational tweak to the major strategic pivot, is grounded in the best possible logic and information. The ultimate goal is to build an organization that not only makes good decisions but learns and improves with every choice it makes.
Ready to operationalize these frameworks and eliminate manual bottlenecks? Flow Genius specializes in creating custom automation and integration solutions that connect your tools and data, turning sophisticated decision-making models into practical, everyday workflows. Visit Flow Genius to discover how we can help you build a smarter, more responsive business.